Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a chronic lung disease that leads to such respiratory problems as breathing difficulty, shortness of breath, and wheezing. The breathing issues occur because of obstructed airflow from the lungs and damaged or clogged lungs.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly known as COPD, is the third most frequent cause of death worldwide. According to the Global Impact of Respiratory Disease report, approximately 200 million people suffer from COPD, and 3.2 million die because of it each year. In the United States alone, 15 million people have been diagnosed with this disease, and many more live with its symptoms, not knowing the cause.
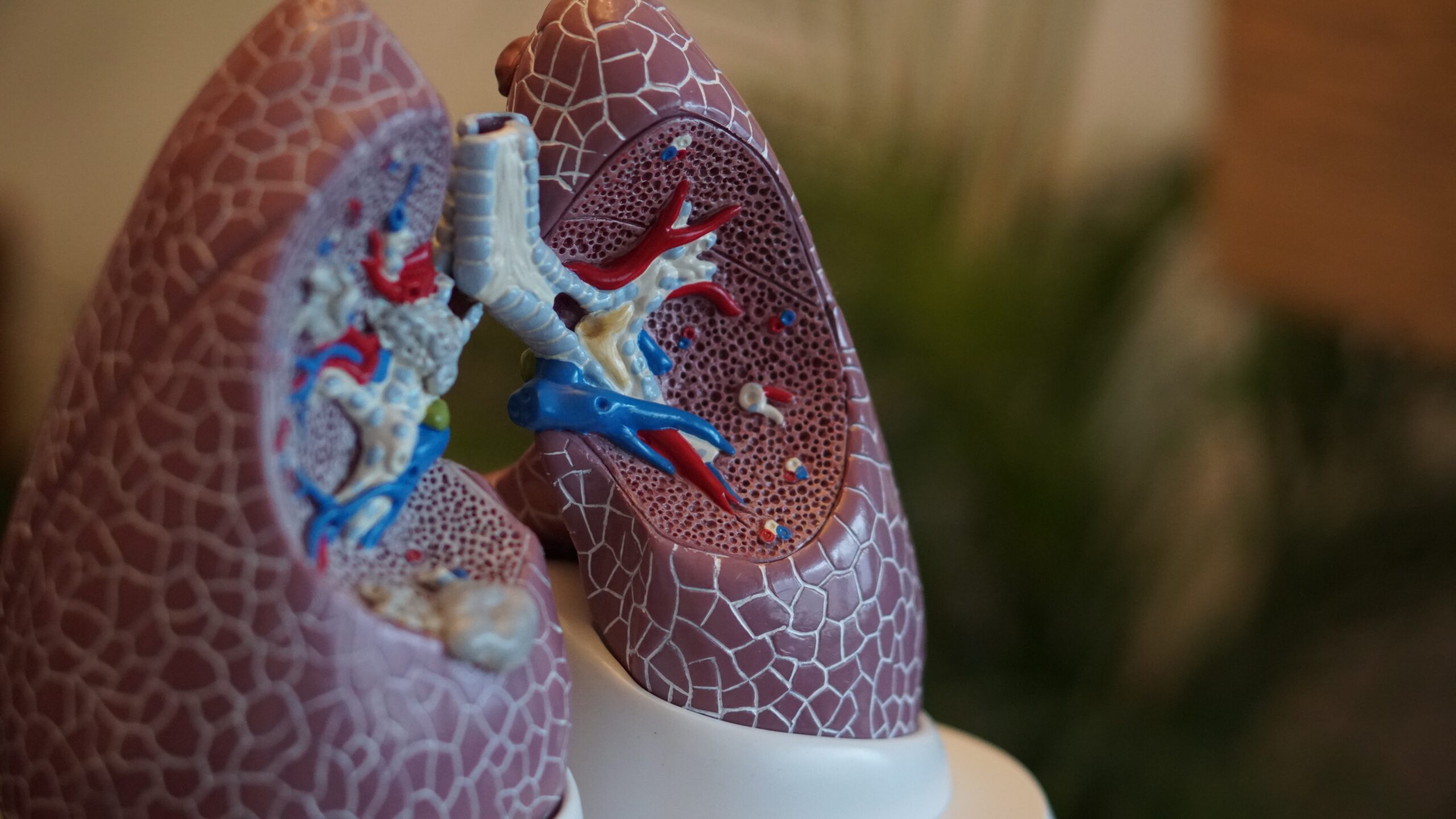
In the USA, COPD refers to two respiratory diseases that may occur due to damaged lungs – emphysema![]() and chronic (long-term) bronchitis
and chronic (long-term) bronchitis![]() . These two conditions often develop at the same time.
. These two conditions often develop at the same time.
Emphysema develops when the lungs are exposed to cigarette smoke or other irritants. As a result, the alveoli, tiny air sacks responsible for gas exchange located at the end of the smallest air passages, get destroyed.
Chronic bronchitis occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes gets inflamed. The bronchial tubes' role is to deliver and receive air from lung sacks. Inflammation of the tubes may lead to persistent daily cough.
The two COPD conditions usually worsen over time and do not improve without adequate treatment. If left untreated, emphysema or chronic bronchitis can challenge everyday life, making it difficult to stay focused on various activities. Moreover, breathing difficulties such as shortness of breath or problems with taking a deep breath can increase anxiety and stress.
COPD cure has yet to be invented. However, The available treatment options help ease and stabilize the symptoms preventing them from worsening. A combination of diet, proper management, lifestyle changes, and precautions allow most COPD patients to achieve desirable life comfort.
COPD may develop due to several reasons, whose common denominator is obstructed airway![]() that reduces the amount of air coming in and out of this body part. Possible causes include the following:
that reduces the amount of air coming in and out of this body part. Possible causes include the following:
Breathing-related issues are a direct consequence of impaired airflow. Body cells require oxygen for proper function – if there is not enough of it because of less air breathed in, all sorts of respiratory issues may develop.
Developing COPD disease is a gradual and lengthy process![]() . Whether it occurs or not depends on many factors. For instance, a person may develop COPD because of prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke, chemicals, or polluted air. But in many cases, several harmful substances and risk factors come into play at once:
. Whether it occurs or not depends on many factors. For instance, a person may develop COPD because of prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke, chemicals, or polluted air. But in many cases, several harmful substances and risk factors come into play at once:
Exposure to tobacco smoke is a leading cause of COPD, which is why it is often called ‘smoker's disease.' However, inflamed or obstructed airways may occur in people who never smoked in their entire lives![]() , which amounts to about 25% of patients with COPD.
, which amounts to about 25% of patients with COPD.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease symptoms usually appear when damage to the lungs is significant. The first symptoms to develop include a daily cough with phlegm and shortness of breath![]() , worsening over time. It especially applies to smokers who continue using tobacco products, people living in polluted areas, or workers exposed to irritants on a daily basis.
, worsening over time. It especially applies to smokers who continue using tobacco products, people living in polluted areas, or workers exposed to irritants on a daily basis.
The possible symptoms that may develop during COPD include:
In the early stages of COPD, respiratory problems may seem like a temporary nuisance that will go away on their own. Unfortunately, that is not the case, and the opposite scenario happens: breathing difficulties and fatigue get worse with time, making it difficult to work, study, engage in sports activities, and carry out daily tasks. Untreated COPD may also result in severe health complications, so seeking professional help early to protect your health and reduce medical expenses is vital.

Poorly managed or untreated COPD may lead to several dangerous health complications. These include:
Diagnosing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease early is vital to avoid complications and severe forms of COPD. If you are experiencing shortness of breath, tightness in the chest, and fatigue, don't hesitate to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your respiratory problems.
During a doctor's visit, you will be asked about your symptoms and medical history, including:
After a physical exam and review of your symptoms and medical history, a doctor may order various tests to confirm COPD and rule out other conditions, including:
The progression and severity of COPD differ from person to person. For this reason, close cooperation with a health provider is vital to create an effective personalized treatment plan.
The primary goals of treatment encompass stopping COPD from progressing, preventing complications, and strategies to manage symptoms to achieve a desirable quality of life.
Depending on several factors, such as a person's lifestyle, working conditions, and type and severity of COPD, the following strategies are used to manage breathing problems:
Living with COPD can be challenging, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, most people can continue their education, career, and favorite activities. Remember to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Table of Contents
Atelectasis is a lung condition in which parts of the alveoli, tiny air sacks in the lung, lose air. When… read more »
A pulmonary embolism develops when a clump, most often a blood clot, gets stuck inside the lung blood vessel. It… read more »

A pulmonologist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the respiratory system, which includes the… read more »

Lung Cancer begins in cells lining breathing entries, regularly starting with bronchial tubes or minor discuss sacs. It may be… read more »

Cough is a natural, necessary reflex that protects the body from factors such as germs and pollens. When it is… read more »

Dyspnea, which individuals also call shortness of breath, occurs when somebody feels awkward while breathing or suddenly realizes they have… read more »
Hypercapnia is a condition in which the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in our blood is increased. This can be… read more »
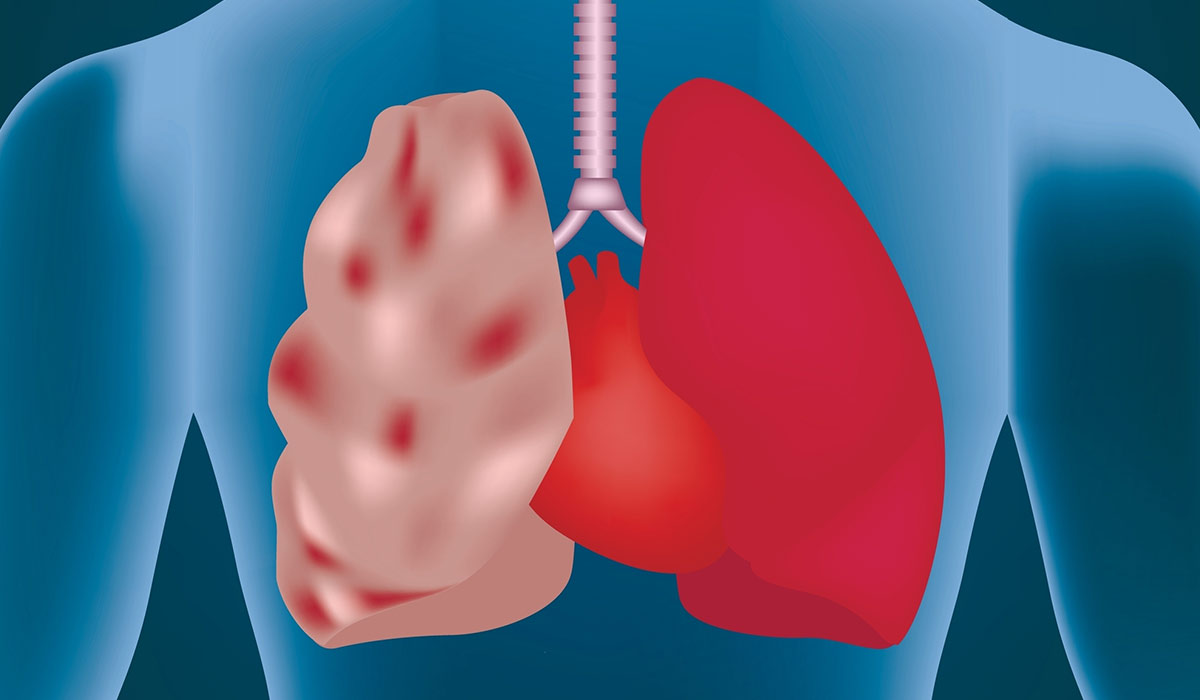
Emphysema is a lung disease that involves excessive aeration of the lungs, which disrupts gas exchange in the body. How… read more »
Pneumothorax is a condition that develops as a result of air entering the pleural cavity. What are the causes and… read more »