Pneumonia is a type of respiratory infection. It affects the lungs. They consist of tiny sacs. These alveoli fill up with air during breathing. However, in pneumonia patients, these sacs get filled with pus and fluid. That makes breathing painful. It also reduces the amount of oxygen intake.
Several microorganisms cause pneumonia. These include viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
Bacterial pneumonia can occur on its own. It can also develop after a common cold or flu.
In adults, there are two typical culprits for this disease. We talk about the influenza virus and rhinovirus. Among children, the most frequent cause of viral illness differs. It is a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Types of pneumonia are divided according to the factor that caused the disease and the location of the inflammation in the lungs.
There are different types of pneumonia classified according to the cause of the disease:
Pneumonia types may also be divided according to the place where the inflammation occurs in the lungs.
Due to damage to the lung defense apparatus, they facilitate the penetration of microorganisms, changing the properties of normal secretion and destroying the respiratory epithelium. Among the viruses, the RS virus plays the most significant role, although there can also be adenoviruses, parainfluenza viruses, enteroviruses, and others.
The highest incidence of viral pneumonia![]() falls in the autumn and winter period. Illness occurs by droplet infection. Inflammation is usually preceded by a few days of runny nose, cough, and a slightly elevated temperature.
falls in the autumn and winter period. Illness occurs by droplet infection. Inflammation is usually preceded by a few days of runny nose, cough, and a slightly elevated temperature.
Viral pneumonia can be mild or severe. If a child's health suddenly deteriorates within a few hours, they may experience paroxysmal whooping cough and rapidly increasing shortness of breath. There can be weakness, pallor, cyanosis, and anxiety. In some cases, apnea may also occur. These symptoms may indicate respiratory failure. They require immediate hospitalization.
Bacterial pneumonia![]() can be primary or secondary to a viral infection. It is predisposed to diseases in which there is stagnation of secretions in the bronchial tree (asthma, cystic fibrosis), congenital defects of the respiratory system and heart, immunodeficiency or aspiration of a foreign body or food content into the respiratory tract.
can be primary or secondary to a viral infection. It is predisposed to diseases in which there is stagnation of secretions in the bronchial tree (asthma, cystic fibrosis), congenital defects of the respiratory system and heart, immunodeficiency or aspiration of a foreign body or food content into the respiratory tract.
Like some viruses, certain types of bacteria are particularly responsible for certain clinical forms of the disease. The most frequently isolated pathogen is Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. It also can be Moraxella catarrhalis. Another common one is Staphylococcus aureus.
Symptoms depend on several factors. For example, the severity of inflammatory changes, age, and the maturity of the respiratory and immune systems. Pneumonia in newborns and small kids increases quickly. Often it is a part of a generalized infection.
Usually first comes a runny nose. This makes breathing challenging. It can cause restlessness and loss of appetite. There is accelerated breathing and shortness of breath. It may happen after a few hours. Cough may be weakly expressed, and instead of elevated body temperature, there is normal or even reduced. In younger children, abdominal pain, bloating, and vomiting may occur as an expression of the toxic effects of microorganisms.
Pneumonia treatment, depending on the severity of the symptoms, takes place at home or in a hospital.
Mycoplasmas are small microorganisms. They can thrive outside of host cells. In humans – as the causative element of infection – they are detected in the respiratory, urinary, and joint cavities. The most common is Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Illness occurs by droplet transmission route, especially within close contact (work, university, school, or kindergarten). Some infections are asymptomatic and in some cases, there is inflammation of the throat, nose, paranasal sinuses, or ear.
This kind of disease is usually manifested by:
Mycoplasma pneumonia![]() is usually mild. However, some complications can be observed. For example, exudative pleurisy, lung abscesses, or respiratory failure. It mainly affects the elderly.
is usually mild. However, some complications can be observed. For example, exudative pleurisy, lung abscesses, or respiratory failure. It mainly affects the elderly.
Particularly dangerous are neurological complications (encephalitis and meningitis, myelitis, phrenic nerve, and others), cardiological (myocarditis and pericarditis), or hematological (thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia).
Other complications include arthritis or pancreatitis. There are also hepatitis, gastroenteritis, and skin rashes. After mycoplasma pneumonia, there may be paroxysmal cough. It is similar to whooping cough. This can last for a long period (even several months).

Microorganisms can remain latent in the body for years. They do not affect the healthy system. However, it causes disease symptoms. But only when the immune system is weakened.
Opportunistic pneumonia![]() can be caused by:
can be caused by:
The symptoms of opportunistic pneumonia are nonspecific. They can be common to all pneumonia types.
Aspiration pneumonia![]() occurs when stomach contents enter the bronchi or lungs, leading to inflammation in the lung tissue and fluid buildup in the alveoli.
occurs when stomach contents enter the bronchi or lungs, leading to inflammation in the lung tissue and fluid buildup in the alveoli.
Diseases are when digestive system bacteria reach the lungs and bronchial tissue. It happens in many situations. They include:
Moreover, alcohol, other stimulants, and some medications also favor the regurgitation of food into the esophagus and respiratory tract.
Symptoms of aspiration pneumonia include:
In some people, pneumonia causes less specific symptoms and may go unnoticed. This type is asymptomatic![]() (atypical).
(atypical).
In some cases, there's no cough or fever. Moreover, the doctor does not hear any alarming changes in the lungs. In such situations, the symptom of the disease is usually drowsiness and general weakness of the body. There may be also intense sweats and shortness of breath.
Developing pneumonia within a few hours after birth may result in sepsis![]() . That is an inflammatory reaction to the infection. It requires professional medical care. This dangerous condition can lead to septic shock and even death.
. That is an inflammatory reaction to the infection. It requires professional medical care. This dangerous condition can lead to septic shock and even death.
The disease-causing bacteria are usually transferred to the baby during childbirth (from the woman's genital tract). It can also happen as a result of nosocomial infection. The risk group includes premature babies. It can also happen to children with respiratory failure. Moreover, the ones intubated are endangered. Kids treated with antibiotics are at risk too.
The cause of pneumonia in an infant![]() can be both a bacterial and viral infection. It is worth mentioning that the respiratory tract in infants is short – its system is not yet fully functional.
can be both a bacterial and viral infection. It is worth mentioning that the respiratory tract in infants is short – its system is not yet fully functional.
The severity of pneumonia in an infant depends on the kid's age, immunity system, and the cause of the disease (bacteria, viruses). However, the most common occurrence is:
Most healthy children can fight off the infection. Their natural defenses help them. But there are some risk factors![]() :
:

Pneumonia can spread![]() in many ways. We have viruses and bacteria that lead to infection. There are in our noses and throats. It occurs if the immune system is weakened. Additionally, these microorganisms spread through droplets. It happens while coughing or sneezing.
in many ways. We have viruses and bacteria that lead to infection. There are in our noses and throats. It occurs if the immune system is weakened. Additionally, these microorganisms spread through droplets. It happens while coughing or sneezing.
There is another way to contract an infection. It is by touching an object with germs. Then you can transfer them to your mouth or nose.
Pneumonia can persist for about two weeks![]() . People with risk factors
. People with risk factors![]() may experience a longer recovery time. Even healthy individuals may feel weak while recovering.
may experience a longer recovery time. Even healthy individuals may feel weak while recovering.
Whether we need to stay in the hospital or be treated at home, the doctor decides in each case based on tests and a chest radiograph. The patient is referred to the hospital in the case of:
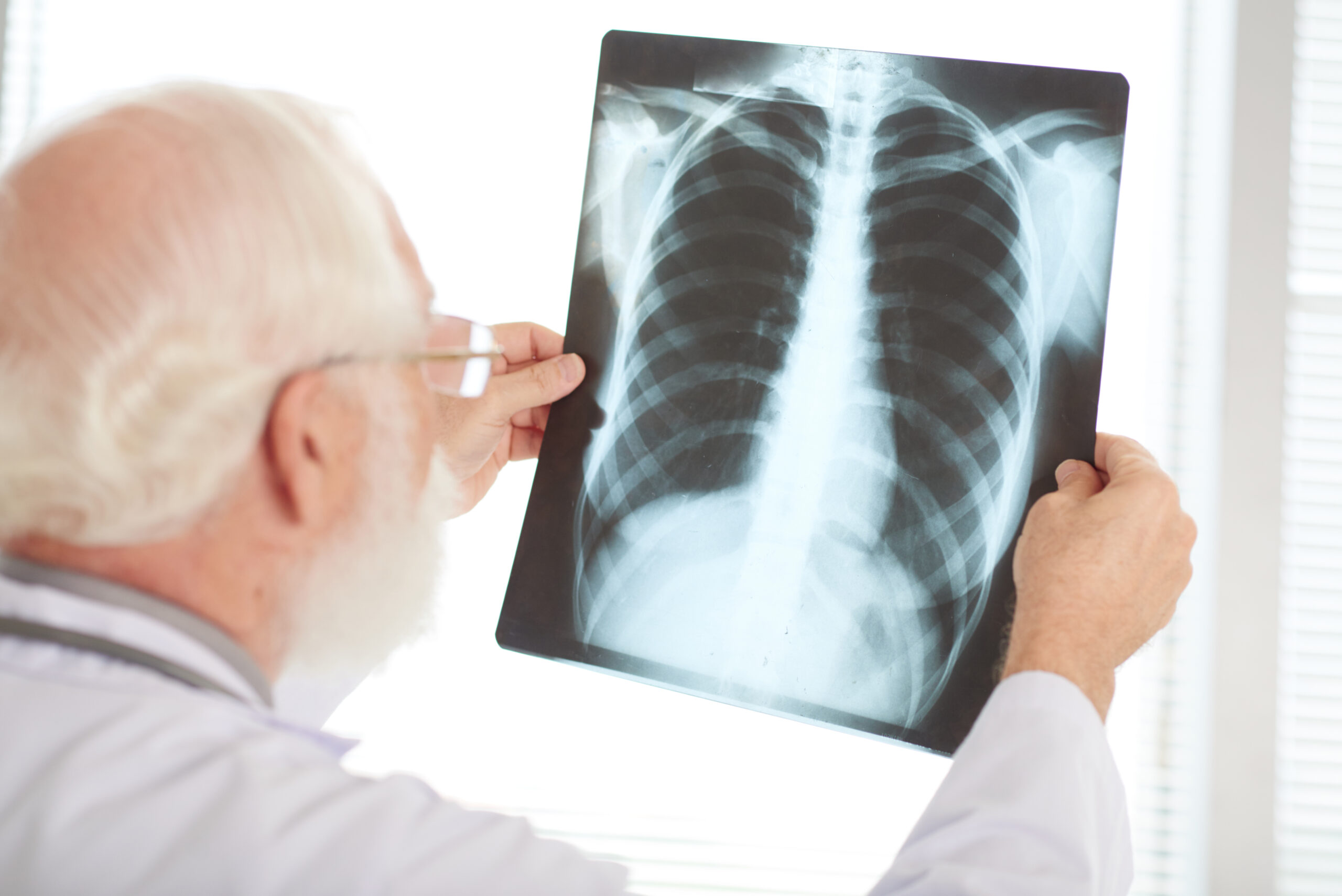
Pneumonia is diagnosed![]() by the doctor based on the history, clinical symptoms, physical examination, and test results. Doctors use the following tests to confirm the diagnosis.
by the doctor based on the history, clinical symptoms, physical examination, and test results. Doctors use the following tests to confirm the diagnosis.
A chest radiograph is an examination to diagnose pneumonia. It can determine its severity. This test also identifies any associated complications.
Blood tests check if an infection is in the bloodstream. If so – we do the blood culture test. This confirms infectious etiology. This test identifies the etiological factor. It helps to target antibiotic therapy.
Another one is a bacteriological examination of sputum. Sputum is a thick fluid produced in the lungs and airways. This test detects respiratory infections. Of course, the ones caused by bacteria or fungi.
Bronchoscopy is used for severe forms of pneumonia. The doctor inserts a bronchoscope tube with a light and camera. It goes through the nose or mouth. Then it's led down the throat. It reaches the windpipe. This helps to see the bronchi and the lungs' bronchioles. We use this procedure to find the cause of a lung problem. It allows a doctor to take mucus or tissue samples for other lab tests.
CT scan of the chest is also helpful. This is an imaging procedure. It uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology. CT produces sharp body images. Detailed photos include bones, muscles, fat, and organs.
Pneumonia can be severe. There are ways to reduce the risk![]() of getting infected.
of getting infected.
Vaccines can help prevent some types of pneumonia. Compared to people who are not vaccinated, the vaccinated ones tend to have:
Vaccines are especially significant for people at high risk of pneumonia, including:
Other ways to prevent pneumonia include:
Pneumonia is a treatable illness that can be effectively managed. With timely treatment, you can prevent the disease from advancing and avoid any severe health complications.
Complications![]() that may appear include:
that may appear include:
Pneumonia is treated![]() with antibiotics. Inform your doctor of any past antibiotic allergies or side effects before taking prescribed antibiotics at home. Hospitalization may be necessary for severe cases. Then the antibiotics may be given through an IV. It depends on the patient's condition.
with antibiotics. Inform your doctor of any past antibiotic allergies or side effects before taking prescribed antibiotics at home. Hospitalization may be necessary for severe cases. Then the antibiotics may be given through an IV. It depends on the patient's condition.
The antibiotic should be taken for about a week. However, in severe cases, it may be even 14 or 21 days. It happens in case of another infection.
Follow the specialist's advice during antibiotic therapy. Do it always. Moreover, read the information on the leaflet.
Table of Contents

A dry cough is a situation in which the cough does not produce any secretions. What is it a symptom… read more »
Whooping cough is an acute infectious disease of the respiratory system caused by bacteria. What are its causes and symptoms?… read more »

Cough is a natural, necessary reflex that protects the body from factors such as germs and pollens. When it is… read more »
Epstein Barr Virus is a pathogen that causes infectious mononucleosis and many other diseases. Learn about the risks associated with… read more »
Bronchitis is a respiratory disease most often caused by viruses. What symptoms does it cause? What is the diagnosis and… read more »
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by mycobacteria. There are many types of tuberculosis with varying symptoms. Learn it all… read more »
A viral infection occurs when a virus invades the body and begins to multiply. Viruses are tiny infectious agents that… read more »
Bacterial infections are diseases caused by the accumulation of bacteria in the body. How to distinguish them from viral infections?… read more »
MRSA infection is a medical condition in which antibiotic-resistant bacteria attack the body. The infection can be asymptomatic or very… read more »