The thyroid hormones control the body's energy balance. Their level determines whether you will burst with energy or feel constantly on the verge of a nap.
In animals that hibernate for the winter, the thyroid gland slows down first – and then hibernation takes over. In humans, it's no different: when your thyroid works too slowly and its hormones are too low, all your cells function at a lower speed.
Hypothyroidism can cause sleepiness![]() , fatigue, a general lack of energy, decreased motivation and mental energy, and reduced willingness to act.
, fatigue, a general lack of energy, decreased motivation and mental energy, and reduced willingness to act.

Since everything works slower, the body needs – and uses – less energy![]() . And it saves the surplus. Even if you did not change anything in your diet or move the same amount all the time – the excess energy will be stored in fat cells.
. And it saves the surplus. Even if you did not change anything in your diet or move the same amount all the time – the excess energy will be stored in fat cells.
Studies have shown that people with hypothyroidism (regardless of the cause) gained from 7 to even 14 kilograms within a year after diagnosis.

Hypothyroidism is often accompanied by feeling cold![]() and freezing. Heat is a byproduct of burning calories. Since the body burns these calories less and more slowly than it used to, less heat energy is produced. Hence, people suffering from hypothyroidism constantly complain that they are cold – even though they are warmly dressed and people around them are dressed lighter and do not feel the cold.
and freezing. Heat is a byproduct of burning calories. Since the body burns these calories less and more slowly than it used to, less heat energy is produced. Hence, people suffering from hypothyroidism constantly complain that they are cold – even though they are warmly dressed and people around them are dressed lighter and do not feel the cold.

Sometimes we may accidentally compress a limb (like when crossing our legs) or maintain an unhealthy position for too long, which can cause numbness and tingling sensations![]() . People with hypothyroidism often experience feeling cold, even when dressed warmly, while those around them may be dressed lighter.
. People with hypothyroidism often experience feeling cold, even when dressed warmly, while those around them may be dressed lighter.
However, if you experience this unpleasant ailment for no specific reason, the tingling occurs unexpectedly, or you feel pain, it's time to see an endocrinologist.

Thyroid hormones regulate the functioning of hair![]() bulbs in both work and life. The cells in hair follicles have a short lifespan, making them more vulnerable to hormone-level changes compared to other cells. Therefore, hair reacts faster to the decreasing level of thyroid hormones than, for example, skin or nails. Hair can also become dry, dull, and brittle.
bulbs in both work and life. The cells in hair follicles have a short lifespan, making them more vulnerable to hormone-level changes compared to other cells. Therefore, hair reacts faster to the decreasing level of thyroid hormones than, for example, skin or nails. Hair can also become dry, dull, and brittle.

Dry and itchy skin![]() is caused by the slowing of your body's metabolism. It can affect the texture and appearance of your skin. It results in a smaller amount of sweat produced and, consequently, a decrease in the moisture of the epidermis and its mechanisms of protection and regeneration.
is caused by the slowing of your body's metabolism. It can affect the texture and appearance of your skin. It results in a smaller amount of sweat produced and, consequently, a decrease in the moisture of the epidermis and its mechanisms of protection and regeneration.
A diseased thyroid gland also manifests itself in the poor condition of the nails. They may become brittle and dry or develop spots and discoloration.

Thyroid disease may be indicated by depression![]() or anxiety disorders
or anxiety disorders![]() , but these symptoms alone are not enough for a diagnosis. Patients may experience mood disturbances gradually or suddenly, such as sustained periods of depression or unexpected panic attacks. Underactive thyroid glands are more commonly associated with mood imbalances, accompanied by a general feeling of malaise, lack of concentration, or mental sluggishness.
, but these symptoms alone are not enough for a diagnosis. Patients may experience mood disturbances gradually or suddenly, such as sustained periods of depression or unexpected panic attacks. Underactive thyroid glands are more commonly associated with mood imbalances, accompanied by a general feeling of malaise, lack of concentration, or mental sluggishness.

Memory and concentration problems can be due to lack of sleep or aging, but your brain's cognitive function can suffer significantly when your thyroid gland stops working correctly. An overactive thyroid gland may result in concentration difficulties. On the other hand, if it's underactive, you may encounter memory problems and a general feeling of brain fog![]() . Appropriate treatment allows you to get rid of this persistent ailment.
. Appropriate treatment allows you to get rid of this persistent ailment.

Thyroid diseases may affect bowel movements by disrupting the digestive process![]() . Hypothyroidism can cause chronic constipation and painful bowel movements. Hyperthyroidism can result in more frequent and urgent bowel movements with diarrhea. Loose stools with a higher volume of liquid can also occur with hyperthyroidism, even if the patient has eaten very little.
. Hypothyroidism can cause chronic constipation and painful bowel movements. Hyperthyroidism can result in more frequent and urgent bowel movements with diarrhea. Loose stools with a higher volume of liquid can also occur with hyperthyroidism, even if the patient has eaten very little.

Thyroid hormones work closely with other hormones (e.g., sex hormones), to regulate the body's functions. Fluctuating levels of thyroid hormones can disrupt hormonal signaling along with other hormonal pathways as well, resulting in disturbing the menstrual cycle![]() . In addition, thyroid hormones also directly affect the ovaries and uterus.
. In addition, thyroid hormones also directly affect the ovaries and uterus.

Lack of or little desire for sexual intercourse may be the result of hypothyroidism. Too little thyroid hormone can contribute to a decrease in libido![]() and sex appetite. Other accompanying symptoms such as weight gain, low energy, and pain can also play a negative role in the quality of your sex life.
and sex appetite. Other accompanying symptoms such as weight gain, low energy, and pain can also play a negative role in the quality of your sex life.

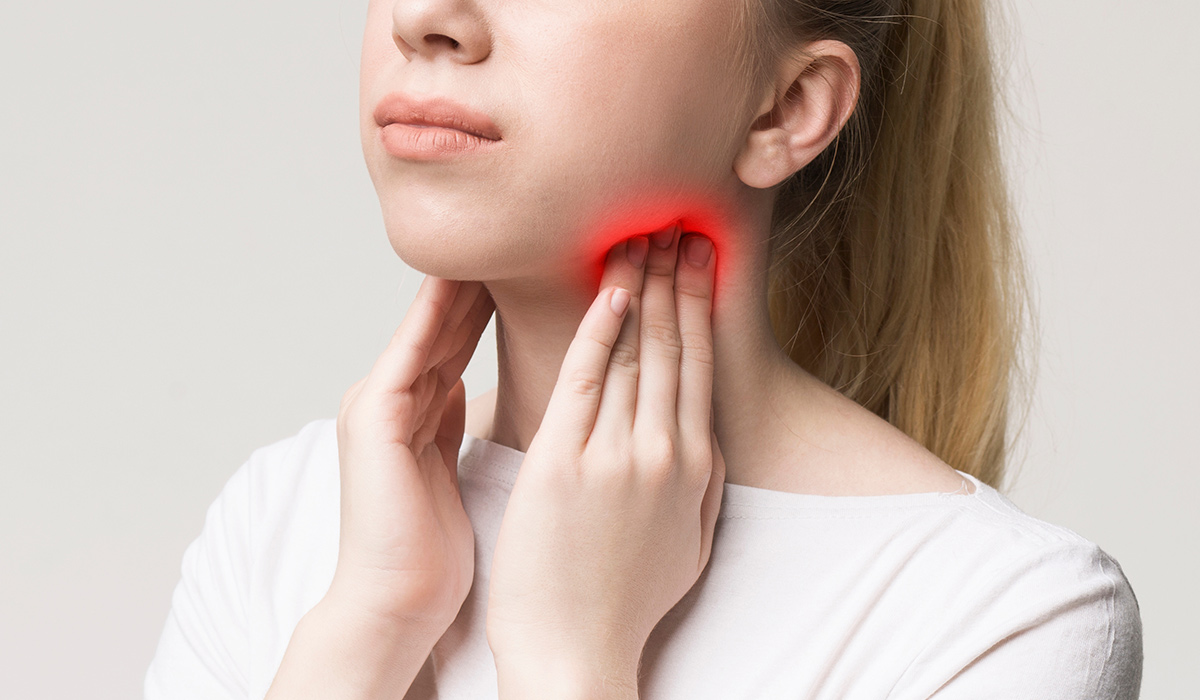
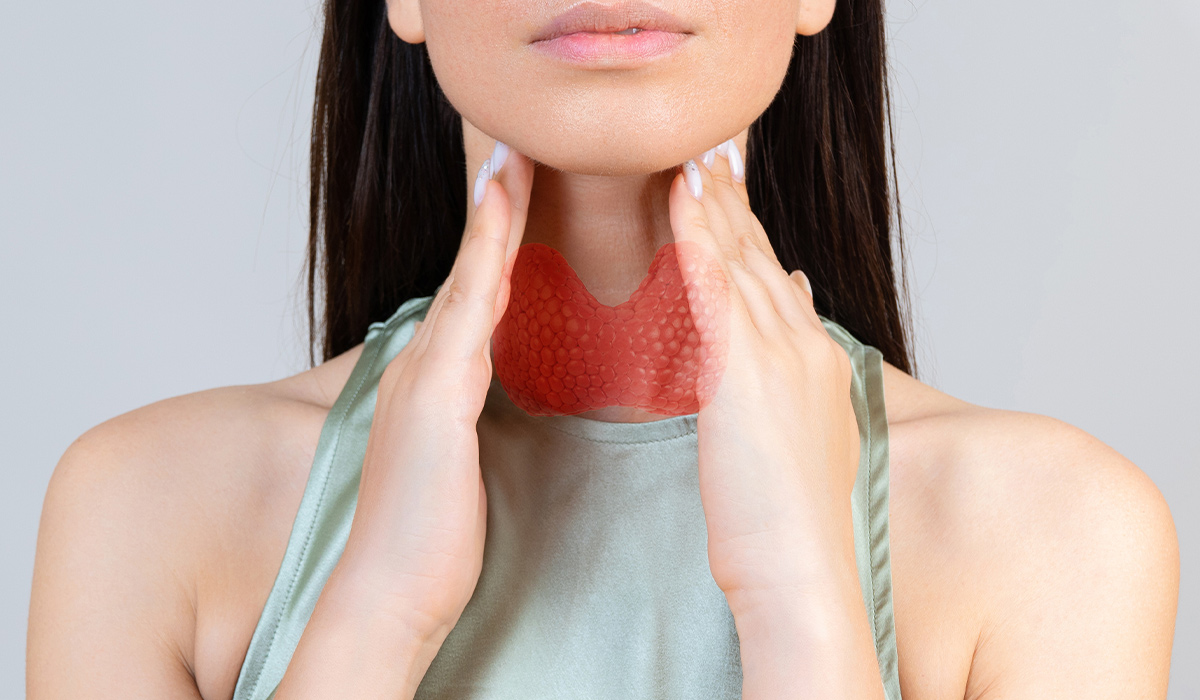
If you notice swelling in your throat![]() or an enlarged thyroid that causes neck pain and a hoarse voice, it may be a goiter. In addition to weight gain, low energy, and pain, other symptoms can also have a detrimental effect on your sexual experience. One such symptom is a swollen throat.
or an enlarged thyroid that causes neck pain and a hoarse voice, it may be a goiter. In addition to weight gain, low energy, and pain, other symptoms can also have a detrimental effect on your sexual experience. One such symptom is a swollen throat.
If you notice swelling in your throat or experience neck pain due to an enlarged thyroid, it is important to seek medical attention. It could just be a result of an underlying condition that is causing the thyroid to grow. If there is a noticeable swelling at the base of the neck, it could indicate the presence of a goiter.

Heart palpitations![]() can feel like your heart is skipping a beat or beating faster than normal. It's possible to experience these feelings either in your chest or at a pulse point within your body.
can feel like your heart is skipping a beat or beating faster than normal. It's possible to experience these feelings either in your chest or at a pulse point within your body.
If you have hypothyroidism, your heart rate may decrease. It is because the thyroid hormone helps regulate heart rate.

This pain can be severe and relentless, hindering your ability to perform daily tasks and movements.
Additionally, you may experience weakness in specific muscle groups and tremors in your hands. Swelling, stiffness, and pain can also occur in your muscles and joints.

Sleep![]() regulates hormonal processes in the body. It also affects the functioning of the thyroid gland.
regulates hormonal processes in the body. It also affects the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Sleep deprivation can lead to changes in thyroid function – increasing TSH secretion. This can lead to hypothyroidism. One of the symptoms of hypothyroidism is slowing down and fatigue and daytime sleepiness additionally intensify problems with night rest.
Problems with night rest can be exacerbated by daytime sleepiness. Furthermore, an underactive or overactive thyroid can also contribute to sleep issues. Too much hormone production causes hyperthyroidism. It can lead to restlessness, rapid heart rate, and insomnia. Therefore, if your thyroid is not functioning correctly, one of the significant elements of therapy is to ensure valuable sleep, reduce excess stress and support the immune system.

Thyroid diseases typically develop over several years without causing any noticeable symptoms, and they are typically painless. The most common types of thyroid diseases include hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, Hashimoto's disease, and Graves-Basedow disease.
This is the disease that is most commonly diagnosed when it comes to thyroid disease.
The thyroid does not produce enough hormones. The primary reason for hypothyroidism![]() is Hashimoto's disease
is Hashimoto's disease![]() . It is chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism can be primary, i.e. due to the gland not working correctly, or secondary – it refers to diseases of the pituitary gland, which is then unable to produce TSH.
. It is chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism can be primary, i.e. due to the gland not working correctly, or secondary – it refers to diseases of the pituitary gland, which is then unable to produce TSH.
Some symptoms include:
Symptoms in everyday life, if severe, can be tiring and bothersome. It's important to take hypothyroidism seriously, as untreated cases can result in serious health problems, such as heart disease and infertility. If you experience any symptoms, it's best to see a doctor and complete the necessary tests. Keep in mind that hypothyroidism develops gradually and may not show noticeable signs at first, so it's crucial not to underestimate any potential symptoms. Hypothyroidism is treated by supplementing with appropriate hormones.
The second most important disease is hyperthyroidism![]() . The cause is also an autoimmune process, i.e. Graves' disease
. The cause is also an autoimmune process, i.e. Graves' disease![]() ; or overactive nodules in the thyroid gland.
; or overactive nodules in the thyroid gland.
When the gland produces an excess of the necessary hormone, it can result in negative effects. An overproduction of thyroid hormone can decrease the release of TSH by the pituitary gland.
It is significant to recognize the following symptoms, which may be similar to those caused by prolonged stress or fatigue but should still be taken seriously:
Hyperthyroidism cannot be underestimated. The disease develops over the years, at first it may not cause any symptoms. However, when they appear, do not underestimate them, but go to the doctor right away. Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to severe medical complications. For example, it can result in cardiac arrhythmias and osteoporosis. Pregnant women and their fetuses are at risk when dealing with hyperthyroidism.
Many factors increase the risk of developing thyroid disease. Chronic stress![]() is considered one of the main culprits. It significantly weakens the immune system, which may contribute to greater susceptibility to inflammation. The state of the gland is also adversely affected by stimulants and various types of environmental toxins.
is considered one of the main culprits. It significantly weakens the immune system, which may contribute to greater susceptibility to inflammation. The state of the gland is also adversely affected by stimulants and various types of environmental toxins.
Nutrients![]() such as iodine, selenium, iron, zinc, selenium, and vitamins from group B, vitamins C, and D are significant.
such as iodine, selenium, iron, zinc, selenium, and vitamins from group B, vitamins C, and D are significant.
Therefore, prophylactically, to avoid thyroid diseases, you should take care of a better lifestyle, i.e. reduce stress, have an adequate amount of sleep, eat properly (including supplementing if necessary), stop smoking, and go out into nature.
To monitor the health of your thyroid gland, do regular preventive tests![]() . They may include measuring the concentration of TSH. This test detects thyroid dysfunction. With an excess of thyroid hormones typical of hyperthyroidism, the concentration of TSH decreases, while with their deficiency – it increases. When the TSH result is abnormal, it is necessary to test the concentration of FT3 and FT4 hormones and further diagnostics.
. They may include measuring the concentration of TSH. This test detects thyroid dysfunction. With an excess of thyroid hormones typical of hyperthyroidism, the concentration of TSH decreases, while with their deficiency – it increases. When the TSH result is abnormal, it is necessary to test the concentration of FT3 and FT4 hormones and further diagnostics.
It is significant to undergo an ultrasound of the thyroid gland for a thorough check-up. It helps to visually assess this gland – its size, structure, and presence of any nodules and their phenotype. Today's devices detect changes as small as a few millimeters. A lesion that should raise concern is usually irregularly bordered, hypoechoic, and has microcalcifications.
If the lesions look suspicious, a fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy may be necessary. It consists of the aspiration of a suspension of cells together with intercellular fluid from the examined lesion by puncturing with a thin needle. Therefore, only cells are taken from the patient, not tissue sections, which are then subjected to cytological examination. During it, the pathologist evaluates their appearance, without assessing the structure of the tissue.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy is usually performed under ultrasound guidance – which helps to precisely collect material even from small lesions. Because thin needles are used, it is performed without anesthesia. It is a simple and quick test, which is usually not accompanied by complications. Cytological evaluation of the material in many cases allows to establish the diagnosis, which in turn helps in qualifying the patient for a possible surgery.
We use pharmacological treatment for many thyroid diseases. In the case of hypothyroidism![]() , you should constantly take medications with hormones that the thyroid produces too little or too much. Their dose is determined individually to the predisposition and stage of the patient's disease. The first effects of the therapy are visible after a few months.
, you should constantly take medications with hormones that the thyroid produces too little or too much. Their dose is determined individually to the predisposition and stage of the patient's disease. The first effects of the therapy are visible after a few months.
In the case of nodular lesions, we use surgical treatment![]() . The patient usually has the entire thyroid gland removed or sometimes one lobe depending on the size of the tumor and the stage of the disease. In the case of papillary or follicular thyroid cancer, adjuvant treatment with radioiodine is sometimes also included. It is designed to destroy the remnants of thyroid tissue and possible micrometastases. Indications for surgery are also benign large lesions that cause compression symptoms on the airways, extending beyond the breastbone to the mediastinum.
. The patient usually has the entire thyroid gland removed or sometimes one lobe depending on the size of the tumor and the stage of the disease. In the case of papillary or follicular thyroid cancer, adjuvant treatment with radioiodine is sometimes also included. It is designed to destroy the remnants of thyroid tissue and possible micrometastases. Indications for surgery are also benign large lesions that cause compression symptoms on the airways, extending beyond the breastbone to the mediastinum.
After a thyroidectomy, the patient must take medicines for the rest of his life to replace the thyroid hormones that the removed gland can no longer produce. The surgical removal of the thyroid gland results in hypothyroidism. Therefore, patients who undergo this surgery are treated similarly to those with hypothyroidism. In addition, after surgery to remove the gland, you should undergo regular check-ups with an endocrinologist, including monitoring of TSH levels and possible modifications of the thyroxine dose.
Asymptomatic, insignificant nodular lesions do not always require surgery. Often it is enough to observe them.
Table of Contents
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the body produces too many hormones. This causes various symptoms and complications. Check out… read more »

Hypothyroidism is a disease caused by insufficient levels of hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Find out, what are the… read more »

The thyroid is an endocrine gland. What hormones does it produce? Learn what are most popular thyroid diseases and what's… read more »
Also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune condition that causes the immune system… read more »
Goiter is an enlargement of this gland. It is not a disease itself, but rather a symptom of a medical… read more »
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disease. May cause hypothyroidism. Check what are the symptoms of Hashimoto's disease and how it… read more »

Graves' disease is one of many autoimmune diseases that affect various organs, glands, and systems throughout the human body. It… read more »

An endocrinologist is a doctor who deals with the organs that secrete hormones. Learn about diseases that are related to… read more »
Weight loss refers to a reduction in total body mass, which can result from decreased caloric intake, increased physical activity,… read more »