Goiter of the thyroid gland is an enlargement of the gland. Usually, the cause of the lesion is not severe, and the goiter is only a cosmetic defect. However, in some situations, it indicates a progressive disease.
Thyroid goiter may be visible to the naked eye. Then, the lower front part of the neck appears widened and thickened. Sometimes, the change may only be noticeable when you raise your head and “crane” your neck.
Patients do not notice thyroid enlargement in the early stages, and they only notice goiter when it is visible on the neck in any position. However, these symptoms should not be ignored even if a health problem does not cause the change. The correct level of thyroid hormones is immensely significant for the functioning of the entire body, so you should take care of the satisfactory condition of the gland. If you notice a thickening, consult a specialist immediately.

As mentioned, thyroid enlargement can have many causes – not all are health or life-threatening. The thyroid![]() is an unpaired gland. It is located in the anterior-lower part of the neck. It produces some hormones, but not every thyroid dysfunction is associated with secretion disorders.
is an unpaired gland. It is located in the anterior-lower part of the neck. It produces some hormones, but not every thyroid dysfunction is associated with secretion disorders.
This gland produces three hormones![]() – thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. These first two substances are particularly significant and take part in several processes
– thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. These first two substances are particularly significant and take part in several processes![]() occurring in the body.
occurring in the body.
The change is called neutral thyroid goiter if the enlarged gland does not affect its hormonal functioning. Often, its symptoms are unnoticeable in the initial phase, but sometimes they can develop significantly. The most common cause of the disorder is iodine deficiency. Neutral, non-toxic thyroid goiter![]() is not a symptom of inflammation or cancer; its treatment depends on the doctor's decision. Sometimes, it is enough to observe and monitor the growth of the lesion.
is not a symptom of inflammation or cancer; its treatment depends on the doctor's decision. Sometimes, it is enough to observe and monitor the growth of the lesion.
As a rule, a harmless form of gland enlargement is also the so-called juvenile goiter![]() , appearing in teenagers during puberty. It occurs much more often in girls than in boys. It does not always require treatment, but it should always be carefully diagnosed and monitored to ensure that severe changes do not develop.
, appearing in teenagers during puberty. It occurs much more often in girls than in boys. It does not always require treatment, but it should always be carefully diagnosed and monitored to ensure that severe changes do not develop.
Thyroid goiter accompanied by nodular lesions is one of the most common abnormalities of this organ and visits to an endocrinologist. Nodules growing on the gland can have two forms:
Nodular thyroid goiter![]() may be neutral or toxic
may be neutral or toxic![]() . The latter is accompanied by excessive secretion of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones. For this reason, it is also often called hyperactive nodular goiter. The symptoms of the change coexist with the symptoms of hyperactivity of the gland, i.e., increased sweating, anxiety, weight loss, or muscle weakness.
. The latter is accompanied by excessive secretion of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones. For this reason, it is also often called hyperactive nodular goiter. The symptoms of the change coexist with the symptoms of hyperactivity of the gland, i.e., increased sweating, anxiety, weight loss, or muscle weakness.
The treatment of nodular thyroid goiter may vary, and a doctor should always decide its course. It may be based on pharmacology or surgical treatment, depending on the disease's etiology, extent, and advancement. Nodular goiter accompanied by benign lesions is usually treated effectively, but the sooner the diagnosis is made and therapy is started, the greater the chances of avoiding complications.
Although nodular thyroid diseases are often a cause of great anxiety for patients, in most cases their treatment is effective and brings satisfactory results. Non-toxic nodular goiter is sometimes diagnosed during imaging tests (mainly during ultrasound examination) or the simplest palpation of the thyroid gland performed during a visit to a specialist. Sometimes, this simple practice is enough to detect anatomical changes, such as enlargement or nodularity of the thyroid gland.
Parenchymal goiter![]() does not have focal lesions but arises from the uniform thyroid parenchyma, which is subject to excessive growth. The structure remains homogeneous; no nodules are observed on palpation or imaging. It should be noted that there is a specific form of goiter in which both nodules and hypertrophy of homogeneous thyroid tissue occur. We are talking about parenchymal-nodular goiter. What usually happens is that homogeneous tissue grows first, and focal lesions appear on it in the next phase.
does not have focal lesions but arises from the uniform thyroid parenchyma, which is subject to excessive growth. The structure remains homogeneous; no nodules are observed on palpation or imaging. It should be noted that there is a specific form of goiter in which both nodules and hypertrophy of homogeneous thyroid tissue occur. We are talking about parenchymal-nodular goiter. What usually happens is that homogeneous tissue grows first, and focal lesions appear on it in the next phase.
Remember that thyroid goiter is a symptom, not a disease itself. Thyroid hyperplasia![]() may result from overproduction of TSH by the pituitary gland. As a result, the level of thyroid hormones in the blood decreases. Most often, however, thyroid goiter results from iodine deficiency, an essential component of thyroid hormones. This condition may also occur as a result of stress and during pregnancy. It also happens that thyroid goiter is a symptom of diseases such as:
may result from overproduction of TSH by the pituitary gland. As a result, the level of thyroid hormones in the blood decreases. Most often, however, thyroid goiter results from iodine deficiency, an essential component of thyroid hormones. This condition may also occur as a result of stress and during pregnancy. It also happens that thyroid goiter is a symptom of diseases such as:
In addition to the characteristic thickening in the lower part of the neck, the enlarged thyroid causes standard symptoms![]() from the respiratory and digestive systems, including:
from the respiratory and digestive systems, including:
In addition to the symptoms listed above, it is worth paying attention to additional symptoms characteristic of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. It makes it easier to diagnose the type of thyroid dysfunction.

The symptoms of hyperthyroidism![]() include:
include:
The symptoms of hypothyroidism![]() include:
include:
Remember that symptoms of thyroid dysfunction may occur in both women and men. For this reason, if you notice disturbing symptoms, do not hesitate to go to a specialist.
The basis for diagnosing![]() nodular goiter is for a doctor to palpate the patient. During this procedure, the specialist can assess the size of the thyroid gland (a normal thyroid should not be palpable) and the presence of nodules.
nodular goiter is for a doctor to palpate the patient. During this procedure, the specialist can assess the size of the thyroid gland (a normal thyroid should not be palpable) and the presence of nodules.
In addition, the diagnostic procedure must include a detailed interview. Your doctor may ask about, among other things:
Based on the interview and palpation![]() , they can sometimes make a preliminary diagnosis, but usually, they refer the patient to additional tests or a visit to a specialist – an endocrinologist. Further diagnosis is usually based on laboratory blood tests that help determine the level of hormones secreted by the gland. However, it is worth remembering that in the case of neutral thyroid goiter, TSH results are good, but tissue hyperplasia still occurs.
, they can sometimes make a preliminary diagnosis, but usually, they refer the patient to additional tests or a visit to a specialist – an endocrinologist. Further diagnosis is usually based on laboratory blood tests that help determine the level of hormones secreted by the gland. However, it is worth remembering that in the case of neutral thyroid goiter, TSH results are good, but tissue hyperplasia still occurs.
Therefore, a blood test![]() alone is not enough and must be supplemented with imaging tests
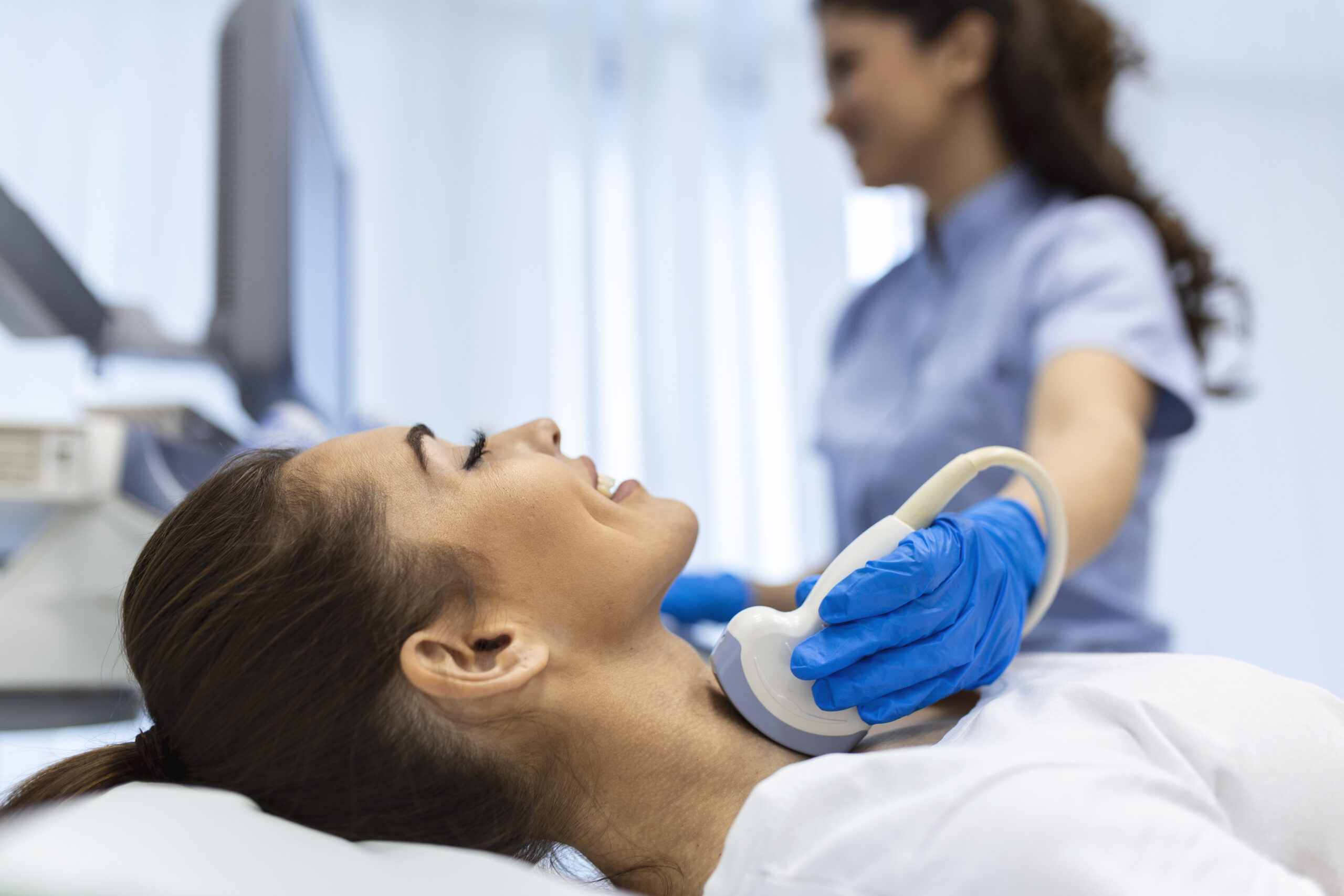
alone is not enough and must be supplemented with imaging tests![]() . The most frequently performed test is thyroid ultrasound, which allows us to assess not only the size of the organ but also its echogenicity. The doctor may also recommend performing scintigraphy – a method that uses radioactive isotopes to create images of pathological changes. In addition to ultrasound and scintigraphy, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is sometimes performed to diagnose the thyroid gland.
. The most frequently performed test is thyroid ultrasound, which allows us to assess not only the size of the organ but also its echogenicity. The doctor may also recommend performing scintigraphy – a method that uses radioactive isotopes to create images of pathological changes. In addition to ultrasound and scintigraphy, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is sometimes performed to diagnose the thyroid gland.
Moreover, fine needle aspiration biopsy![]() is used to distinguish whether a lesion is benign or needs to be looked at more closely (for example, whether it is cancerous). This procedure involves inserting a needle through the skin, which allows cells to be collected from the suspected lesion. This makes it possible to perform a microscopic evaluation of cells taken from the lesion in the laboratory.
is used to distinguish whether a lesion is benign or needs to be looked at more closely (for example, whether it is cancerous). This procedure involves inserting a needle through the skin, which allows cells to be collected from the suspected lesion. This makes it possible to perform a microscopic evaluation of cells taken from the lesion in the laboratory.
The prognosis is good if the disease progresses slowly and changes are mild. In such situations, only systematic testing and treatment monitoring are required. However, the most severe complication of nodular goiter is the development of thyroid cancer. Then, you need to pay more attention to the suspicious change.
The need for treatment and the type of therapy implemented depends on the type of goiter, its size, the cause of its development, the level of its advancement, the form of changes, and the patient's general health condition.
In some cases, treatment![]() is not necessary at all, and the specialist monitors the development of the lesion. For example, neutral parenchymal goiter most often does not require treatment. In most cases, it is caused by iodine deficiency – therefore, iodine supplementation
is not necessary at all, and the specialist monitors the development of the lesion. For example, neutral parenchymal goiter most often does not require treatment. In most cases, it is caused by iodine deficiency – therefore, iodine supplementation![]() will be effective in this case.
will be effective in this case.
However, if the goiter is large and bothersome and presses on neighboring organs, the doctor may recommend surgical or pharmacological treatment![]() (depending on the cause of the problem).
(depending on the cause of the problem).
If the cause of an enlarged goiter is health problems, the most important thing is to treat the disease that contributed to the development of the goiter, not the goiter that is its consequence. In autoimmune diseases, pharmacology is most often used. If we suffer from hyperthyroidism, the doctor may suggest taking antithyroid drugs – thioamides, β-blockers, as well as treatment with various types of iodine, l***************e, sodium perchlorate, or glucocorticosteroids. In turn, in the case of cancer, it is often combined with surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy.
In some cases, it is necessary to perform surgery![]() . Recommendations for the procedure include:
. Recommendations for the procedure include:
One of the procedures is thyroidectomy![]() , i.e., complete removal of the thyroid gland. It is an invasive procedure. Indications for removal of goiter and the entire thyroid gland include some goiter with focal lesions, some goiter associated with Hashimoto's disease, recurrent goiter, or cancerous goiter.
, i.e., complete removal of the thyroid gland. It is an invasive procedure. Indications for removal of goiter and the entire thyroid gland include some goiter with focal lesions, some goiter associated with Hashimoto's disease, recurrent goiter, or cancerous goiter.
Your doctor may decide to remove the gland partially. Strumectomy is a less complicated surgery. The most frequently treated patients are neutral nodular goiter, hyperactive nodular goiter, neutral parenchymal goiter, hyperactive parenchymal goiter, or goiter resulting from thyroiditis.
General anesthesia is commonly used when performing thyroid goiter surgery. The length of the cutting line depends on the size of the crop. After cutting the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, and the broad neck muscle, the doctor identifies the thyroid gland. After an appropriately performed procedure, the muscles and skin are sewn together.
Thyroid removal procedure carries the risk of complications. Most often, however, they are not dangerous and disappear shortly after the procedure. Typically, patients may experience discomfort around the postoperative wound, neck pain, or difficulty swallowing saliva. More severe complications may also occur during surgery, including:
Patients who have had their thyroid removed usually go home the day after surgery. If complications occur, it may be necessary to extend hospitalization. The recovery period and return to daily activities depend primarily on the type of disease, the extent of the procedure, and the method used. Usually, it is about two weeks. During this period, you should refrain from excessive physical exercise to prevent the wound from spreading and bleeding. After surgery, patients should undergo follow-up visits to their doctor to monitor their thyroid gland. The natural consequence after removal of the entire gland is hypothyroidism. Therefore, in most cases, lifelong l***********e supplementation is necessary.
The presence of goiter on the thyroid gland is always the basis for medical consultation, thorough diagnosis, and, if necessary, implementation of appropriate treatment. For this reason, no home methods should replace traditional therapy recommended by a specialist. However, home remedies for thyroid goiter may support conventional treatment.
The basis is to introduce changes in the diet, which should be rich in appropriate microelements that positively affect the functioning of the gland. These are primarily:
You can also consider supplementation, but it is worth consulting a specialist before taking a new product. It is also essential to limit the consumption of products containing large amounts of substances that reduce the possibility of iodine absorption, such as cruciferous vegetables, legumes, and turnip vegetables.
An individually tailored and properly balanced diet, a rich source of nutrients significant for properly synthesizing T3 and T4 thyroid hormones and limiting unhealthy foods, is of great importance for the patient's health. Moreover, more specific daily dietary guidelines may depend on the cause of the problem. For this reason, it is worth contacting a specialist and asking for a menu.
Some people recommend turning to nature and using herbs. Recommended plants include sage, lemon balm, rosemary, horsetail, speedwell, knotweed, nettle, and ashwagandha. Before starting any herbal therapy, it is worth consulting a specialist.
In addition to your diet, it is worth taking care of regular, moderate physical activity, avoiding stressors, as well as effective rest and restful sleep. These methods help maintain good overall body condition and support hormonal balance.
Table of Contents
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the body produces too many hormones. This causes various symptoms and complications. Check out… read more »

The thyroid is an endocrine gland. What hormones does it produce? Learn what are most popular thyroid diseases and what's… read more »

The thyroid is a small organ whose hormones regulate the body's metabolism. Check what are the signs of thyroid problems.… read more »

Hypothyroidism is a disease caused by insufficient levels of hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Find out, what are the… read more »
Also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune condition that causes the immune system… read more »

Graves' disease is one of many autoimmune diseases that affect various organs, glands, and systems throughout the human body. It… read more »
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disease. May cause hypothyroidism. Check what are the symptoms of Hashimoto's disease and how it… read more »

An endocrinologist is a doctor who deals with the organs that secrete hormones. Learn about diseases that are related to… read more »

Hay fever is one of the symptoms of allergies. It may appear immediately after contact with the allergen or after… read more »