Diarrhea can last several days and deprive the body of water and minerals necessary for survival. Diarrhea is characterized by passing three or more loose or liquid stools per day or more frequent bowel movements than usual for an individual. Passing formed stools frequently is not considered diarrhea; the same goes for loose stools in breastfed infants.
Usually, it is a symptom of a gastrointestinal infection. If so, it can be caused by a variety of organisms. The condition can be spread through contaminated food or drinking water or from person to person due to poor hygiene practices.
Interventions to prevent diarrhea can reduce the risk of the disease. That includes:
Tests carried out in the diagnosis![]() include:
include:
Moreover, the laboratory test includes:
The specialist examination includes a colonoscopy or gastroscopy of the gastrointestinal tract. The doctor may take the affected areas for histological analysis. X-ray or ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging may also be performed to identify possible anatomical abnormalities.
The symptoms![]() vary depending on the severity and the cause of the diarrhea.
vary depending on the severity and the cause of the diarrhea.
You may encounter some or all of these symptoms if you have this condition. The main symptom of this condition is loose or watery stool.
Other symptoms of mild type diarrhea may include:
If you have severe diarrhea, there may be symptoms such as:
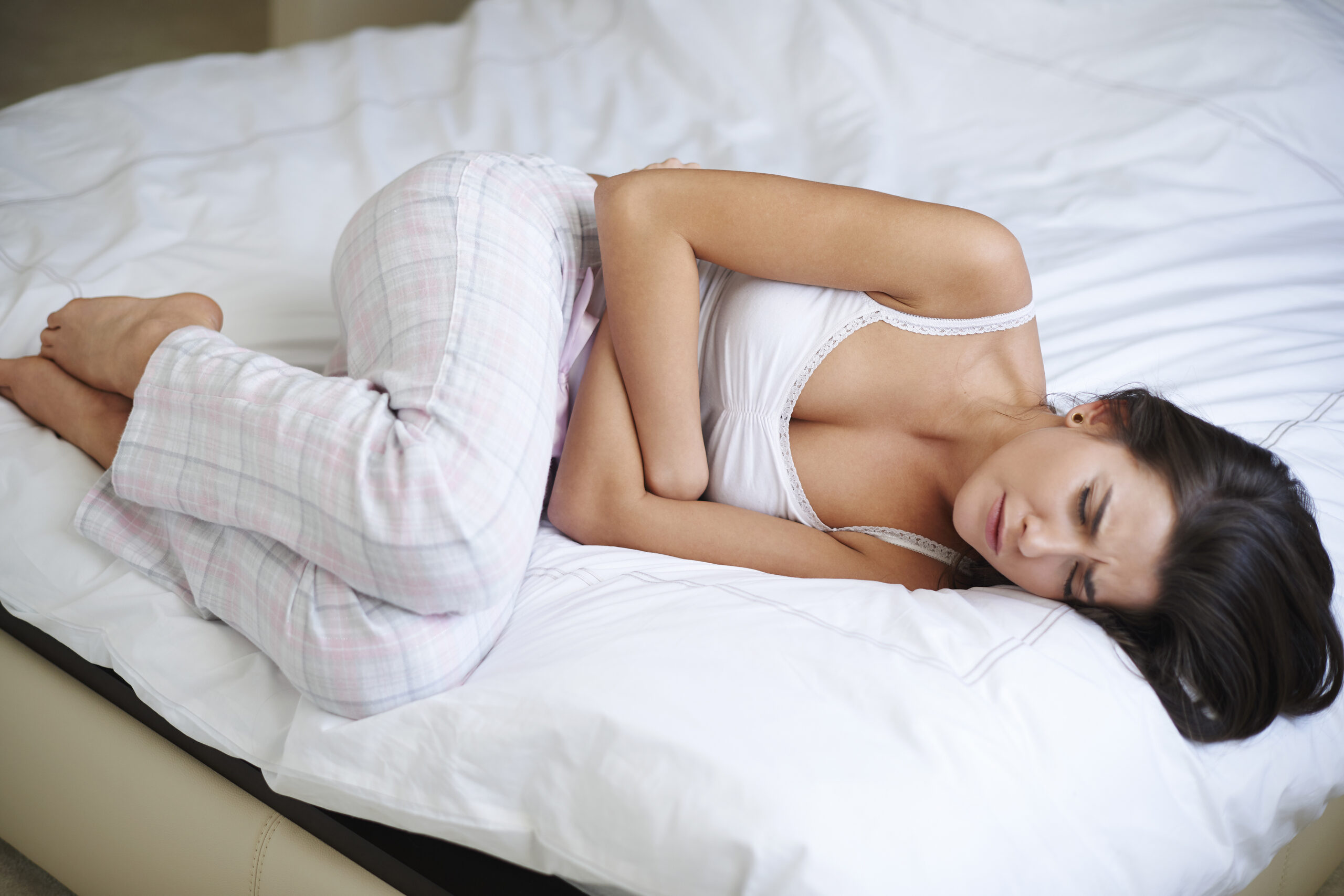

There are two clinical types of this condition: acute and chronic.
Acute diarrhea![]() is a common problem that almost all of us face in our lives. Having a chronic
is a common problem that almost all of us face in our lives. Having a chronic![]() condition can affect both overall health and quality of life. That's why it's significant to know how to recognize the different types of diarrhea and take appropriate action to treat the symptoms and underlying causes.
condition can affect both overall health and quality of life. That's why it's significant to know how to recognize the different types of diarrhea and take appropriate action to treat the symptoms and underlying causes.
Acute diarrhea comes on suddenly. It is often associated with food ingestion containing a bacterium, parasite, or toxin. It is characterized as the abrupt onset of three or more watery bowel movements per day, which typically subsides within two weeks.
The chronic type is when we have loose stools for at least four weeks. There are many possible causes of chronic diarrhea. In this case, treatment will consist of removing the condition's cause and treating the complications to stop the symptoms.
In the case of chronic diarrhea, it is necessary to consult a doctor. The symptoms can be dangerous in the long run but also more severe conditions such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
Certain substances that cannot be absorbed through the colon wall can lead to osmotic diarrhea![]() . This excess of importance in the intestine causes an increase of water in the feces, resulting in the condition.
. This excess of importance in the intestine causes an increase of water in the feces, resulting in the condition.
Some types of food, like certain fruits and beans, and sugar substitutes found in diet foods, sweets, and chewing gum (such as sorbitol and m******l) may cause osmotic diarrhea. Additionally, lactase deficiency can also result in this condition.
The small intestine has an enzyme called lactase. It converts milk sugar or lactose into glucose and galactose. The bloodstream can then absorb them. However, with lactase deficiency – lactose is not digested correctly. This results in lactose accumulation in the intestine, which leads to osmotic diarrhea. This condition is commonly known as lactose intolerance.
The quantity of osmotic substances consumed determines the severity of the condition. Diarrhea ceases when the individual discontinues food and drink intake. Blood present in the digestive tract also functions as an osmotic agent, leading to the production of black, tarry stools. Additionally, the overgrowth of natural intestinal bacteria or the growth of foreign bacteria in the intestines can cause osmotic diarrhea. The use of antibiotics may destroy normal gut bacteria and trigger this ailment.
A type of stool called secretory happens when the small and large intestines release salts like sodium chloride and water. It can be caused by toxins like the one produced by cholera infection or certain viral infections.
When the lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed![]() , ulcerated, or swollen and releases proteins, blood, mucus, and other fluids, it leads to a condition where the stool gains volume and fluid content. Multiple diseases can cause this condition:
, ulcerated, or swollen and releases proteins, blood, mucus, and other fluids, it leads to a condition where the stool gains volume and fluid content. Multiple diseases can cause this condition:
When the rectal lining is affected, people often feel an urgent and frequent bowel movement because the inflamed rectum is more sensitive to dilation (distension) by the stool.
We can also classify diarrhea by stool appearance:
A normal stool in babies can vary in color and consistency. Even newborns have multiple bowel movements every day.
Normal baby stool may look yellow, brown, brown, or green. It can be liquid, soft, thick like a paste, or more formed. A baby may have several nappies a day or just one or two. The contents of your baby's diaper are influenced by their age and diet.
Diarrhea is a symptom of infections caused![]() by many organisms. Most of them are transmitted through water contaminated with feces. Condition is more common when there is a lack of proper sanitation and hygiene and safe water for drinking, cooking, and cleaning.
by many organisms. Most of them are transmitted through water contaminated with feces. Condition is more common when there is a lack of proper sanitation and hygiene and safe water for drinking, cooking, and cleaning.
In low-income countries, moderate to severe diarrhea is most commonly caused by Rotavirus and Escherichia coli. Other pathogens like Cryptosporidium and Shigella species may also be significant contributors to the development of diarrhea. It's substantial to take into account site-specific patterns of causation.
Children who pass away due to diarrhea usually experience malnutrition![]() , which increases their vulnerability to this ailment. In turn, each episode of the disease aggravates their malnutrition.
, which increases their vulnerability to this ailment. In turn, each episode of the disease aggravates their malnutrition.
Of particular concern is water contaminated with human or animal feces, for example, from sewage and septic tanks.
Diarrhea can spread through human-to-human contact, especially if personal hygiene is lacking. Also, unsanitary food preparation or storage can significantly cause the illness. Unsafe household water storage and handling is also a significant risk factor.
With disturbing symptoms, it is worth contacting a doctor without delay. The fastest way to do this is by arranging an online teleconsultation with an internist. The doctor can provide suitable prescriptions for medications and give guidance on the next steps for treatment.
Viruses often cause acute diarrhea. Rotavirus![]() is the most common in children and norovirus in adults. If you experience acute diarrhea for a short time, it may be due to one of the following problems:
is the most common in children and norovirus in adults. If you experience acute diarrhea for a short time, it may be due to one of the following problems:
Chronic diarrhea can be a symptom of a more severe or chronic condition like:
Most antibiotics![]() can cause this condition. Antibiotics can change the balance of bacteria naturally found in the gut, allowing certain bacteria to grow.
can cause this condition. Antibiotics can change the balance of bacteria naturally found in the gut, allowing certain bacteria to grow.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea can start any time while taking an antibiotic or soon after. If you experience any side effects, contact your doctor to discuss the most suitable option to alleviate them.
We treat![]() this condition with fluids, antibacterial drugs, and a proper diet. They are often conducted in a hospital. Also, it is worth remembering about prevention.
this condition with fluids, antibacterial drugs, and a proper diet. They are often conducted in a hospital. Also, it is worth remembering about prevention.
Diarrhea can be a dangerous disease, which is sometimes even life-threatening. Diarrhea often causes dehydration![]() in patients, so they should be given as much fluid as possible containing – sodium, potassium, and chlorine. Dehydration is especially dangerous in young children.
in patients, so they should be given as much fluid as possible containing – sodium, potassium, and chlorine. Dehydration is especially dangerous in young children.
In treatment, we often use medicinal charcoal, which binds toxins and bacteria together and causes water to leak into the intestine and cause diarrhea.
Doctors usually recommend hydration and electrolytes to treat acute diarrhea. Diarrhea is not always a reason to see a doctor, but it is necessary when there are:
You can also naturally deal with diarrhea, using what we have in the kitchen. However, this applies only to the occurrence of mild and short-term diarrhea. If symptoms persist, consult your physician and begin appropriate pharmacotherapy.
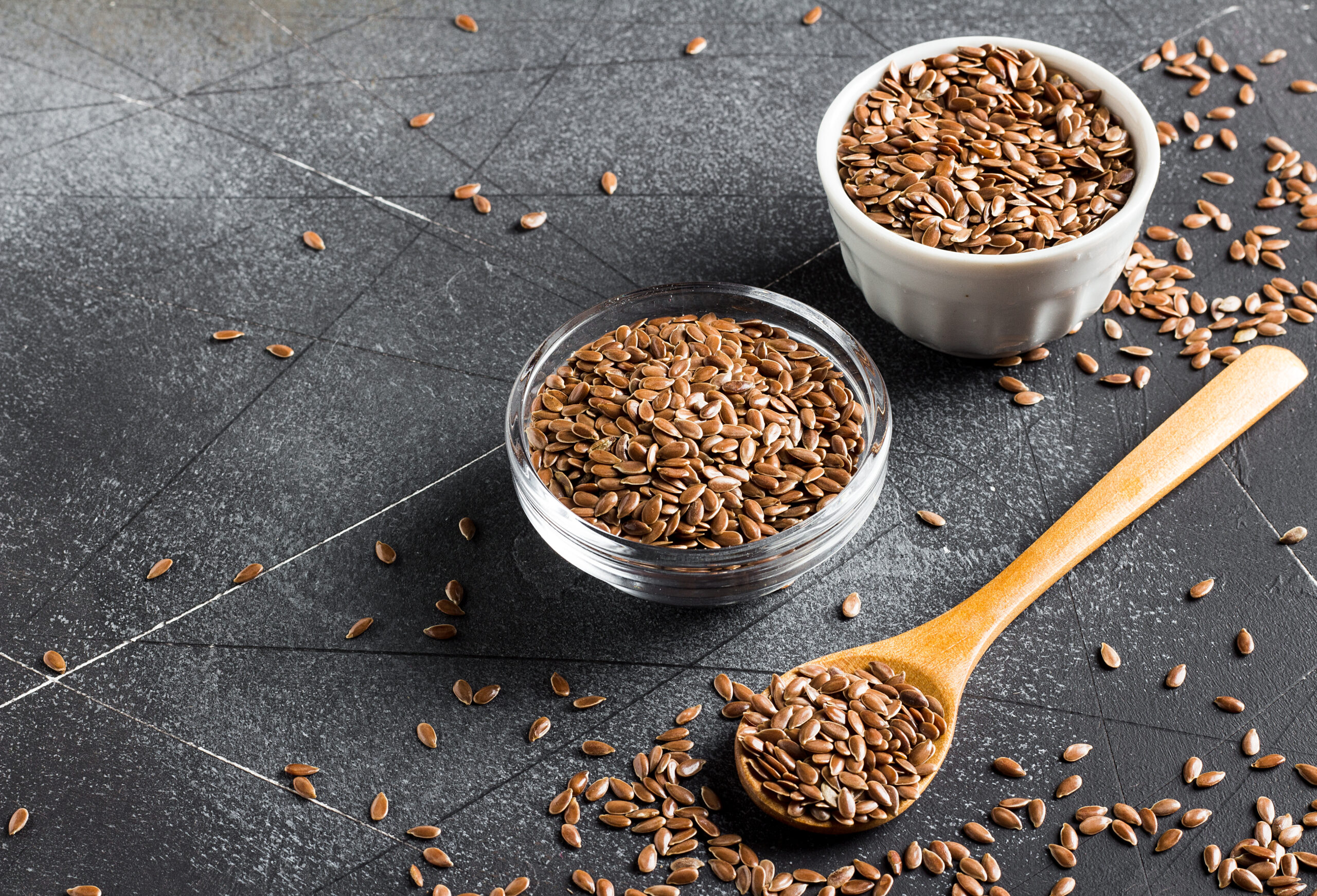
An effective home remedy for diarrhea is flaxseed jelly![]() . A tablespoon of grains is boiled in half a glass of water until a thick gruel is formed. The mixture prepared in this way should be drunk.
. A tablespoon of grains is boiled in half a glass of water until a thick gruel is formed. The mixture prepared in this way should be drunk.
Linseed has extraordinary properties because it can stimulate intestinal motility in the case of constipation and relieve diarrhea.

Dark chocolate and cocoa![]() can also help treat diarrhea. However, they must be in pure form – without added sugar, which is a breeding ground for bacteria.
can also help treat diarrhea. However, they must be in pure form – without added sugar, which is a breeding ground for bacteria.
You should also ensure adequate hydration![]() . In addition to water, medicinal herbs, mainly chamomile, will help. However, be careful because some of them (like mint and lemon balm) – can be irritating and cause vomiting.
. In addition to water, medicinal herbs, mainly chamomile, will help. However, be careful because some of them (like mint and lemon balm) – can be irritating and cause vomiting.
There are several ways to reduce the likelihood of diarrhea![]() .
.
Avoid infection through good hygiene habits. It is important to wash your hands with soap and water after using the bathroom, cooking, and eating to prevent diarrhea. Thoroughly cleaning your hands can lead to substantial results in maintaining good health for yourself and your loved ones.
It is significant to keep vaccinations in mind, especially for preventing rotavirus, which can cause diarrhea. The rotavirus vaccine is administered to infants in multiple stages throughout their first year.
To avoid getting diarrhea, maintain the proper temperature for food, avoid consuming expired items, cook food to the recommended temperature, and handle all food items carefully.
Be mindful of what you consume while traveling. Drinking water or other beverages that haven't been prepared correctly can lead to a traveler's diarrhea. It is most likely in developing countries. There are a few tips to follow to avoid diarrhea.
Watch what you drink. It is recommended to avoid drinking tap water, using ice cubes made from tap water, brushing teeth with tap water, and consuming unpasteurized milk, dairy products, or juices. It is significant to exercise caution when consuming local street food, as well as when eating raw or undercooked meat and shellfish, as well as raw fruits and vegetables. If you're unsure, it's best to consume bottled water or hot beverages like coffee or tea that have been properly cooked.
Table of Contents
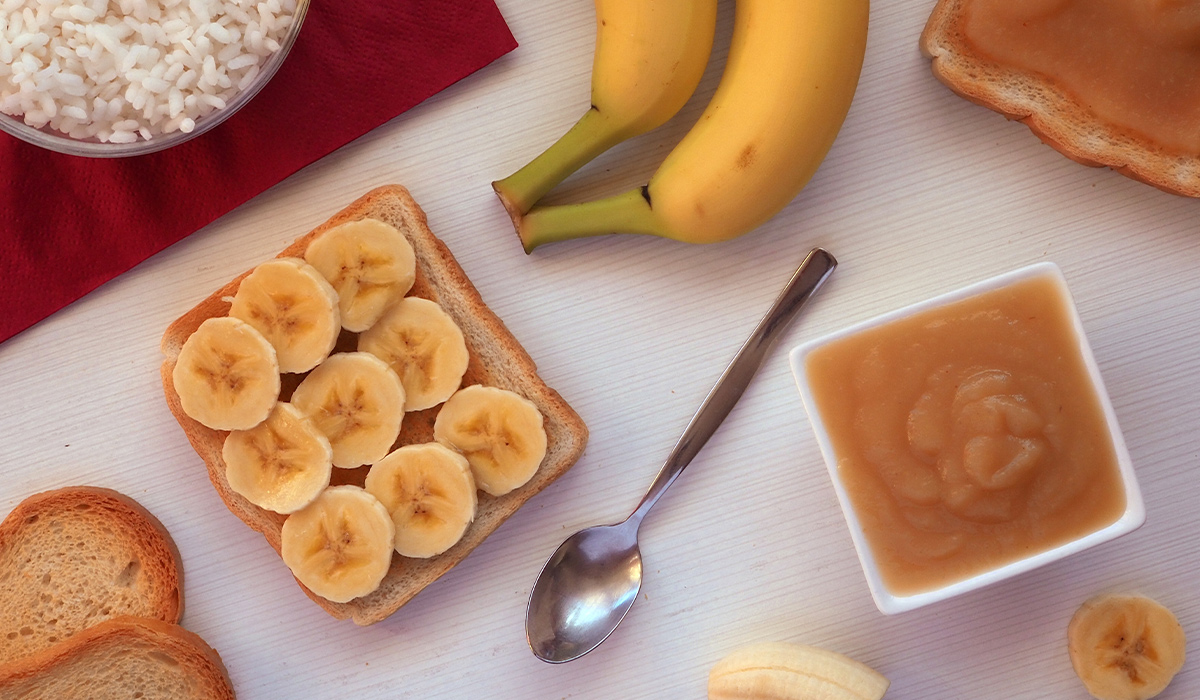

The BRAT Diet is very effective method of combating diarrhea and vomiting. What products are recommended for these ailments? read more »
Appendicitis has various forms. Most often it appears as an acute inflammation requiring immediate medical intervention. Learn the most important… read more »

If food is spoiled, undercooked, or contains certain types of bacteria, toxins, or other harmful substances, it may cause food… read more »
Salmonella bacteria infect both humans and animals. They can be found mainly in poultry but also in the meat of… read more »

Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anal canal. They are accompanied by various symptoms – how to recognize them? What… read more »

A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the human digestive system. What does a visit to… read more »
Giardiasis is a disease that causes symptoms of diarrhea. Some people are at greater risk of a severe course and… read more »

Staph infection is a common disease. How can you get infected with this bacteria? How to avoid it? Learn all… read more »
Adenovirus is a pathogen commonly found in the environment. Find out how to recognise adenoviral infections. Learn about treatment and… read more »