Breast cancer is a common type of cancer many people worldwide have. It happens when cells in the breast grow too fast without control. The breast is made up of sections called lobes, which are broken down into smaller parts known as lobules, and it also has connective tissue, fat, and milk ducts.
The milk ducts are paths that let milk move through the breast. The connective and fat tissue wrap around the lobules and ducts, keeping the entire gland in place.
Several types of breast cancer vary based on the cells they originate from. Most cancers arise from the cells of the ducts or lobules of the breast. It can occur in both women and men, although it is much more common in women.
Untreated breast cancer inevitably leads to death. Its growth may be slow or fast and may gradually lead to skin ulceration, metastases, and destruction of the breast.

Doctors determine several types and subtypes of cancer. It’s essential to identify it correctly to adjust therapy appropriate to the type of cancer. Find out about the most common types of breast cancer:
Subtypes of breast cancer are distinguished based on the receptors on their surface. Receptors can bind various substances, such as hormones circulating in the blood, which may help the tumor grow. Identifying the types of receptors![]() in the tumor enables implementing a treatment tailored for the subtype. Breast cancer can be:
in the tumor enables implementing a treatment tailored for the subtype. Breast cancer can be:
More than 80% of women with this kind of cancer are women over 50 years old. It affects mainly women but can also happen in men. Estimated new cases among women in the United States were around300,000![]() in 2023, with less than 3000 among males.
in 2023, with less than 3000 among males.
In addition to being the most common cancer, it is also one of the leading causes of death among women in the world. Every year, around 700,000![]() people die from it globally.
people die from it globally.
Like most cancers, breast cancer develops as a result of mutation, which emerges in an individual’s breast cells. As a result of this mutation, cells start to multiply uncontrollably and form groups of mutant cells, which form a cancerous lump.
Some people are at a higher risk of getting breast cancer due to their family history, genetic factors, or lifestyle. The risk factors include:
For a long time, breast cancer doesn’t give any symptoms. That’s why it is crucial to have regular breast self-examinations and mammograms. People with breast tumors might feel or observe irregular lumps or skin thickening. The most common site of breast cancer is in the upper outer part of the breast.
Other characteristic symptoms include:
Sometimes, the first symptom of cancer is the appearance of metastases, e.g., in the lymph nodes of the armpit.
Doctors find out if someone has breast cancer by checking the person, using special picture tests, and taking lab tests. If they see something unusual in the breast on a picture test, the doctor will take a small piece of the weird tissue to figure out what kind it is.
Doctors check breasts for health during an exam. They look for unusual signs like redness, rash, and if one side looks different, including the nipple. Then, the doctor checks by feeling the breast and underarms for any lumps that shouldn't be there.
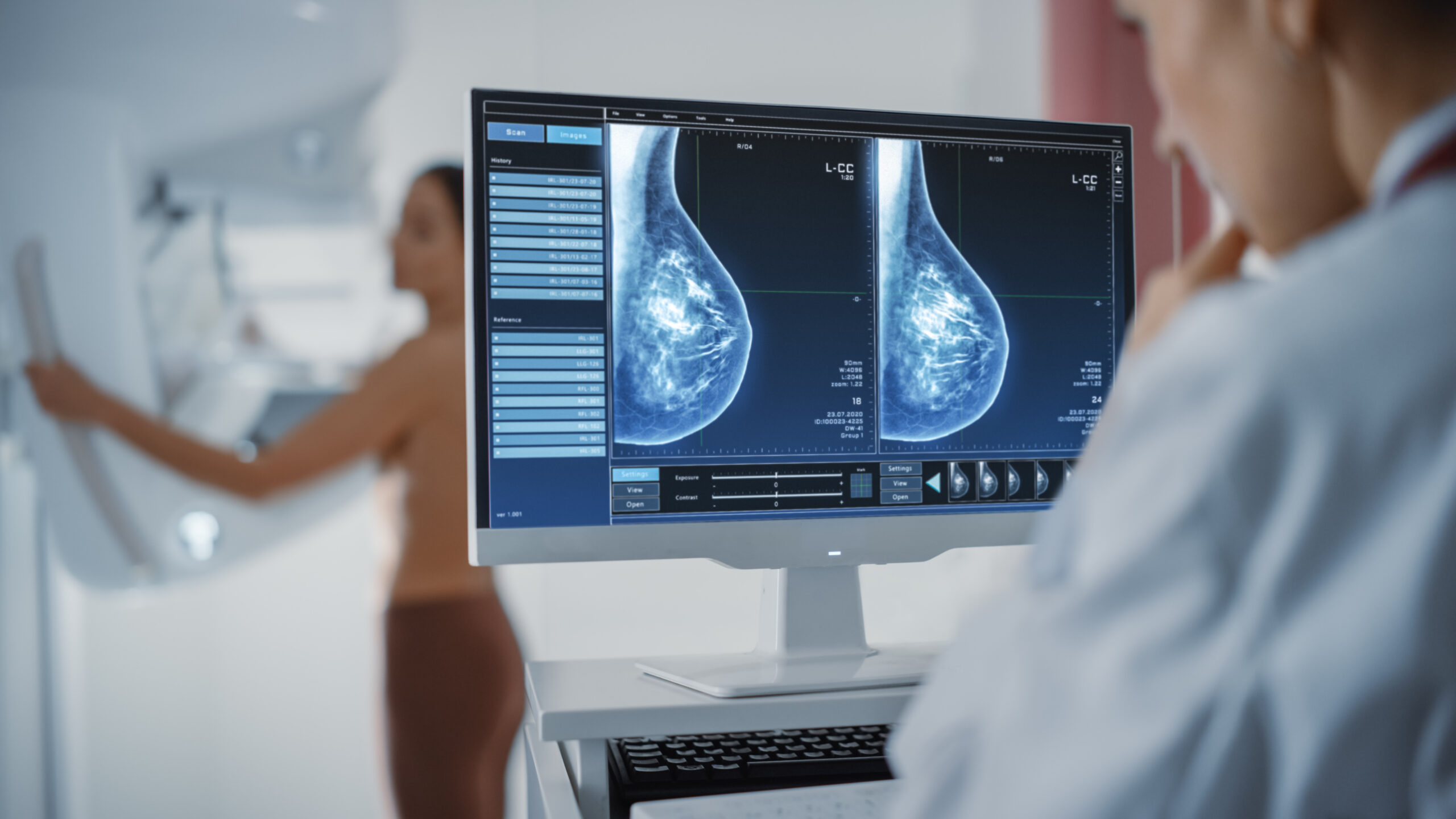
The primary imaging test for breast cancer is a mammogram, which is an X-ray of the breast. The examination is generally not painful, but some women experience short-term discomfort due to the need to compress their breasts during the examination. However, pressure is necessary for the test to be reliable.
Another kind of test is breast ultrasound, which is an examination that uses sound waves to obtain an image of the internal organs. Although a mammogram is the “gold standard” of breast tumor diagnosis, an ultrasound![]() is more valuable in the case of high-density breasts, i.e., breasts with a high concentration of glandular tissue, which is most often present in young women. On mammograms, glandular tissue is white, and so is the possible tumor, which makes high-density breasts prone to “hide” small cancer on the mammogram. Therefore, an ultrasound examination is more reliable in such cases.
is more valuable in the case of high-density breasts, i.e., breasts with a high concentration of glandular tissue, which is most often present in young women. On mammograms, glandular tissue is white, and so is the possible tumor, which makes high-density breasts prone to “hide” small cancer on the mammogram. Therefore, an ultrasound examination is more reliable in such cases.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a test that enables one to obtain a more detailed picture of the breasts. It typically involves the injection of a dye into a vein.
When a tumor is found in the imaging tests, sometimes it is necessary to remove a small part of it for testing in the lab. A healthcare professional obtains tissue samples using a needle inserted through the skin into the chest. This procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. A biopsy is necessary to diagnose the type of disease and establish a treatment plan.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor determines the advancement (stage) of the disease. To assess the advancement of breast cancer, imaging tests are standardly performed. Those include:
Additionally, the doctor may order a computed tomography of the brain and an assessment of the bones for the presence of metastases. The stage of the disease is determined based on the size of the tumor, metastases in the lymph nodes, and metastases in the other parts of the body. Sometimes, the stage can be determined only after the cancer removal surgery.
Stages of the cancer![]() are indicated by numbers 0 to 4, with 0 being the cancer localized only in the tissue it originates from and 4 being the most advanced cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
are indicated by numbers 0 to 4, with 0 being the cancer localized only in the tissue it originates from and 4 being the most advanced cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Surgery is most often the top choice for treating breast cancer. How much surgery is needed can change based on how far along the cancer is. Sometimes, doctors remove the tumor and put a little bit around it. Other times, they might have to take out the whole breast. If the cancer is far along, treatment might focus more on making symptoms more straightforward to handle.
The treatment options include:
Early, quite common complications that may occur during radiation therapy include redness and skin pain, which disappears after the use of painkillers. The skin may look similar to sunburn – special moisturizing creams are used after radiotherapy.
Additionally, you may experience discomfort when swallowing and general weakness at the end of treatment.
Complete prevention of cancer development is not always possible. However, there are steps you can take to lower your risk. Those steps include:
Checking yourself regularly for any signs of cancer and getting mammograms are key steps in stopping serious cancer issues. Every woman should check herself once a month. If you're past menopause, do it on the same day each month. If you're younger and still get your period, it's best to do it a few days after your period ends.
Self-exams![]() involve touching both breasts and armpit areas with the pads of three middle fingers. It should be performed in the shower while lying down, and visual observation should be made for any abnormalities in front of the mirror.
involve touching both breasts and armpit areas with the pads of three middle fingers. It should be performed in the shower while lying down, and visual observation should be made for any abnormalities in front of the mirror.
Experts suggest that women between 50 and 74 should have mammograms every two years. In women with higher risk, such as women with a family history of breast cancer, the age they should start regular screening is higher.

Nowadays, more and more people are being diagnosed with breast cancer at the early stages of the disease, which leads to an improvement in survival rates. It should be remembered that cancer is detected in different people at different stages of advancement; the tumors are of various sizes, and cancer may have multiple types.
If a disease is diagnosed at early stages (stage 0 or 1), the prognosis is good, and the 5-year survival rate is 100%.
In stage 2, 93%![]() of people survive five years from the diagnosis, and for stage 3 it is only 72%. When the disease spreads throughout the body, the prognosis gets much worse. In stage 4 of the disease, only 22% of patients survive five years.
of people survive five years from the diagnosis, and for stage 3 it is only 72%. When the disease spreads throughout the body, the prognosis gets much worse. In stage 4 of the disease, only 22% of patients survive five years.
It should be kept in mind that those numbers are only estimates based on statistics. Healthcare professionals approach each patient individually, and the statistical survival rate can’t be treated as an individual’s chance of survival.
Complications of breast cancer are associated with metastases to the bones, brain, and liver. Other possible complications are related to the surgery and its complications. Cancer removal surgery, like any other surgery, carries a risk of complications. The most common ones include infection, nerve damage, blood clots, pain, and lymphedema, a swelling of the arms that happens when lymph nodes are removed.
You should contact your healthcare provider if you notice any worrying symptoms, such as:
If you have a family history of breast cancer, ask your doctor for steps you can take to protect yourself.
Regular screening is the best way to diagnose the disease as early as possible. Experts recommend that every woman between 50 and 74 has a mammogram every two years. Early detection of breast cancer gives you the best chances of recovery.
Table of Contents
Mastitis is a condition that can affect many women, especially during the postpartum period. What symptoms does it cause? What… read more »
Breast pain, called mastalgia in therapeutic terms, is a problem that numerous ladies confront. It may well be just a… read more »

Breastfeeding is the process of feeding a baby with milk directly from the mother's breasts. It is a highly recommended… read more »
Cancer is the second most common cause of death in the US. It can affect any body part and spread… read more »

Brain tumors are abnormal growths located in the brain. It can be malignant or benign. Symptoms and treatment depend on… read more »
Glioblastoma is a brain cancer with a poor prognosis. Discover the first signs of the disease and the latest treatments.… read more »
Beta blockers are a class of medications primarily used to manage conditions related to the cardiovascular system. How do they… read more »
Liver cancer is a tumor that is found in the liver. The most common symptoms include jaundice, unexpected weight loss,… read more »
The first symptoms of pancreatic cancer are nonspecific, so it is difficult to make a quick diagnosis. Learn about pancreatic… read more »