Cancer arises due to excessive cell proliferation, uncontrolled by the body. Under normal conditions, the growth of all our cells is controlled. But when one cell's control signals malfunction and the cell's life cycle is disrupted, the cell begins to divide intensely—uncontrolled growth proceeds, resulting in an overly proliferated mass – cancer.
Cancer begins when a normal cell becomes cancerous. This happens when something disrupts the DNA, changing the code that monitors the cell's life cycle. One or more of many risk factors can contribute to such cells. The most commonly observed mutation in pancreatic cancer is a change in the so-called KRAS![]() oncogene, and the location of the resulting tumor is the head and body of the pancreas.
oncogene, and the location of the resulting tumor is the head and body of the pancreas.
Pancreatic cancer can produce nonspecific symptoms that, when ignored, delay diagnosis. Specific tests are required for diagnosis. A complete cure for pancreatic cancer is possible with surgery.
Pancreatic cancer is more likely to affect seniors. Most pancreatic cancer patients are diagnosed after age 60. Pancreatic cancer is more common in men than in women, although the difference is small.
Functions of the pancreas can include a variety of roles it plays within the body. You can find the pancreas close to the stomach, bile duct, spleen, and liver. The glandular organ, the pancreas, significantly affects metabolism. When it comes to the human body, this organ has two primary functions, which are:
The pancreas supplies the small intestine with enzymes![]() for digesting food. This function is associated with the so-called pancreatic islands. Production of pancreatic juice containing enzymes (lipase, amylase, trypsin) is needed to digest our food. The result is the extraction of ingredients by the body.
for digesting food. This function is associated with the so-called pancreatic islands. Production of pancreatic juice containing enzymes (lipase, amylase, trypsin) is needed to digest our food. The result is the extraction of ingredients by the body.
The second function of the pancreas is the production of hormones![]() (insulin and glucagon). This allows the pancreas to regulate blood glucose levels. A malfunctioning pancreas that stops producing insulin causes diabetes. Diabetes (type 1) is a disease in chronic form. It involves immune system cells attacking cells in the pancreas.
(insulin and glucagon). This allows the pancreas to regulate blood glucose levels. A malfunctioning pancreas that stops producing insulin causes diabetes. Diabetes (type 1) is a disease in chronic form. It involves immune system cells attacking cells in the pancreas.
On the other hand, if people have an unhealthy lifestyle and there is too much sugar, fats, and alcohol in their diet – the pancreas is weakened, and its work is disrupted. As a result, insulin resistance begins to develop in the body. General pain in the upper abdomen can indicate that the pancreas requires our attention.
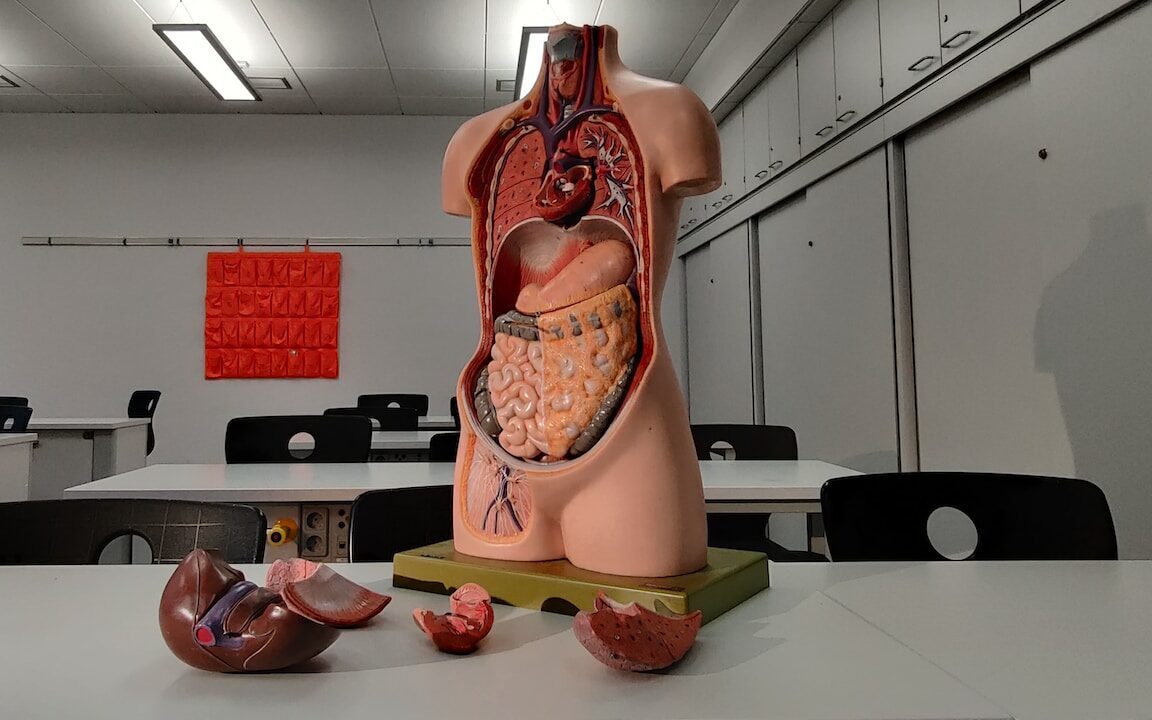
Many diseases associated with the pancreas can be listed. These include acute pancreatitis. The condition results from agents that damage the pancreatic follicle cell, impairing enzyme secretion. The state is most often caused by alcohol abuse and diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
On the other hand, the proliferation of pathological cells results in the development of pancreatic cancer, which originates in the exocrine or endocrine part.
Two groups of pancreatic cancers can be distinguished: those originating from the exocrine part of this organ or the endocrine part.
In most cases, adenocarcinomas originate from the exocrine part of the pancreas and are responsible for pancreatic cancer. A rarer type of pancreatic cancer develops in the endocrine function. In this case, tumors develop from cells accountable for producing insulin and glucagon hormones, which regulate normal glucose levels.
Certain factors increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer. What aspect causes pancreatic cancer is an individual issue. Several risk factors can simultaneously affect the development of the disease. Causes of pancreatic cancer include:
Chronic pancreatitis – One of the causes of pancreatic cancer may be its chronic inflammation![]() . Chronic pancreatitis is a severe and chronic disease of the pancreas that gradually diminishes its function – the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and insulin. It leads to irreversible morphological changes within this organ. Patients with chronic pancreatitis are in a risk of death from pancreatic cancer.
. Chronic pancreatitis is a severe and chronic disease of the pancreas that gradually diminishes its function – the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and insulin. It leads to irreversible morphological changes within this organ. Patients with chronic pancreatitis are in a risk of death from pancreatic cancer.
Cigarettes and alcohol – Stimulants also influence the development of this type of cancer. Smoking cigarettes![]() at least doubles the likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer. Alcohol can affect pancreatic inflammation. Exceptionally high alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of the disease.
at least doubles the likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer. Alcohol can affect pancreatic inflammation. Exceptionally high alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of the disease.
Diet – Also, an improper diet has an impact on pancreatic cancer. Being overweight and obese, combined with coexisting type 2 diabetes or diseases resulting from alcoholism, increase the risk of cancer. Unhealthy devoid of fruits and vegetables stresses the pancreas and exposes it to inflammation.
Infections – Scientists have discovered that bacteria and viruses may be responsible for developing pancreatic cancer. These include, among others:
People diagnosed with these bacteria and viruses were much more likely to develop the disease.
Pesticides – When a person is exposed to chemicals, it increases the risk of pancreatic cancer. Such substances include pesticides![]() . Such chemicals protect crops from insects, for example. Pesticides in the human body cause cancerous changes. So prolonged contact with pesticides can increase the risk of cancer. A way to reduce the intake of harmful substances is to wash and peel vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
. Such chemicals protect crops from insects, for example. Pesticides in the human body cause cancerous changes. So prolonged contact with pesticides can increase the risk of cancer. A way to reduce the intake of harmful substances is to wash and peel vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
Genes – Genetic predisposition is also essential. The risk of developing pancreatic cancer is exceptionally high in relatives of people with familial pancreatic cancer. It is diagnosed in patients with pancreatic cancer in at least two first-line relatives.
Pancreatic cancer is a disease that, because of the difficult diagnosis, is often fatal. Initially, pancreatic cancer is usually asymptomatic![]() . Symptoms of pancreatic cancer typically occur late, when the cancer is already advanced.
. Symptoms of pancreatic cancer typically occur late, when the cancer is already advanced.
Pancreatic cancer can develop asymptomatically for a long time. On the other hand, early symptoms are possible, but they are not characteristic and may indicate other diseases. Therefore, cancer is difficult to detect in its early stages. The first signs of pancreatic cancer include:
Pancreatic pain can be experienced as intense and piercing pain in the upper abdomen and back pain![]() . A characteristic symptom is also the subsidence of pain when bending forward. The pain can be constant (including at night) or episodic, of varying severity. Abdominal pain is a common symptom, but sometimes it can appear only in advanced stages of cancer.
. A characteristic symptom is also the subsidence of pain when bending forward. The pain can be constant (including at night) or episodic, of varying severity. Abdominal pain is a common symptom, but sometimes it can appear only in advanced stages of cancer.
Nausea, vomiting can be another symptom of pancreatic cancer. Nausea alone is far more common than vomiting. Also, fatty diarrhea is a crucial symptom of pancreatic cancer. The characteristic symptom of this type of diarrhea is passing stool with a high fat content. This can be recognized by the fact that the stool is light in color and has a putrid odor.
Unpleasant gastrointestinal sensations can affect the loss of appetite. Patients often do not feel hungry; fullness accompanies them before and after meals. This involves loss of appetite and, consequently, weight loss![]() . Thus, a symptom of pancreatic cancer is sudden weight loss, which is not due to one's diet or physical activity.
. Thus, a symptom of pancreatic cancer is sudden weight loss, which is not due to one's diet or physical activity.
One of the symptoms of pancreatic cancer is the appearance of hyperglycemia. Notably, the onset of glycemic disturbances![]() usually occurs before the diagnosis of a pancreatic tumor. The beginning of type 2 diabetes or the worsening of its symptoms can be an early sign of pancreatic cancer.
usually occurs before the diagnosis of a pancreatic tumor. The beginning of type 2 diabetes or the worsening of its symptoms can be an early sign of pancreatic cancer.
Patients with diabetes develop glycemic fluctuations that are difficult to treat. Patients without diabetes, on the other hand, may have significantly elevated blood glucose levels.
The distressing symptoms noticed and reported by the patient at the doctor's office usually indicate the significant size of the tumor and the late stage of the disease, which is difficult or even impossible to treat. The final, fourth stage of pancreatic cancer is characterized by metastasis to more distant organs. The tumor is then challenging to treat. Late symptoms of pancreatic cancer include:
Jaundice![]() is one of the most noticeable symptoms of pancreatic cancer. It is caused by the pressure of the developing cancer on the bile duct. Mechanical jaundice gives apparent symptoms. Such as dark urine or discolored stool. Elevated bilirubin levels also cause yellowing of the outer membranes of the eyes and mouth. Jaundice can also be a symptom of cancer metastasis to nearby organs.
is one of the most noticeable symptoms of pancreatic cancer. It is caused by the pressure of the developing cancer on the bile duct. Mechanical jaundice gives apparent symptoms. Such as dark urine or discolored stool. Elevated bilirubin levels also cause yellowing of the outer membranes of the eyes and mouth. Jaundice can also be a symptom of cancer metastasis to nearby organs.
Another sign of pancreatic cancer is the process of homeostasis. Cholestasis occurs when the flow of bile, which is essential for digesting food, is blocked. The most common symptoms of cholestasis include generalized itching of the skin, exacerbated when the body is warm and during the evening and night hours.
Pancreatic cancer can also produce thrombotic and embolic symptoms. Venous thromboembolism may precede the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. According to many experts, the appearance of thrombosis should signal the patient to monitor his health for cancer. The main symptoms of thrombophlebitis include pain and swelling in the lower extremities, sometimes bruising or redness of the skin.
Unfortunately, the prognosis of pancreatic cancer is not hopeful. This type of cancer is usually detected late. In most cases, the disease is diagnosed at an advanced stage.
In contrast, the chance to improve this statistic is timely diagnosis and effective treatment. The prelude to diagnosis is the patient's history. Tests are then conducted that reveal the problem. The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer requires the following tests:
Ultrasound![]() is the initial examination of those reporting worrisome abdominal symptoms. In patients with jaundice, it shows dilatation of the extrahepatic bile ducts and the presence of a pancreatic head tumor.
is the initial examination of those reporting worrisome abdominal symptoms. In patients with jaundice, it shows dilatation of the extrahepatic bile ducts and the presence of a pancreatic head tumor.
A broader diagnosis is possible with a CT scan![]() . It is reliable for imaging the entire pancreas, especially in patients with complex ultrasound evaluation. MRI determines the cancer stage and whether it is amenable to surgery.
. It is reliable for imaging the entire pancreas, especially in patients with complex ultrasound evaluation. MRI determines the cancer stage and whether it is amenable to surgery.
The main indication for a pancreatic biopsy![]() is the suspicion of pancreatic cancer on abdominal ultrasound or CT scan. Essential for a definitive diagnosis is the result of the histopathological examination performed. A biopsy of the pancreas or altered nodes can be performed during an endoscopic ultrasound.
is the suspicion of pancreatic cancer on abdominal ultrasound or CT scan. Essential for a definitive diagnosis is the result of the histopathological examination performed. A biopsy of the pancreas or altered nodes can be performed during an endoscopic ultrasound.
In the case of suspicion of this cancer, blood tests are also ordered, which include evaluation of the activity of digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas. Also, the concentration of tumor markers![]() is usually measured in the blood.
is usually measured in the blood.
The biochemical marker for pancreatic cancer is the CA 19-9 protein. Determination of the CA 19-9 concentration is aimed at determining the stage of the disease and conducting disease surveillance.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma has an outstandingly unfavorable prognosis. In the United States, about 10% of patients survive five years after diagnosis. The main reason is that the disease is insidious in nature and develops for a long time without producing any symptoms.
A better prognosis is given to cancer located in the endocrine part than in the exocrine function. Prognosis depends on the differentiation and stage at the time of diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. The more advanced stage of the disease, the more difficult it is to cure the patient. Resection of the tumor at an early stage is the only chance to cure the patient.
There are many treatments available. They are chosen based on the type of cancer, its location, the extent and stage at which it was diagnosed, and the health and well-being of the patient. Treatment can be single, sequential, or a mixture of therapies. Treatments for pancreatic cancer include:
The method involves the use of anti-cancer drugs. Most anti-cancer drugs inhibit DNA synthesis or other cell life cycle processes. These drugs destroy cancer cells by inhibiting growth or reproduction at some cell life cycle stages. It can be delivered intravenously or orally or by other means, depending on the drug and the type of cancer.
Medications are used not only to treat cancer but also to remove the effects of cancer. Since anti-cancer drugs generally work, cancer cells and all cells are burdened by their impact. The result can be hair loss, poor appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and sores on the lips and mouth. Many of the side effects can be controlled with modern drugs.
This is a type of cancer treatment using ionizing radiation. Radiation therapy involves irradiating the area affected by cancer to destroy cells. The radiation destroys either the cells or the genetic material of the cells in the place to be treated, thereby preventing the cell from growing.
Radiation therapy can improve survival in early pancreatic cancer. Chemotherapy can be a combination treatment with radiation therapy (chemoradiotherapy), which is considered primarily in cases of locally advanced tumors.
Some specialists believe that such radiotherapy to the pancreas does not provide enough benefit. There are suggestions that yes pancreas is extremely resistant to irradiation. However, there are also studies that indicate that the higher the dose of chemoradiotherapy, the greater the benefit to the patient.
Surgery plays an essential role in treating patients with pancreatic cancer. The possibility of a complete cure for pancreatic cancer is provided by resection, which is the surgical removal of part or even the entire pancreas. Sometimes the surrounding tissues and lymph nodes of the tumor are also removed. Surgical procedures can be performed using either lasers or conventional medical tools.
Pancreatic tumor resectability is possible when the patient's condition predisposes to it. Among other things, the patient must not have distant metastases. Usually, despite radical surgery, treatment results are not satisfactory, and therefore chemotherapy is practical in every case.
For hormone-dependent cancers, hormone therapy![]() , otherwise known as hormone therapy, proves effective. It involves regulating hormones to prevent the action of hormones that affect cancer growth. Hormone therapy is used to treat early stage cancer. It is also used as a complementary treatment. Hormone type of cancer therapy is a pharmacological treatment. Unlike chemotherapy, it has low toxicity and fewer side effects.
, otherwise known as hormone therapy, proves effective. It involves regulating hormones to prevent the action of hormones that affect cancer growth. Hormone therapy is used to treat early stage cancer. It is also used as a complementary treatment. Hormone type of cancer therapy is a pharmacological treatment. Unlike chemotherapy, it has low toxicity and fewer side effects.
This therapeutic method uses the action of the patient's immune system. It fights the disease and reduces the side effects caused by other therapies. This method uses drugs from the checkpoint inhibitor group. These types of medicines enable the tumor to avoid immune attack.
Checkpoint inhibitors do not damage cancer cells; they only reduce the tumor's ability to hide from the immune system. Therefore, immunotherapy![]() does not cause any complications and is well tolerated. When combined with chemotherapy, this treatment shows promising results.
does not cause any complications and is well tolerated. When combined with chemotherapy, this treatment shows promising results.
Cancer can be caused by various factors, so sometimes it cannot be prevented. But leading a healthy lifestyle will definitely help lower the risk. Preventive measures for pancreatic cancer include:

Prevention of pancreatic cancer primarily involves smoking cessation. It is important to keep in mind that regular smoking can contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer. In addition, it also causes many other harmful changes. Alcohol is another stimulant that increases the risk of pancreatic cancer. It is particularly associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Limiting the consumption of alcoholic beverages can help reduce this risk.
In general, a healthy diet that does not burden the organ that is the pancreas is recommended. It is also important to lose excess weight and by limiting fatty foods. Consuming animal fats and red meat increases the risk of cancer. Movement and physical activity are often used in cancer prevention. It helps lose weight and also increases the body's immunity.
Control of chronic diseases – diabetes and inflammation of the pancreas – is also essential. The presence of these diseases can lead to the development of pancreatic cancer. If pancreatic cancer has occurred in someone in the family, it is also advisable to perform regular examinations.
Pancreatic cancer belongs to a group of malignant forms with an aggressive course and low cure rates. This is due not only to the nonspecific symptoms, which can be ignored for a long time, thus delaying diagnosis but also to the location of the pancreas. Various factors can influence the occurrence of pancreatic cancer. Genetic predisposition and an unhealthy lifestyle, among others, are indicated. Pancreatic cancer can also develop in the wake of diabetes or pancreatitis. The first symptoms of pancreatic cancer are nonspecific, mainly abdominal pain, nausea, and weight loss. These signs can indicate different types of diseases.
In contrast, later symptoms are more specific. Pancreatic cancer causes jaundice, skin, and thrombotic symptoms. Various types of tests can diagnose pancreatic cancer. On the other hand, treatment consists of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy. Surgical procedures are also prevalent, but they are not always feasible. The choice of treatment depends on the situation and patient's condition. The prognosis of pancreatic cancer is not good; most cases end in death. Early detection of symptoms and preventive measures can help defeat the cancer.
Table of Contents
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. It usually presents itself with abdominal pain and can be extremely dangerous. What… read more »

An endocrinologist is a doctor who deals with the organs that secrete hormones. Learn about diseases that are related to… read more »

Brain tumors are abnormal growths located in the brain. It can be malignant or benign. Symptoms and treatment depend on… read more »

When blood glucose levels are too high, it leads to a hyperglycemia. Discover effective ways to reduce your sugar levels… read more »
Glioblastoma is a brain cancer with a poor prognosis. Discover the first signs of the disease and the latest treatments.… read more »

A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the human digestive system. What does a visit to… read more »

Diabetes is a disease involving elevated blood glucose levels. What are the causes of diabetes? How can it be treated?… read more »
Cancer is the second most common cause of death in the US. It can affect any body part and spread… read more »
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is a condition that can cause uncharacteristic symptoms. Treatment is important as the disease can be fatal. Learn… read more »