Neuropathic pain is a persistent discomfort. It can feel like burning, numbness, tingling, or sudden electric shocks. Some patients experience intense sensations of heat or cold. It can occur spontaneously or during movement.
This type of pain is often accompanied by a dull or cramping sensation that may be located deep in the tissues and intense pressure. Additionally, patients may experience short-term, strong, and piercing sensations that feel like electric shocks. These sensations can occur both at rest and during movements.
Other pain sensations include hyperalgesia, also known as hyperesthesia. We deal with it when the patient feels pain much greater than the one that a given stimulus should cause, for example, a pinprick or a light scratch with a fingernail turns out to be very painful. The extreme form of hyperesthesia is allodynia – in this case, the patient feels it as a painful sensation that has no right to result in even minimal pain, e.g., touch, stroking, heat, or cold.
In turn, hyperpathy is a pain reaction inadequate to the stimulus, which appears with a delay, radiates beyond the area of the damaged nerve, and lasts long after the irritation process is over. Another sensory disorder is hypoalgesia, which is characterized by a weakened sense of touch or temperature.
All the described symptoms are not only painful or at least unpleasant but also dangerous because the nervous system has a problem with signaling us situations that are harmful to health: damaged nerves will not transmit a pain signal or alarm about too high or low temperature.

The tingling of the skin is a feeling of something crawling under the skin. It may be accompanied by numbness. Tingling and numbness of the skin are symptoms of the so-called paresthesia – they are caused by irritation of the sensory nerves in various mechanisms, e.g., in the course of degenerative processes, during nerve inflammation, with pressure on the nerves.
Body tingling![]() can occur in a completely healthy person as a result of temporary pressure on the nerve, staying in one position, or intense effort – e.g., with your head in your hands, tingling in your fingers after prolonged use of a computer or telephone keyboard.
can occur in a completely healthy person as a result of temporary pressure on the nerve, staying in one position, or intense effort – e.g., with your head in your hands, tingling in your fingers after prolonged use of a computer or telephone keyboard.

Neuropathy can cause extreme sensitivity![]() in certain areas of your body or throughout your entire body. For example, if you've ever had a “dead leg,” you may have experienced how even the slightest touch can cause a feeling like pins and needles. It happens because neurons and nerves have a binary function – they're either “on” or “off.” To fire, they must first surpass an activation threshold. Neuropathy can cause nerves to become more easily excited, meaning they no longer require the same amount of stimulation to fire. This can cause even the slightest touch to feel overwhelming.
in certain areas of your body or throughout your entire body. For example, if you've ever had a “dead leg,” you may have experienced how even the slightest touch can cause a feeling like pins and needles. It happens because neurons and nerves have a binary function – they're either “on” or “off.” To fire, they must first surpass an activation threshold. Neuropathy can cause nerves to become more easily excited, meaning they no longer require the same amount of stimulation to fire. This can cause even the slightest touch to feel overwhelming.
If someone has nerve damage, they might face challenges regulating their body temperature![]() . They could struggle to sweat even during hot weather or experience excessive sweating when it is cold outside. High temperatures can be especially unbearable because their bodies cannot efficiently cool off.
. They could struggle to sweat even during hot weather or experience excessive sweating when it is cold outside. High temperatures can be especially unbearable because their bodies cannot efficiently cool off.
Additionally, they may feel cold chills and struggle to warm up. These are all indicators of nerve damage. It's significant to talk about these symptoms with a doctor to determine the underlying cause. Once the root of the issue is identified, the correct treatment can be administered to provide long-term comfort.

Nerves are integral to our body's functions. They transmit messages to and from the brain, as well as control our movements. They also aid in our understanding of the ambient temperature of our surroundings by transmitting information about heat and responding to environmental changes.
If our nerves become damaged, whether it be short or long-term, it can result in a feeling of extreme coldness![]() in that area. A typical example is experiencing a sudden chill in the arm after sitting on it for too long.
in that area. A typical example is experiencing a sudden chill in the arm after sitting on it for too long.

When neuropathy affects the nerves that control muscle![]() movements, it can cause symptoms such as muscle twitching and cramping. Those with hereditary neuropathy may also experience muscle weakness. In severe cases, motor neuropathy can lead to paralysis in certain muscle areas and moving challenging.
movements, it can cause symptoms such as muscle twitching and cramping. Those with hereditary neuropathy may also experience muscle weakness. In severe cases, motor neuropathy can lead to paralysis in certain muscle areas and moving challenging.
Diabetes-related neuropathy![]() , called radiculoplexus, can cause muscle atrophy and weakness in the buttocks and thighs, typically on one side of the body. Standing up after prolonged sitting can be difficult for those with this type of neuropathy.
, called radiculoplexus, can cause muscle atrophy and weakness in the buttocks and thighs, typically on one side of the body. Standing up after prolonged sitting can be difficult for those with this type of neuropathy.

Damage to peripheral nerves can cause a variety of symptoms. These may include sensory disturbances and motor weakness, which can progress to complete paralysis of the muscles controlled by the affected nerve.
When nerves lose their function, muscles start to weaken over time. In addition, damaged peripheral nerves containing autonomic fibers can result in unusual sweating, changes in skin color![]() (such as paleness, redness, or bruising), warmth, and skin thinning or atrophy.
(such as paleness, redness, or bruising), warmth, and skin thinning or atrophy.

Sensory disturbances usually begin on both feet in the form of hypoesthesia or hyperaesthesia in the typical sock area. This is often accompanied by autonomic dysfunction such as decreased sweating or edema. Then there is the involvement of the upper limbs and movement disorders![]() in the form of more severe paresis in the peripheral parts of the limbs.
in the form of more severe paresis in the peripheral parts of the limbs.

The functioning of the bladder![]() is under constant control of both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Unfortunately, there are neurological diseases that disrupt neurotransmission. If the transmission of nerve impulses related to urination is disturbed, then embarrassing problems can arise, causing discomfort to the patient. These include urinary incontinence, regurgitation of urine into the kidneys, and kidney failure.
is under constant control of both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Unfortunately, there are neurological diseases that disrupt neurotransmission. If the transmission of nerve impulses related to urination is disturbed, then embarrassing problems can arise, causing discomfort to the patient. These include urinary incontinence, regurgitation of urine into the kidneys, and kidney failure.

One of the symptoms of neuropathy is known as “diabetic foot” – which affects the feet![]() . It manifests as burning, tingling, and numbness. If left untreated, it can cause nerve and blood vessel damage that may eventually lead to foot amputation.
. It manifests as burning, tingling, and numbness. If left untreated, it can cause nerve and blood vessel damage that may eventually lead to foot amputation.
Diabetic neuropathy usually affects the peripheral nerves, responsible for sensation primarily in the hands and feet. Patients may also suffer from damage to the nerve fibers of the autonomic (vegetative) system, regulating the work of the digestive tract, heart, or intestines.

Diabetic neuropathy is one of the factors that can raise the risk of hypoglycemia unawareness![]() .
.
The autonomic nerves play a significant role in signaling the endocrine system to release stress hormones. It leads to symptoms like hand tremors, anxiety, and the release of glucose stores from the liver and muscles. However, if these nerves are damaged, the body's warning system can malfunction – as a result the body does not recognize low sugar levels, leading to no symptoms of the condition.
Disorders resulting from neuropathy of the gastrointestinal tract![]() can affect any of its sections, i.e., the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, or bile ducts. The most common symptoms include:
can affect any of its sections, i.e., the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, or bile ducts. The most common symptoms include:

In the beginning, the patient may experience subtle symptoms, e.g., blurring of the image. It then progresses to a complete loss of visual acuity. Usually, the disorder affects one eye![]() – but it can also occur in both of them. If the disease affects two eyes, the intensity of symptoms may be uneven.
– but it can also occur in both of them. If the disease affects two eyes, the intensity of symptoms may be uneven.
Some patients may also experience pain when moving their eyes. Symptoms and their intensity and type occur due to the form of neuropathy.

Neuropathy can cause changes in your brain![]() . Your brain contains billions of neurons that act like nerves, transmitting messages throughout your body. If these neurons are disrupted, the messages may not reach their intended destination.
. Your brain contains billions of neurons that act like nerves, transmitting messages throughout your body. If these neurons are disrupted, the messages may not reach their intended destination.
Some patients develop cranial neuropathy, which affects the brain stem. It can result in pain and discomfort throughout your body, making your skin extremely sensitive to touch and causing pins and needles sensations.

Mood changes![]() can be a sign of a neurological disease, whether it is due to the disease advancing or the patient becoming aware of it. Depression is a prevalent mood disorder. But it is worth remembering that conditions that impact the frontal lobes of the brain can also cause mood swings, anxiety, or feelings of extreme happiness.
can be a sign of a neurological disease, whether it is due to the disease advancing or the patient becoming aware of it. Depression is a prevalent mood disorder. But it is worth remembering that conditions that impact the frontal lobes of the brain can also cause mood swings, anxiety, or feelings of extreme happiness.

Focus on your mental and physical comfort. Intensification of symptoms is often a source of unnecessary stress, which is why complementary methods, such as massage![]() and relaxation, are also used in neuropathy treatment. They help to reduce the ailments resulting from excessive muscle tension.
and relaxation, are also used in neuropathy treatment. They help to reduce the ailments resulting from excessive muscle tension.
If the pain is getting worse, your doctor may also prescribe medicines![]() to reduce nerve pain by altering nerve impulses, anti-inflammatories, or painkillers.
to reduce nerve pain by altering nerve impulses, anti-inflammatories, or painkillers.
Thanks to rehabilitation![]() , you will speed up the process of nerve regeneration. It is worth focusing on endurance training, during which you will increase your breathing rate and increase your heart rate. Also, don't forget about balance exercises. For better results, work with a physiotherapist who will teach you movements that improve coordination. Other physical therapies are also effective:
, you will speed up the process of nerve regeneration. It is worth focusing on endurance training, during which you will increase your breathing rate and increase your heart rate. Also, don't forget about balance exercises. For better results, work with a physiotherapist who will teach you movements that improve coordination. Other physical therapies are also effective:
Peripheral neuropathy can be relieved with the use of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)![]() . This technique involves applying a low-intensity electric current to lessen the strength of pain signals in the spinal cord and brain.
. This technique involves applying a low-intensity electric current to lessen the strength of pain signals in the spinal cord and brain.
However, remember that each case is treated individually. These tips for daily activities can also help you:
While dealing with your illness can be tedious and difficult, remember that you are not alone. Don’t be afraid to ask your loved ones for help. In the event of mood changes or other psychological problems, it is worth consulting a psychologist or psychotherapist.
The initial diagnosis may scare you. However, remember that in peripheral neuropathy, pain can be relieved. Rehabilitation will reduce the existing ailments, and the medications prescribed by the doctor will improve your comfort.
Do not delay going to the doctor and do not underestimate the next symptoms. Thanks to this, you will get back in shape faster and feel better.
Table of Contents

Neuropathy is a disease that influences nerves. Learn what are the symptoms and causes of neuropathy. Check out how it… read more »
Nerve damage, also known as neuropathy, could be a condition that influences the body's nervous framework. The nervous framework is a… read more »
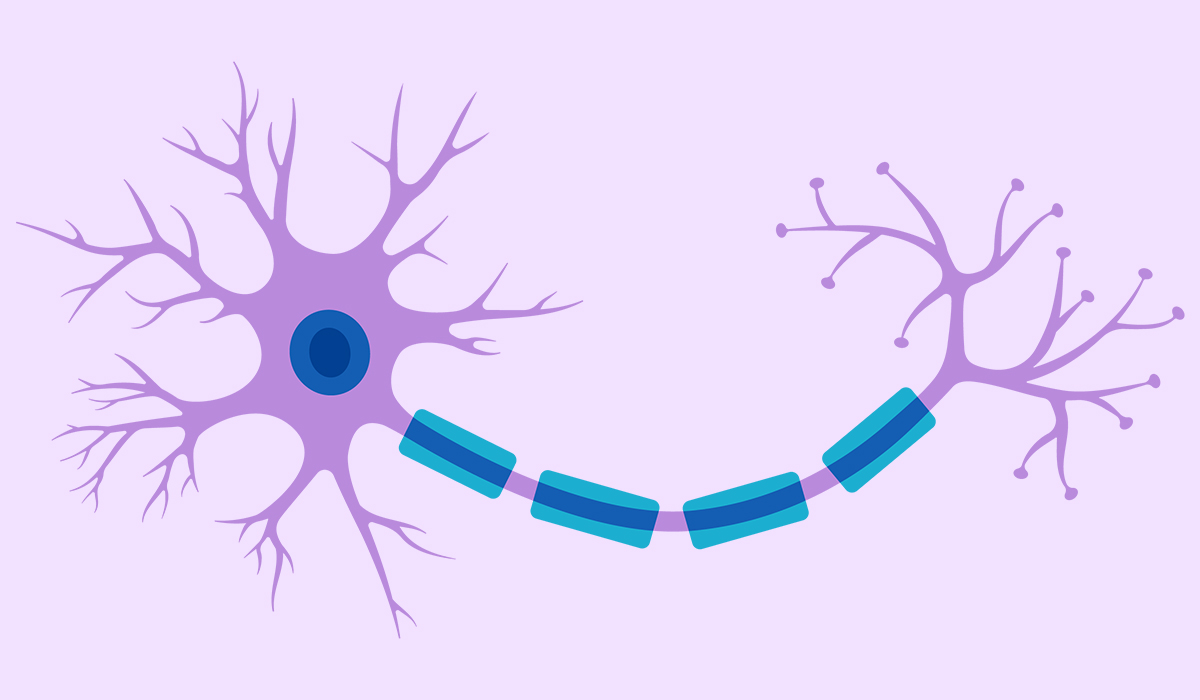
Nerve is a bundle of fibers made up of neurons that transmit sensory and motor information between different body parts… read more »
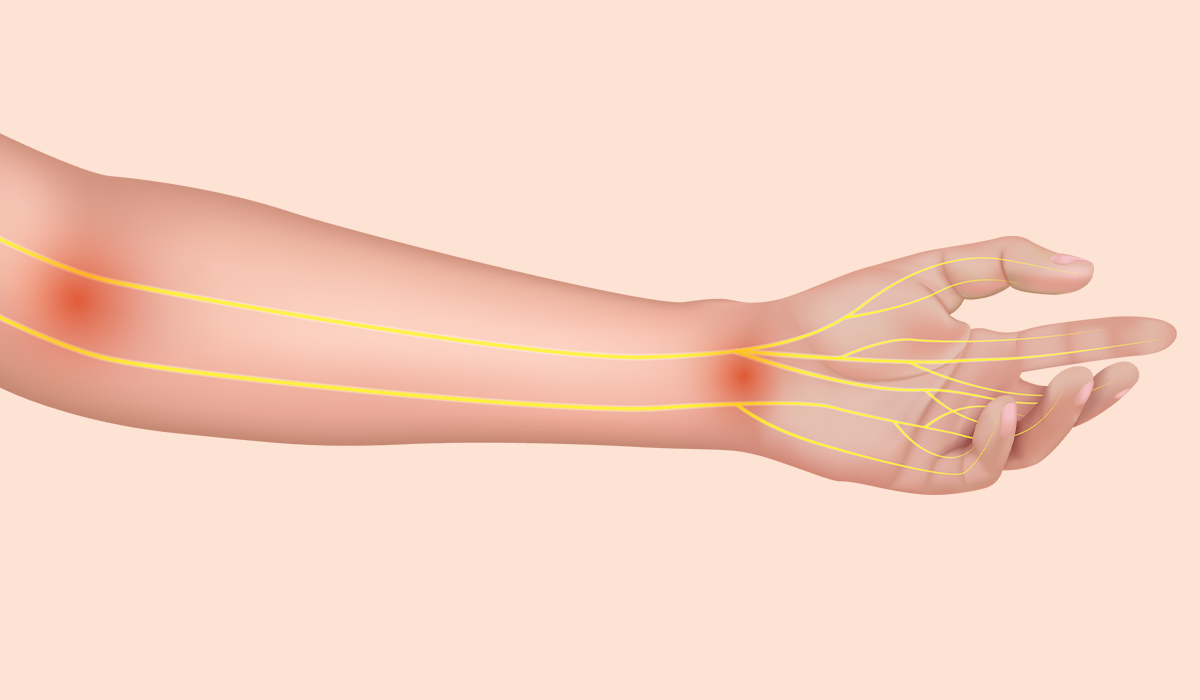
Nerve pain, which specialists refer to as neuropathic pain, maybe a complex and regularly troublesome condition emerging from harm to the nervous… read more »

Diabetes is a disease involving elevated blood glucose levels. What are the causes of diabetes? How can it be treated?… read more »

Ataxia is a motor coordination issue when individuals struggle with exact movements, holding the correct posture, or having standard walking… read more »
There are many factors to consider while trying to find the reason for the right arm and shoulder pain. Even… read more »

Neuralgia, moreover called nerve torment, is a solid throb that feels like cutting or burning and follows the way of… read more »
Lyme disease is difficult to diagnose. Therefore, it often goes undiagnosed for years, leading to complications. If you want to… read more »