Gallstones are deposits that have formed in the gallbladder due to the precipitation of bile components. They often give no signs for an extended period. But when they do – what should you look for?
Gallstones![]() are deposits created in the gallbladder
are deposits created in the gallbladder![]() . They are a result of the precipitation of bile elements. These include bilirubin, protein, cholesterol deposits, or calcium carbonate.
. They are a result of the precipitation of bile elements. These include bilirubin, protein, cholesterol deposits, or calcium carbonate.
The gallbladder keeps the bile. The liver creates it. We need it for fat digestion. It goes through the bile ducts from the sac to the duodenum during eating. That is where the digestive processes start.
In this journey, in some people, bile components precipitate. They clump together to form bile deposits (stones). Mostly, they have a diverse composition. However, there may also be homogeneous ones, e.g., only from cholesterol crystals. They can be as little – resemble grains of sand or peas. But they may also be the size of a walnut.
Gallstones are mostly a female problem. Deposits are formed 2-3 times more often in women than men.
Obese people, those who use fasting or drastic diets, and those with metabolic diseases are at risk of forming stones. People who have given birth use hormonal contraceptives or therapy are also at risk. It is because of the influence of sex hormones on deposit development.
Cholelithiasis is a multifactorial![]() disease.
disease.
The part of genetic factors is emphasized in its formation. Stones are formed due to enzyme disorders in the liver and dyskinesia (contractility disorders) of the bile ducts.
Factors predisposing to their development include:
Moreover, a fatty diet contributes to a change in the bile composition and the precipitation of bile salts. These are deposited on the exfoliated epithelium of the bile ducts. They are joined by cholesterol and calcium, which calcifies the whole and causes gallstone formation.
We usually do not feel the stones that rest loosely in the gallbladder. But we may discover them accidentally. It may happen while undergoing a control ultrasound of the abdominal cavity while checking the kidneys or liver functioning.
However, sometimes, they irritate the mucous membrane of the sac, disrupting its work. Then, we feel discomfort in the abdomen. We experience belching and bloating. The right hypochondrium or upper abdomen may have a fullness or creasing.
All of these can be signals that the gallbladder is failing. Eating something fatty, difficult to digest, or too much can cause the problem. Mild symptoms![]() usually go away on their own.
usually go away on their own.
The problem begins when a stone temporarily blocks the bile flow from the gallbladder to the bile ducts. Then, suddenly, you get intense pain (colic![]() ) in the epigastrium under the right costal arch. It can radiate to the back and suitable shoulder blades. We can even feel it in the neck and collarbones. There may be nausea and vomiting. The attack length varies.
) in the epigastrium under the right costal arch. It can radiate to the back and suitable shoulder blades. We can even feel it in the neck and collarbones. There may be nausea and vomiting. The attack length varies.

Prolonged pain attacks for over 3 hours may indicate acute inflammation of the gallbladder due to cystic duct blockage by a calculus. Then, vomiting, bloating, chills, and fever usually join the pain.
As a result of the blockage of the outflow of bile, inflammatory fluid collects in the sac. The follicle enlarges, becomes tense, and hardens. The bile pigments methodically get into the blood. Ultimately, a watery liquid stays in the sac. They are called hydroceles![]() . If it becomes infected, an empyema forms.
. If it becomes infected, an empyema forms.
Acute cholecystitis can lead to cholangitis, pancreatitis, and peritonitis. So do not underestimate it.
Already based on typical symptoms, e.g., usual pain and a big bubble that provides resistance to pressure, the doctor recognizes inflammation.
But to decide ultrasound of the abdominal cavity![]() is needed. It permits the specialist to evaluate the size of the gallbladder and its wall's thickness, the location and proportions of deposits, and the patency of the bile ducts.
is needed. It permits the specialist to evaluate the size of the gallbladder and its wall's thickness, the location and proportions of deposits, and the patency of the bile ducts.
The procedure can catch even the tiniest ailments. The image may be “unreadable” in the case of high obesity or when a large amount of gas accumulates in the intestines.
Laboratory tests are also significant for making a diagnosis![]() . Your doctor may recommend liver tests. It checks the liver enzyme level in the blood.
. Your doctor may recommend liver tests. It checks the liver enzyme level in the blood.
Standards may slightly differ from each other. They depend on, e.g., the apparatus and reagents used for the analysis. Individuals with gallbladder or bile duct inflammation have more elevated levels of biochemical indicators (e.g., bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase) and a higher number of white blood cells.
If you think you have gallstones, get an abdominal ultrasound. If your doctor is unsure or suspects cancer![]() , a CT scan may be necessary.
, a CT scan may be necessary.
The therapy of gallstones relies on the condition's manifestation, the placement of deposits, and potential complications. If colic occurs occasionally and is not strong, you can take relaxants, cholagogues, and anti-inflammatory agents with silymarin. You may also use herbal medicaments with a similar impact. You have to remember that this helps only temporarily. It is not curing the disease.
If we have diagnosed gallstones that do not require immediate surgical treatment, the first step in alleviating its symptoms should be to introduce changes in nutrition. What are the most important rules of the gallstone diet?
Follow an easily digestible diet![]() with limited fat intake, especially of animal origin. Reduce the supply of products rich in dietary fiber. Base the menu on carbohydrates and low-fat protein products. Eliminate highly processed foods and dishes rich in hot spices. Enrich the diet with products that are a source of vitamin C, which supports the treatment of inflammation.
with limited fat intake, especially of animal origin. Reduce the supply of products rich in dietary fiber. Base the menu on carbohydrates and low-fat protein products. Eliminate highly processed foods and dishes rich in hot spices. Enrich the diet with products that are a source of vitamin C, which supports the treatment of inflammation.
Eat your meals regularly, every 3-4 hours. It prevents excessive strain on the digestive system. Do not consume your last meal after 2-3 hours before bed. Significantly, it is light and small in volume.
Dishes should be prepared using culinary techniques, such as cooking in water, steaming, grilling, and baking without adding fat. Eliminate frying.
To conclude, a diet for gallstone disease should be based on:

Gallbladder stones require giving up products such as:
Usually, if someone has had an attack, there is a high chance that the attack will recur, even if you change your diet.
If deposits “sit quietly” in the gallbladder, usually gallstones are not treated. However, when they provoke pain or colic episodes, removing the gallbladder before difficulties arise is more reasonable. The complications include inflammation or gallstone displacement toward the bile duct. The procedure is executed instantly if there is hydrocele or empyema of the sac.
Initial treatment involves potent antispasmodics, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory medication when dealing with acute inflammation. Only when the inflammation has subsided will surgery![]() be considered. Nonetheless, there may be situations where surgery is needed immediately, which can result in complications.
be considered. Nonetheless, there may be situations where surgery is needed immediately, which can result in complications.
A quick visit to a specialist requires jaundice (the condition when the skin becomes yellow), as it suggests liver dysfunction.
The choice of the technique by which the gallstones will be removed depends on the severity of the condition and general health. We use laparoscopy![]() in “easier” issues – when the specialist does not foresee any difficulties. However, this technique is not used for emergencies, e.g., in the case of acute inflammation of the sac. It also will not be performed in obese individuals when the carcass could stop the instruments from getting to the follicle.
in “easier” issues – when the specialist does not foresee any difficulties. However, this technique is not used for emergencies, e.g., in the case of acute inflammation of the sac. It also will not be performed in obese individuals when the carcass could stop the instruments from getting to the follicle.
The doctor makes four little skin incisions on the belly during the laparoscopic process. Then, they insert through them the instruments. Then, the peritoneal cavity is filled with air. The abdominal integuments rise, and the belly becomes like a balloon – thanks to this, the doctor can observe the operating field and manipulate the instruments. Special clips close the arteries and cystic ducts before removing the change.
Laparoscopy is also the standard method used in acute disorders associated with gallstones. Sometimes, doctors do open surgery![]() .
.
The digestive system needs to get used to the new circumstances. Now, the bile flows directly from the liver to the duodenum. That is why you should change your diet for 4-6 weeks. Choose lightly digestible foods, e.g., lean meat, fish, and dairy products. Eat about 4 or 5 meals in small portions. Remember to drink 2 liters of water.
Then, you can start to slowly enrich the diet. If you can, do it with a specialist. Always observe how your organism behaves. Most individuals return to their usual eating methods after having their gallstones removed. Remember to tell your doctor if alarming signs happen.
The specialist may suspect that the changes are in the bill ducts![]() . Doctors use a test called ERCP to check if a gallbladder stone is in the bile ducts. After giving contrast, they insert a scope through the mouth to see the duct on a screen.
. Doctors use a test called ERCP to check if a gallbladder stone is in the bile ducts. After giving contrast, they insert a scope through the mouth to see the duct on a screen.
If the original diagnosis is verified, the doctor removes the changes. Often, they use a coagulator (electric surgical knife) to incise the bile duct sphincter and clear it. The larger stones sometimes have to be crushed.
It immediately brings relief and reduces pain. However, it does not fix the problem because subsequent stones can block the bile ducts. Thus, after the inflammation reduces, you still need to remove the gallbladder with stones.

Of course, it is possible, but only after surgical removal of the gallbladder![]() , as well as the stones present inside. The threat of complications after the procedure is low.
, as well as the stones present inside. The threat of complications after the procedure is low.
As mentioned above, recurrence of gallstones may occur in patients for whom surgical treatment is impossible and who are subjected to pharmacological treatment.
Familiarize yourself with the offers of facilities that offer gallbladder removal surgery.
Finding clear ways to prevent gallstones is impossible because the causes of formation are not clearly explained.
However, some factors, such as obesity, can be prevented by modifying the diet![]() . Changing eating habits should be accompanied by increased physical activity
. Changing eating habits should be accompanied by increased physical activity![]() . It should be gradually increased in duration – the goal is 150-300 minutes a week, but even a few minutes of physical activity during the day is better than no exercise. Moderate-intensity aerobic (aerobic) activity is recommended for obese people.
. It should be gradually increased in duration – the goal is 150-300 minutes a week, but even a few minutes of physical activity during the day is better than no exercise. Moderate-intensity aerobic (aerobic) activity is recommended for obese people.
The recommended forms of movement are:
It is also worth taking care of spontaneous activity, e.g., using the stairs instead of the elevator, walking while talking on the phone, or moving on foot. Due to the risk of excessive strain on the ankle and knee joints, avoiding running and jumping exercises is better.
As mentioned above, some individuals try dissolving gallstones with herbal oral preparations to avoid surgery. Those medicaments can be purchased at some herbal and health food stores. Most doctors, however, approach this type of therapy with skepticism.
Gallstones dissolve gradually – so treatment can take months or even years. However, only a few cholesterol deposits can be dissolved without calcification, which does not happen to everyone. If therapy is successful, there is no assurance that new gallstones will not develop.
Remember to consult every treatment method with your doctor. We know that surgery may not seem like an ideal solution. But for some people, it can protect against many unpleasant symptoms in the future.
Table of Contents
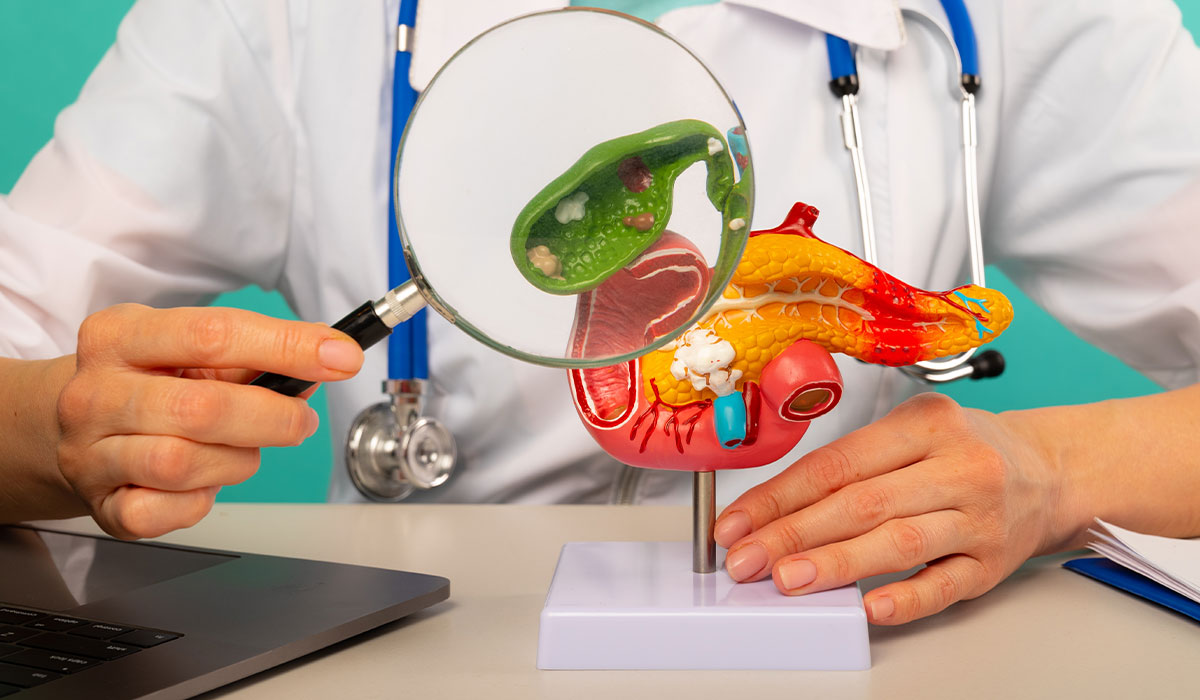
The gallbladder performs very important functions in the human body. Problems with its functioning can lead to diseases. Learn about… read more »
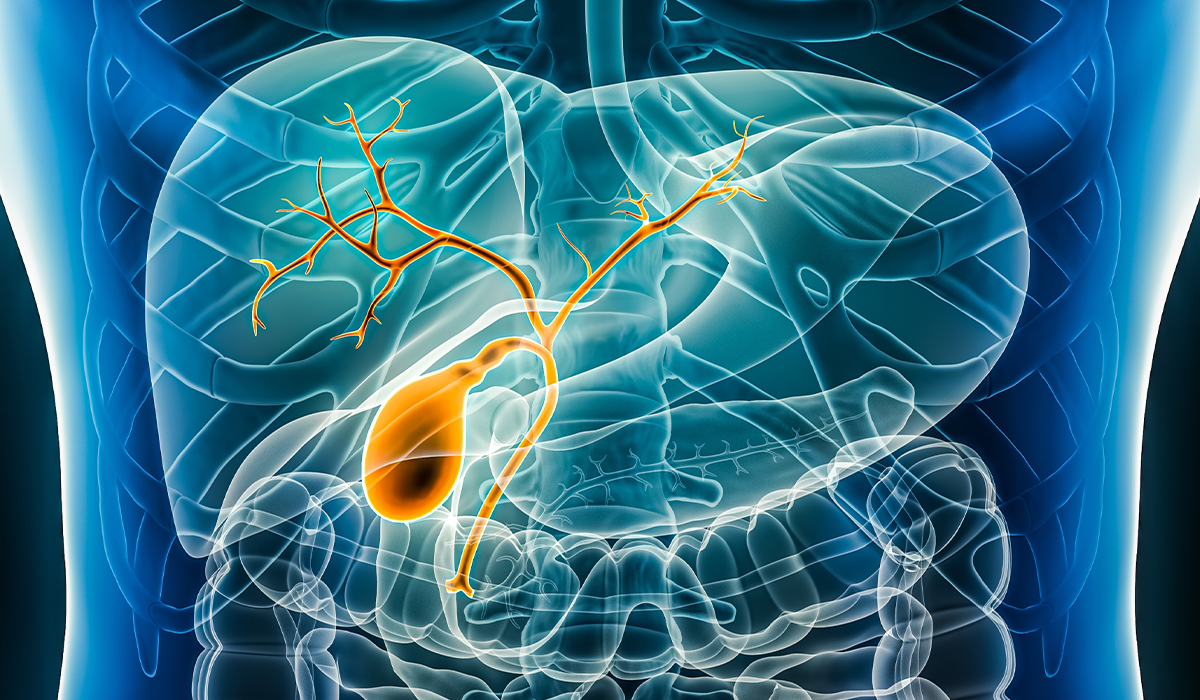
Bile is a green-yellow liquid that the liver prepares and stores in the gallbladder. It's key for breaking down and… read more »

Kidney stones can form for a variety of reasons. Learn about factors that increase the risk of kidney stones. See… read more »
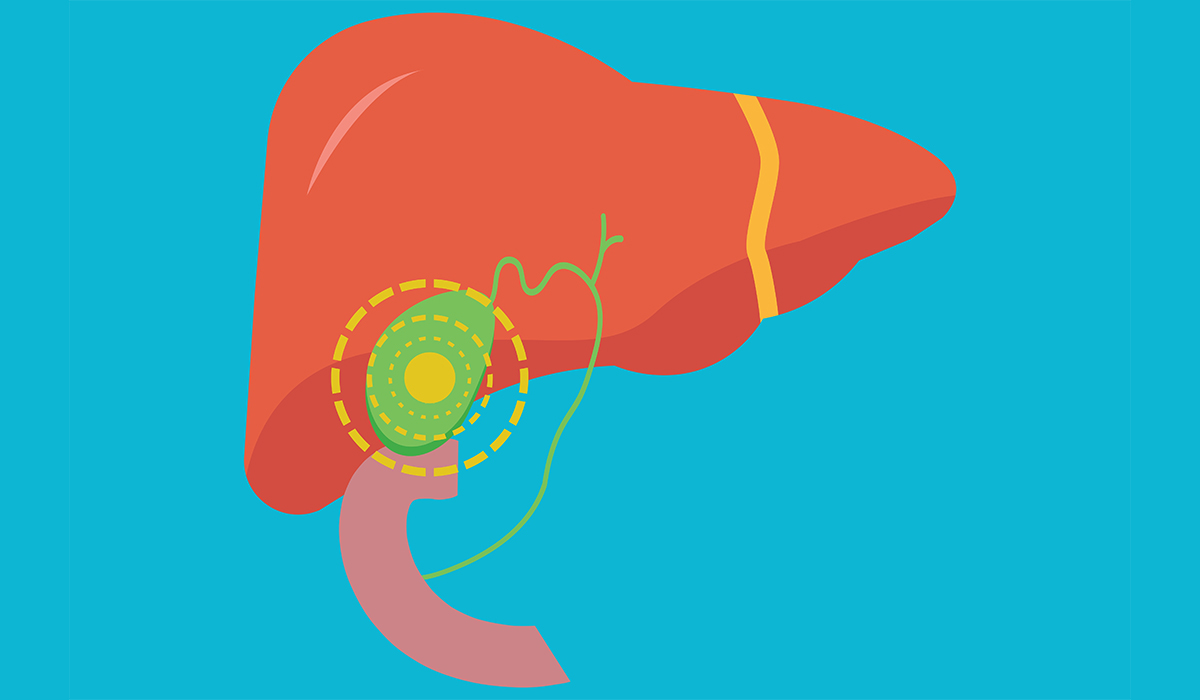
Cholecystitis is a medical term used to describe gallbladder inflammation. Often called acute cholecystitis by specialists, it is a condition… read more »
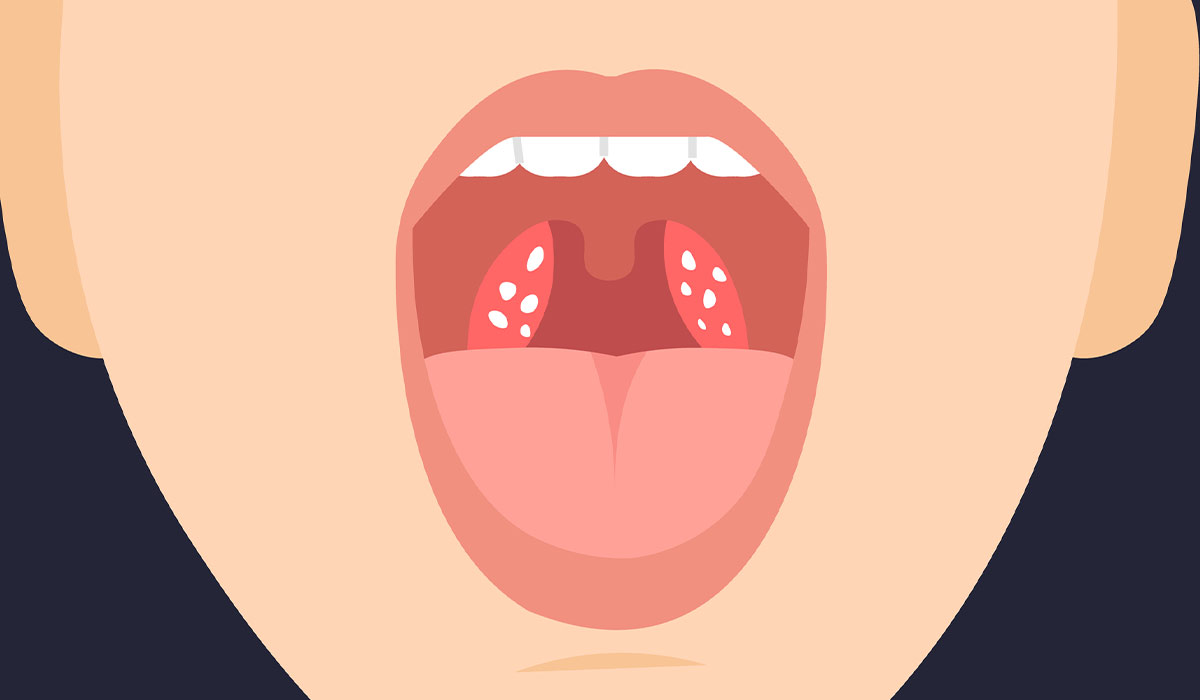
Tonsil stones are a common condition affecting millions of people each year. It occurs due to the buildup of debris… read more »

Jaundice is a disease symptom that involves yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera. What are its causes? How… read more »

A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the human digestive system. What does a visit to… read more »
Kidney pain, also known as renal pain, begins from the pair of bean-shaped organs at the back of your stomach… read more »

Hyperlipidemia is a disorder with high levels of lipids (cholesterol or triglycerides) in the blood. It can lead to serious… read more »