Once a person gets infected with the Varicella-Zoster Virus and gets over chickenpox, they risk developing shingles as an adult. It does not happen for most people, as the virus remains inactive in some of the person's nerve cells.
Once the immune system gets weakened, the virus may cause a shingles outbreak, leading to painful spots on one side of the body, fever, rash, and blisters. This occurrence is referred to as the reactivation of the virus.
The dormant virus in the person's nerve cells does not cause any issues for most people who have gotten over chickenpox. In addition, once the outbreak starts, it does not necessarily cause all the symptoms associated with the virus.
Pain caused by shingles is usually concentrated in a specific area![]() on the side of the body. In its early stages, it is characterized by symptoms similar to other infections, such as fever, coldness, and weakness. Initially, the disease may seem like a regular cold before painful sensations and skin symptoms develop. Issues that you can experience after contracting varicella-zoster virus include:
on the side of the body. In its early stages, it is characterized by symptoms similar to other infections, such as fever, coldness, and weakness. Initially, the disease may seem like a regular cold before painful sensations and skin symptoms develop. Issues that you can experience after contracting varicella-zoster virus include:
If pain occurs on one side of the body, it helps narrow down the possible causes of the symptoms. That is the case for most people – pain concentrated in a small body area can be intense and develop as one of the first symptoms. It can affect various body parts so shingles may mimic kidney, heart, or lung problems.
Skin symptoms usually develop within 1-5 days after the pain. Skin burning and tingling sensations come first, followed by a red rash and fluid-filled blisters. 7-10 days after the start of the viral infection, fluid inside the blisters dries out, which causes crusty blisters called scabs. After a couple of weeks, the crusty blisters disappear from the skin.
Shingles outbreaks do not always go by the book. Some people may experience mild symptoms like itching without painful sensations and rash. On the other hand, shingles may cause serious complications. In rare instances, blisters that develop near an ear or eye may do significant damage and cause hearing loss, blindness, temporary paralysis of the face, and encephalitis (brain inflammation). Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice blisters around your eyes or ears.

The reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus causes a shingles outbreak. After a person gets over chickenpox, the virus stays dormant until it attacks again, causing shingles.
Varicella-zoster belongs to a group of viruses known as herpes viruses. Viruses from this group lead to such diseases as genital herpes and cold sores.
Evaluating whether a patient is infected with the varicella-zoster virus or not is not difficult if they undergo chickenpox. Visible rash and blisters on the person's body also indicate shingles as the cause. However, in some instances, more than a medical history and physical examination may be required to diagnose. This is because shingles may resemble other conditions that cause a rash. These may include:
In such a scenario, a doctor may take a swab from a lesion![]() to test it at a lab, do a blood test, and do other tests to pinpoint the cause of the rash precisely.
to test it at a lab, do a blood test, and do other tests to pinpoint the cause of the rash precisely.
Conventional treatment of shingles involves taking antiviral drugs and topical shingles cream with capsaicin in case of intense pain. A doctor may also prescribe injections of steroids, local anesthetics, topical numbing agents, antidepressants, narcotic-containing medications like codeine, and anticonvulsants.
Because there is no cure for the varicella-zoster virus, antibiotics do not work against shingles. It is essential to stick to a doctor's advice and not take any antiviral medications not mentioned by your doctor. If intense pain is the main issue you are dealing with, you can take pain relievers.
Another treatment option includes the shingles vaccine recommended by CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) for anyone over 60. The vaccine was licensed in 2006 and is used as a preventative treatment for shingles![]() . According to CDC, it halves the risk of developing shingles. It is safe to use but shouldn't be taken by pregnant women or women who plan to get pregnant.
. According to CDC, it halves the risk of developing shingles. It is safe to use but shouldn't be taken by pregnant women or women who plan to get pregnant.
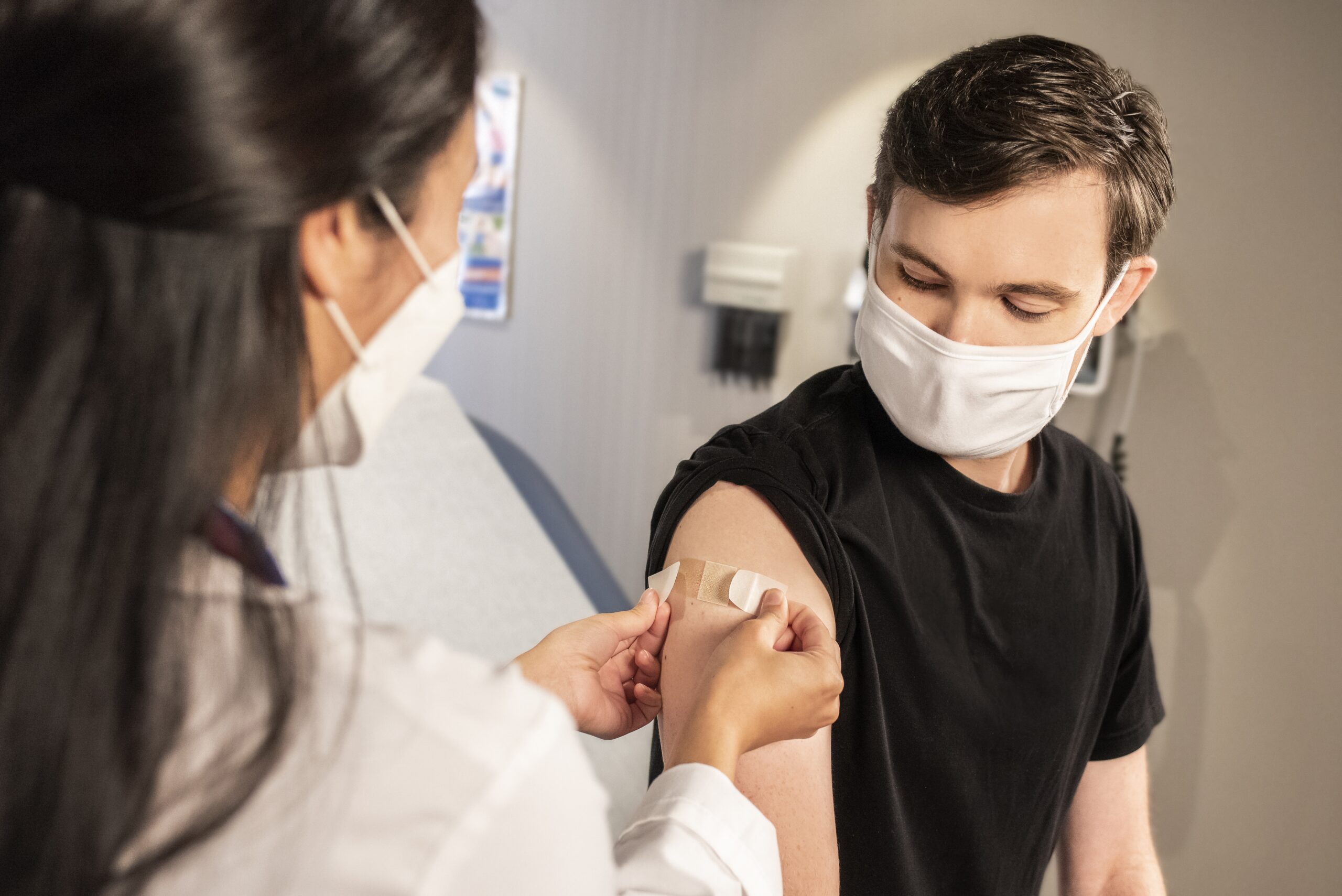
Shingles outbreak is more likely to develop in some people. Except for getting over chickenpox in the past, the following risk factors contribute to developing this viral infection:
Although anyone infected with the varicella-zoster virus in the past is at risk of developing shingles, the chance primarily increases with age. People who are younger than 40 years old rarely experience any symptoms. The risk increases with age and also applies to the severity of symptoms. Scientists currently examine why age is such a significant contributing factor to this disease. The most promising theory is that the immune system keeps the virus from reactivating, preventing any shingles symptoms from developing. Once it is weakened due to age, or certain diseases, it has a much higher chance of successful attack.
Shingles may sometimes lead to additional, more severe health problems. These include:
Home remedies for shingles are easy to find, cheap, and safe. They won't cure this condition, but they are a great addition to conventional treatment options.
The easiest way to help the body fight shingles is a diet consisting of well-balanced food with antioxidants, vitamins, and micro- and macro-nutrients. The below foods are particularly effective against symptoms caused by the virus:
Onions and garlic: They both contain allicin, a compound that increases the immune system's performance.
Foods packed with vitamin C: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that boosts the immune system and aids healing processes in the body. You can find it in fruits and vegetables such as citrus, bell pepper, cabbage, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Foods rich in B-complex vitamins: Vitamins from B groups participate in many bodily functions, so it is essential to include them in a diet during a shingles outbreak.
Green leafy vegetables: Immune system can also be boosted by beta carotene and calcium that are naturally found in green leafy vegetables such as cabbage, spinach, kale, lettuce, and watercress.
Avoiding certain foods is essential in strengthening your body against shingles and other viral infections. The foods listed below are not recommended while getting over shingles disease:
Highly-processed foods contain added sugar, salt, and omega-6 fatty acids that weaken the immune system and may lead to inflammation. It's best to avoid them when the body is fighting against a virus.
Intense pain and itching may be problematic and distract you from your daily activities. Here are ten tips that will help you better manage the pain and skin issues caused by the varicella-zoster virus:
Although shingles disease has no cure, it can be successfully treated with conventional methods. Its symptoms can be intense and distracting but can be resolved with painkillers, antiviral medicines, numbing agents, and natural remedies, including essential oils, supplements, and a well-balanced diet.
It is essential to leave blisters alone and not scratch them because it may lead to further complications like infection. Keeping the affected area clean also prevents unnecessary skin issues that can worsen the symptoms of shingles.