Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that causes the skin barrier to weaken, impairing its ability to protect the body from outside elements and retain moisture. The skin becomes dry, red/hyperpigmented, itchy, thickened, and bumpy. The urge to scratch the skin is often irresistible. Excessive scratching can lead to the formation of blisters and skin infections. It can affect people at any age, from newborns to the elderly.
According to National Eczema Association, more than 31 millions![]() of Americans are suffering from some form of eczema. Eczema is a collective term describing seven types of dermatitis. The terms dermatitis and eczema are often used interchangeably, which is not incorrect. However, not all dermatitis is eczema. All eczema is dermatitis.
of Americans are suffering from some form of eczema. Eczema is a collective term describing seven types of dermatitis. The terms dermatitis and eczema are often used interchangeably, which is not incorrect. However, not all dermatitis is eczema. All eczema is dermatitis.![]()
Eczema can come in mild, moderate, or severe forms. Most people suffering from it experience periods when symptoms are less noticeable, followed by periods when the condition becomes more acute. These periods are called ‘flare-ups'. Flare-ups are usually caused by triggers which will be discussed later in the text.
Symptoms of dermatitis occurring in specific areas of your body may be indicative of the trigger. Typically dry, scaly, itchy skin is found on:
Less commonly, it can also appear on:
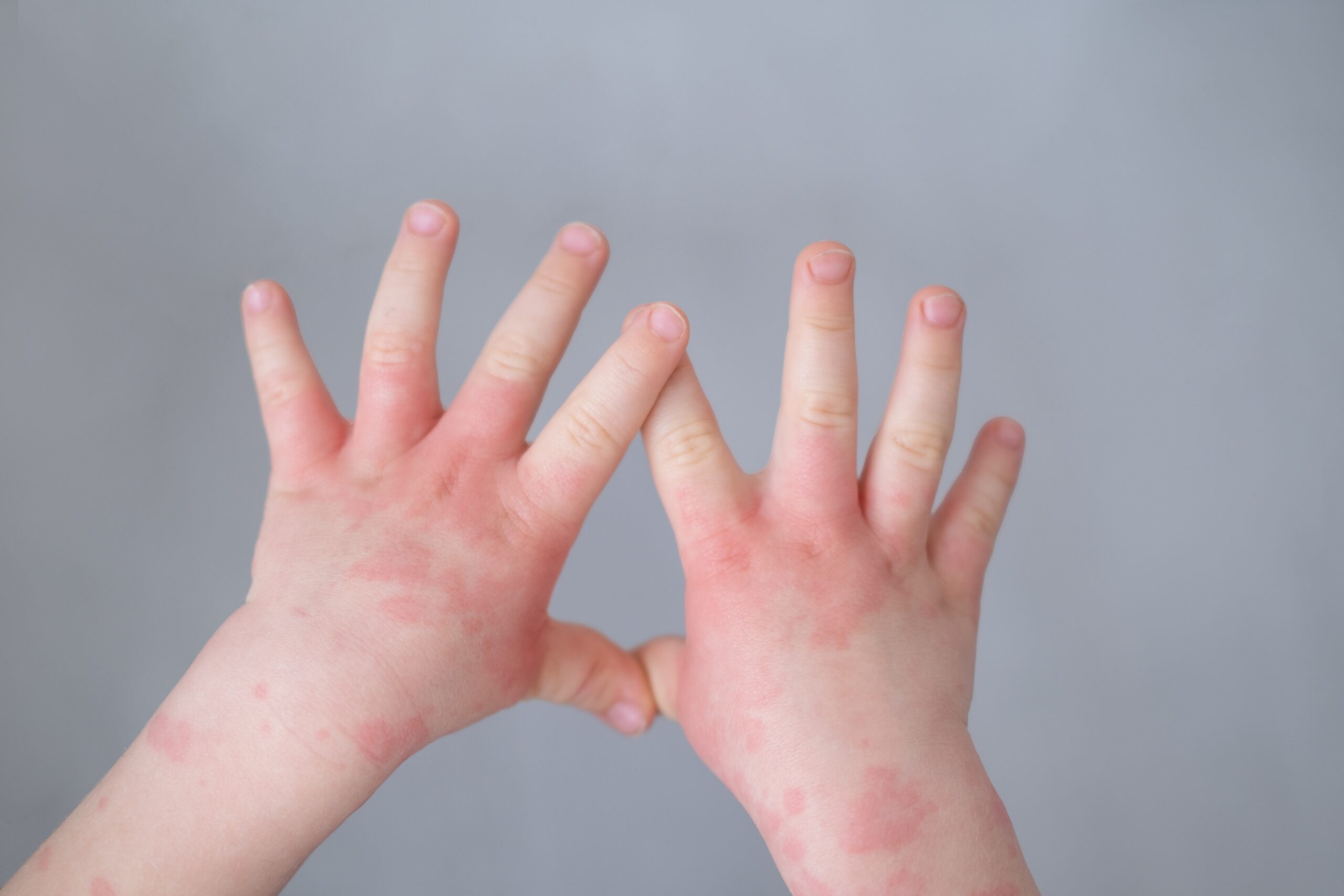
Although itchy, red, or hyperpigmented and dry skin are common symptoms for all types of eczema, there are several other symptoms that can determine which one of seven ![]() different types of eczema you are suffering from. It is important to be diagnosed correctly by a healthcare professional, as different types of eczema have specific triggers. One person can have more than one type of eczema. The main types of eczema are:
different types of eczema you are suffering from. It is important to be diagnosed correctly by a healthcare professional, as different types of eczema have specific triggers. One person can have more than one type of eczema. The main types of eczema are:

There are a lot of factors contributing to the appearance, extent, and intensity of the symptoms of dermatitis. It can vary from person to person depending on their skincare routine, severity, or coexistence of several types of eczema. On lighter skin, the rash is usually red, while on darker skin tones, it can present as hyperpigmentation or gray and purple areas of skin. People with eczema usually experience flare-ups interluded by periods when symptoms are less severe. Symptoms may vary depending on the type of eczema, but generally speaking, the symptoms are:
Determining the triggers of your flare-ups is a colossal step to managing the symptoms of eczema. If you are able to diagnose the trigger, you might be able to begin avoiding it. This could stop the flare-ups and improve the quality of your life.
Detailed past medical history and the history of flare-ups are powerful tools in determining the triggers. Your dermatologist will collect all the available facts and, like a detective, try to trace the source of your problems. The triggers are very often not obvious to the patients themselves. If it is unclear what triggers your flare-ups, you might be referred for allergy testing. These can include patch testing, skin prick testing, or blood tests. It is important to know what type of eczema you have. A skin biopsy or skin scraping test can be useful in diagnosis. Different types of dermatitis will have different triggers.

Treatment of dermatitis is bespoke to the patient and depends on the type and severity of the condition as well as a response to the previous treatments. First-line treatments![]() usually include avoiding the triggers and using emollients and topical steroids.
usually include avoiding the triggers and using emollients and topical steroids.
Emollients can come in the form of creams, lotions, ointments, gels, and sprays. Emollients prevent your skin from drying, reducing the likelihood of a flare-up. A good skin care routine is very important in managing dermatitis. Emollients should be used as often as possible, at least twice a day. You can use your emollient as a wash instead of soap. For each application, you should apply at least 50g (7 dessert spoons)![]() to the whole body. You should always smooth the emollient down with the direction of the hair growth rather than rubbing it into your skin, which can cause folliculitis.
to the whole body. You should always smooth the emollient down with the direction of the hair growth rather than rubbing it into your skin, which can cause folliculitis.
Topical steroids![]() are used alongside emollients to treat eczema flare-ups in short treatment bursts to control inflammation. Topical steroids are not recommended for long-term use due to possible side effects. The right strength will be prescribed by a dermatologist based on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient. Topical steroids are only effective when used with emollients. The best practice is to apply steroids around 20 minutes after applying emollients to allow absorption. A fingertip unit might be a useful indication of the correct amount of topical steroids application.
are used alongside emollients to treat eczema flare-ups in short treatment bursts to control inflammation. Topical steroids are not recommended for long-term use due to possible side effects. The right strength will be prescribed by a dermatologist based on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient. Topical steroids are only effective when used with emollients. The best practice is to apply steroids around 20 minutes after applying emollients to allow absorption. A fingertip unit might be a useful indication of the correct amount of topical steroids application.
For severe eczema that doesn't respond to topical steroids, treatments like phototherapy, oral steroids, or immunosuppressant drugs can be used. Phototherapy![]() is a treatment utilizing UV radiation to treat skin conditions. Sometimes symptoms of eczema can ease with sun exposure. Phototherapy, however, is performed in controlled settings where the healthcare professional can make sure you receive the right dose of UV radiation without putting you in danger of sun exposure carries. Phototherapy treatment is usually performed over 12 to 16 weeks in treatment sessions 2 or 3 times a week.
is a treatment utilizing UV radiation to treat skin conditions. Sometimes symptoms of eczema can ease with sun exposure. Phototherapy, however, is performed in controlled settings where the healthcare professional can make sure you receive the right dose of UV radiation without putting you in danger of sun exposure carries. Phototherapy treatment is usually performed over 12 to 16 weeks in treatment sessions 2 or 3 times a week.
Oral steroids![]() can be used in managing eczema that does not respond to topical steroids or as an urgent treatment for acute reactions to allergens. These are prescribed by dermatologists and are not suitable as a long-term solution due to the side effects.
can be used in managing eczema that does not respond to topical steroids or as an urgent treatment for acute reactions to allergens. These are prescribed by dermatologists and are not suitable as a long-term solution due to the side effects.
Since dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction due to excessive immune response, immunosuppressants![]() are being used as a treatment for it. It comes in the form of tablets or injections. These are very strong medications and must be used under a supervision of a specialist doctor. Blood tests will be run before commencing the immunosuppressant treatment to ensure you are suitable for the drug. These will be repeated frequently throughout the course to monitor your blood count as well as liver and kidney function. Additional tests might be recommended by your health care professional.
are being used as a treatment for it. It comes in the form of tablets or injections. These are very strong medications and must be used under a supervision of a specialist doctor. Blood tests will be run before commencing the immunosuppressant treatment to ensure you are suitable for the drug. These will be repeated frequently throughout the course to monitor your blood count as well as liver and kidney function. Additional tests might be recommended by your health care professional.
Identifying triggers, implementing a good skincare routine, and getting the right treatment are vital for managing eczema, as it can impact daily living and sleep quality. Untreated eczema can lead to inflammation and even a systemic reaction. People with chronically itchy skin can be more susceptible![]() to depression. Using low-pH skin cleansers, cold compresses, wearing soft, breathable fabrics made from natural fabrics, and moisturizing frequently can help with the itchiness.
to depression. Using low-pH skin cleansers, cold compresses, wearing soft, breathable fabrics made from natural fabrics, and moisturizing frequently can help with the itchiness.
The best way to prevent dermatitis is to keep your skin hydrated.
Eczema is a non-contagious skin condition that leads to skin inflammation through the deterioration of the skin's protective barrier. There are various types of eczema, all of which have one common symptom – itchy skin. Stress is a very important risk factor, as well as a family history of eczema and allergies. Symptoms can be managed by avoiding triggers, keeping your skin moisturized, and undergoing treatments for dermatitis. Eczema can be easily mistaken for other skin conditions, e.g., psoriasis, so talk to your healthcare professional to get the correct diagnosis and the best possible outcome of treatment.
Table of Contents

Psoriasis is characterized primarily by skin lesions that result from impaired epidermal regeneration. Learn about all types and signs of… read more »
Dry skin is a bothersome problem that can affect everybody. Find out what dries out your skin. Learn about moisturising… read more »

Diaper rash is when little kids and babies sometimes get a rash from wearing nappies if their skin is wet… read more »
About 3.9% of the adult population in the USA is affected by gout, a painful form of arthritis that affects… read more »

Itchy scalp is a fairly common condition that can have many causes. What are the most popular? What to do… read more »
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin infection especially in children. Find out how to recognise molluscum contagiosum skin lesions. Learn… read more »

Dry scalp is a condition characterized by the scalp skin becoming dry, irritated, and flaky. It often results in itching… read more »

Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is sometimes mistaken for acne, allergic reactions, eczema, and other skin conditions.… read more »

Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which our body begins attacking itself. Find out what are the causes, symptoms,… read more »