Scarlet fever is an infectious disease caused by bacteria. It mainly affects children, but it can also occur in adults. The infection is caused by bacteria called group A Streptococcus that produce toxins. The bacteria causing this disease are also the cause of strep throat.
In some patients, strep throat may develop into scarlet fever. This is only possible when the strain of bacteria responsible for the development of strep throat produces a toxin to which the patient is not immune. If strep throat is caused by a strain of bacteria that does not produce toxins (poison), then scarlet fever will not occur.
Scarlet fever can be diagnosed based on its characteristic symptoms. However, the course of the disease may not be typical, and the symptoms may also suggest other conditions. Then, additional tests are helpful. These include a test for group A strep antigens and a throat swab. It may also be beneficial to perform a complete blood count (an increased number of white blood cells may be detected) and a C-reactive protein (CRP) test. The Centor scale![]() , which allows for determining the probability of streptococcal infection, also has diagnostic value.
, which allows for determining the probability of streptococcal infection, also has diagnostic value.
Treatment of scarlet fever requires the use of antibiotics. Patients are also given medications that quickly relieve the troublesome symptoms of scarlet fever and improve comfort. Hospital treatment is needed if the disease is severe.
Scarlet fever is caused by group A strep bacteria. The disease occurs due to the action of toxins produced by these bacteria.
The classic form of the disease manifests itself only in people who are sensitive to the effects of toxins, that is, not resistant to them. If you have immunity to toxins secreted by group A strep, only strep throat occurs after streptococcus infection.
The source of infection is a person suffering from strep throat or scarlet fever. You can get infected:
Children are the main ones affected, but the disease rarely occurs in adults. Infection most often occurs in nurseries and schools. Illnesses occur more often in the autumn and winter seasons. After exposure to the bacterium, symptoms of the disease usually appear after 2 to 5 days.
It is a highly contagious disease. Without treatment, you are contagious for 1-2 weeks after symptoms appear.
With treatment, symptoms disappear after 2-4 days. Bacteria are no longer spread 24 hours![]() after taking the first dose of antibiotic – after which you can return to nursery, school, or work.
after taking the first dose of antibiotic – after which you can return to nursery, school, or work.
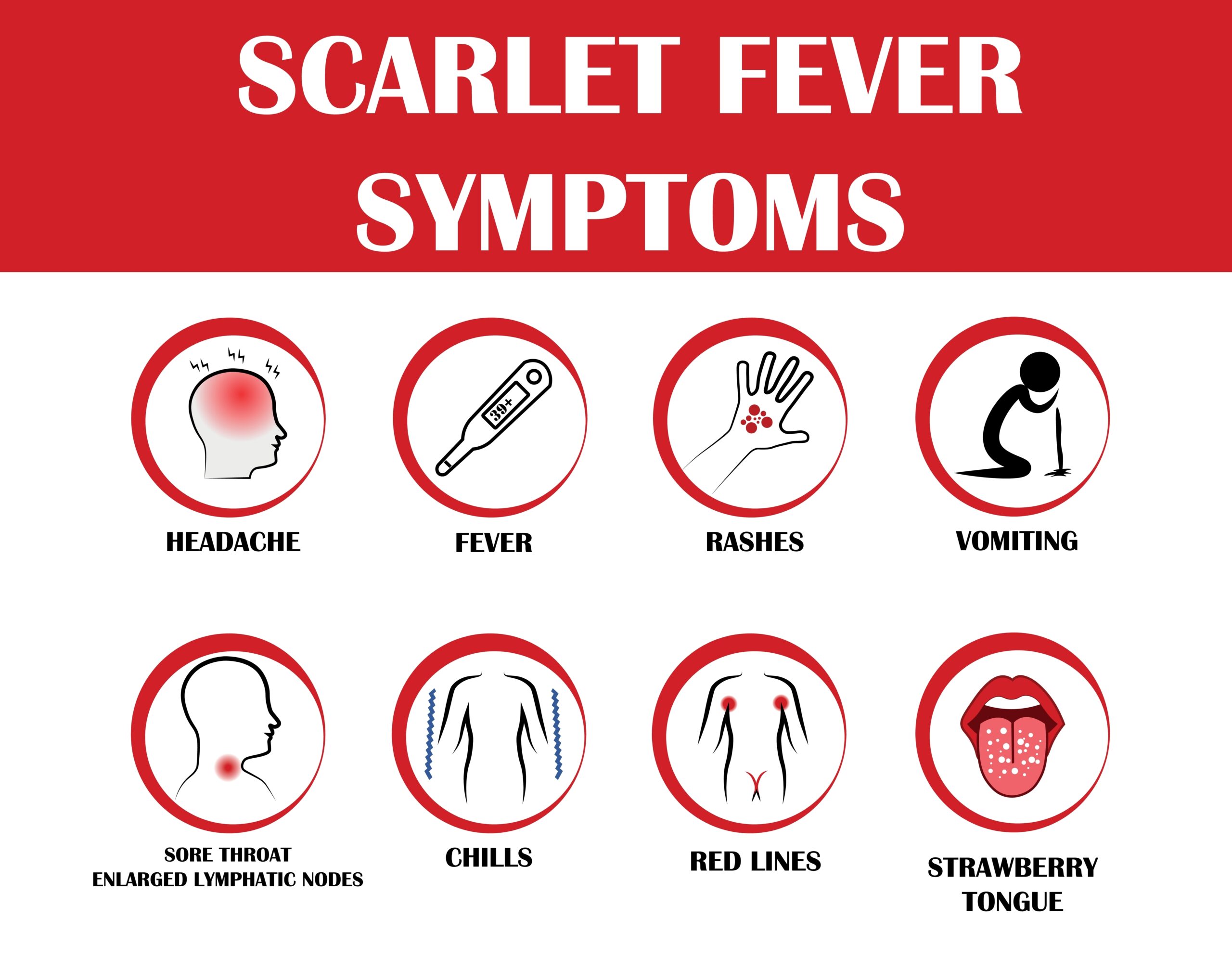
Scarlet fever has a sudden onset. Common symptoms include a severe sore throat, pain when swallowing, headache, fever above 38 degrees Celsius, inflammation of the throat, and swelling of the tonsils.
In addition, some individuals may experience abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. Furthermore, the throat in scarlet fever appears bright red, and the tongue may have a white coating. After several days, the tongue typically turns red, and red spots may become visible on the palate's mucous membrane. It may be accompanied by tender (painful to touch) and enlarged anterior neck lymph nodes.
There is no cough or runny nose during scarlet fever.
Scarlet fever beginning is sudden and acute. As the name of the disease suggests, the disease involves fever. The body temperature during the infection can exceed 38 degrees Celsius. A sick person may experience chills and muscle pain.
The skin rash usually appears on the second day of the disease. However, it may occur earlier or later – up to 7 days from the onset of symptoms.
The rash is characterized by:
The rash initially appears as flat spots that later turn into rough lumps.
Initially, it appears in the neck, armpits, and groin area and then covers the rest of the body – the torso, buttocks, and cheeks. However, the skin around the mouth remains pale.
Due to the excessive fragility of blood vessels, small linear blood spots may appear on the bends of skin folds (e.g., in the groin).
The disease is characterized by gradual peeling of the skin areas affected by the rash, which occurs after approximately seven days. Skin peeling usually involves the skin around the fingers, groin, and toes. This may take up to several weeks.
During the disease, a white coating appears on the tongue. Then, the tongue turns intensely red. This is the so-called “strawberry” tongue. “Strawberry tongue” is a term used to describe the tongue's appearance during certain diseases, especially scarlet fever. The characteristic appearance is caused by inflammation of the lingual papillae (taste buds), followed by peeling, leaving a red color and bumps on the tongue.
During the infection, throat and neck symptoms include:
The disease spreads mainly through droplets, sometimes through bacteria-contaminated objects, underwear, bedding, and surfaces. Rarely does the infection spread through food.
Risk factors contributing to the development of the disease include not following hygiene rules and staying in large crowds (schools, nurseries, public transport).
In most cases, scarlet fever is diagnosed based on its characteristic symptoms. However, there are atypical cases that may cause diagnostic difficulties. The symptoms may resemble an allergic reaction, especially if the rash is very itchy. Therefore, after asking about the signs and examining the patient, the doctor may decide to perform additional tests to confirm scarlet fever. It is possible to do:
Antibiotics (antibacterial drugs) are used to treat scarlet fever. Their use:
When undergoing antibiotic treatment, adhering to the doctor's instructions and taking the prescribed medication regularly is crucial. This ensures a consistent concentration of the antibiotic in your body, which is necessary for its antibacterial effectiveness. The doctor determines the duration of the treatment, and it is important not to stop it prematurely, even if the symptoms improve. Discontinuing the treatment too soon can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Antibiotics start working quickly, and within 24 hours of taking the first dose, the infected person is no longer contagious. Additionally, you can use antipyretics![]() (medicines that reduce body temperature) and painkillers to alleviate discomfort. These medications will not impact the duration of the illness, but they can enhance the patient's comfort. In children, it is advisable to take ibuprofen or paracetamol based on body weight or as advised by the doctor. It is important to note that ibuprofen and paracetamol should not be taken together unless explicitly recommended by the doctor. These medications can be used alongside antibiotic therapy if necessary. They can help alleviate headaches, sore throat, and stomach pain and reduce high body temperature.
(medicines that reduce body temperature) and painkillers to alleviate discomfort. These medications will not impact the duration of the illness, but they can enhance the patient's comfort. In children, it is advisable to take ibuprofen or paracetamol based on body weight or as advised by the doctor. It is important to note that ibuprofen and paracetamol should not be taken together unless explicitly recommended by the doctor. These medications can be used alongside antibiotic therapy if necessary. They can help alleviate headaches, sore throat, and stomach pain and reduce high body temperature.
If you experience an itchy rash that causes discomfort, you can use antihistamine pills or calamine lotion to relieve the itching.
Unfortunately, there is currently no vaccine available for scarlet fever. Contracting the disease provides immunity to the toxin responsible for causing its symptoms. To prevent group A strep infection, practicing proper hand hygiene and following basic hygiene protocols is crucial.
Children diagnosed with scarlet fever should not attend nursery or school until the first day after introducing the antibiotic. After 24 hours of antibiotic therapy, the child stops infecting other people.
Early detection of scarlet fever is essential because although it is not as dangerous as it used to be, it can cause many serious complications, such as:
One of the most common complications is a throat abscess. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing, trismus![]() (when the jaw muscles are so tense that you cannot open your mouth), and fever. It may result in the need for antibiotic therapy or even incision of the abscess.
(when the jaw muscles are so tense that you cannot open your mouth), and fever. It may result in the need for antibiotic therapy or even incision of the abscess.
Untreated scarlet fever can also lead to ear infections![]() . Symptoms then include ear pain, hearing problems, and fever. This is usually treated with antibiotics.
. Symptoms then include ear pain, hearing problems, and fever. This is usually treated with antibiotics.
Another complication of untreated scarlet fever is rheumatic fever. It causes arthritis (painful joints), heart pain, and mobility problems. This is a hazardous complication because it can result in severe heart damage.
Scarlet fever is one of the most common diseases in children. Unlike most of them, you can get sick from it many times. Re-infection of a child or adult occurs due to contact with streptococcus, which produces a different toxin.
During primary infection, antibodies against a specific toxin are produced. Subsequent contact with precisely the same bacteria will not cause disease. However, it should be remembered that streptococci can have various toxins. Therefore, exposure to bacteria that produce a different toxin may trigger the disease to develop again.
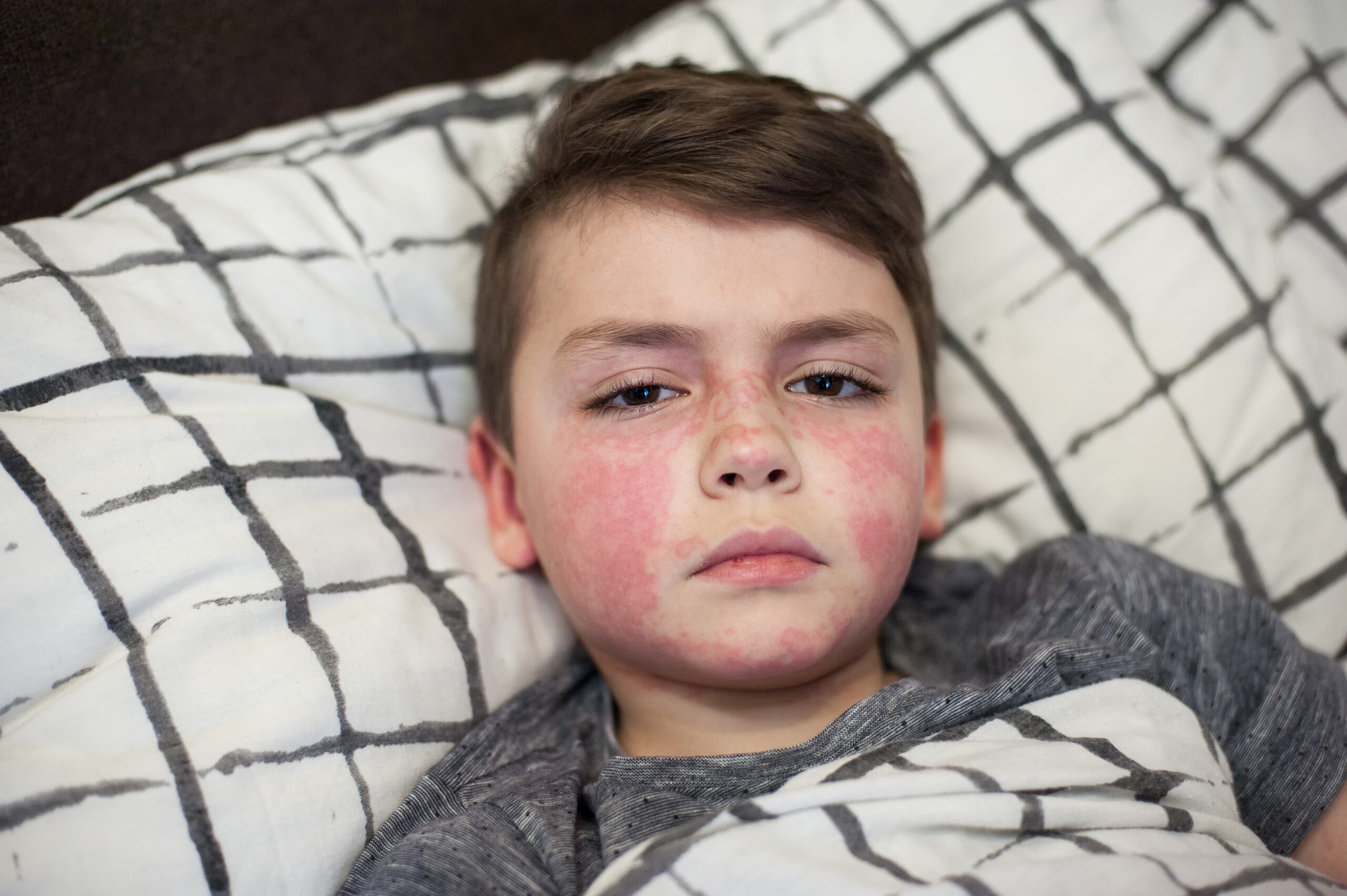
Many diseases may resemble scarlet fever in some aspects. One of them is Kawasaki disease![]() . It attacks blood vessels, and the associated symptoms may affect various tissues and organs. Enlarged lymph nodes, a rash resembling scarlet fever with subsequent skin peeling, fever, and a “strawberry tongue” are observed. The initial symptom is usually conjunctivitis, which does not occur with scarlet fever. Another symptom that helps distinguish between these two diseases is severe redness of the skin around the mouth.
. It attacks blood vessels, and the associated symptoms may affect various tissues and organs. Enlarged lymph nodes, a rash resembling scarlet fever with subsequent skin peeling, fever, and a “strawberry tongue” are observed. The initial symptom is usually conjunctivitis, which does not occur with scarlet fever. Another symptom that helps distinguish between these two diseases is severe redness of the skin around the mouth.
Scarlet fever in children should also be differentiated from three-day fever, rubella, and mononucleosis. Mononucleosis also occurs with a high fever that lasts much longer, as well as inflammation of the throat and enlarged lymph nodes. A less common mononucleosis symptom is a rash typical of scarlet fever.
A detailed question about the symptoms, as well as a throat swab to detect group A strep, enable the correct diagnosis to be made.
There is no evidence that scarlet fever harms pregnant women or causes fetal harm. The disease rarely occurs in adults. Pregnant women most often become infected with bacteria from their children who attend school or kindergarten.
If an infection is detected in one of the children, another person should be entrusted with caring for the sick child to reduce the risk of infecting the pregnant woman. It is also necessary to wash your hands frequently.
The appearance of symptoms of the disease in a pregnant woman requires a visit to a doctor.
Antibiotics![]() are then used, considered safe for the developing baby, and do not threaten pregnancy. Scarlet fever is an infectious disease that may go away without any treatment. However, experts suggest using an antibiotic due to its ability to minimize symptom duration, lessen complication risks, and cut down on bacterial spread within a day of starting therapy.
are then used, considered safe for the developing baby, and do not threaten pregnancy. Scarlet fever is an infectious disease that may go away without any treatment. However, experts suggest using an antibiotic due to its ability to minimize symptom duration, lessen complication risks, and cut down on bacterial spread within a day of starting therapy.
If you or your child experience symptoms of the disease, it's important to reach out to your doctor right away. Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic, and taking it exactly as prescribed is crucial. Taking antibacterial medication can help prevent complications and reduce the length of the infection.
Additionally, you can take a few steps to alleviate symptoms and enhance your or your child's well-being. These include:
If you or your child show signs of scarlet fever, such as a high temperature, rash, white coating on the tongue, or a very red tongue, it's important to contact a doctor. It's also crucial to contact a healthcare professional if you feel unwell and have been in contact with someone with scarlet fever. Additionally, if the symptoms persist after a week of starting treatment and consulting with your doctor, you should contact your GP again.
Another situation in which contact with a medical professional is necessary is when you become ill again after recovering from scarlet fever. This may be a sign of complication development, such as rheumatoid fever.
Remember that the disease is contagious, so call your doctor before visiting them. This can help arrange your appointment in a way that protects others from getting infected.
Table of Contents
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that affects the throat and tonsils. Around 11 million people are infected with this… read more »

Kawasaki disease is a systemic disease that mainly affects young children and causes inflammation of the walls of blood vessels.… read more »

Diaper rash is when little kids and babies sometimes get a rash from wearing nappies if their skin is wet… read more »

Tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease caused by viruses or a bacterium responsible for strep throat. It commonly affects children, but… read more »

The muscles of the tongue are entirely located inside the buccal cavity. Moreover, separated from upgrading our gustatory recognition, it… read more »

Rubella is an infectious disease caused by a specific type of virus. It is most commonly diagnosed in children. Find… read more »
Pathogens are disease-causing germs. They can include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and worms. How are they spreading? What diseases do… read more »

Discover Sore Throat Remedies for quick and effective pain relief. Many herbs and foods have healing properties. Learn how to… read more »

Antibiotics are drugs used for a variety of ailments. Learn about the most common side effects of antibiotics and how… read more »