A pediatrician's primary responsibility is to diagnose and treat diseases in children and adolescents. However, their duties go beyond that. They must continually monitor a child's development by ordering and interpreting tests, administering vaccinations, and diagnosing developmental disorders. It is crucial for a pediatric specialist to offer guidance to parents on child and infant care and disease prevention.
Moreover, this doctor must possess the right character traits – liking children, communicating effectively with them, showing patience, and responding appropriately when a young patient is uncooperative. This relationship differs significantly from interactions with adults. Sensitivity and intuition are also essential in this profession because a child may not always be able to articulate their symptoms.

A pediatrician and family doctor's tasks within primary care are carrying out the so-called health balance sheets. The specialists recommend that a health assessment be carried out at the age of![]() :
:
During a health assessment![]() , a doctor will:
, a doctor will:
You should always see a pediatrician if you are concerned about any symptoms of illness in your child, in particular:
Finding the right pediatrician might not be easy. In any case, be prepared that the search for a pediatrician will take you some time, so start it before the birth. Start with your local clinic – and maybe a miracle will happen. It turns out that it employs an excellent doctor, who all mothers in the area praise. But it's better not to go there yourself – visiting a place where many sick people visit every day is not recommended in advanced pregnancy.
Ask someone close to you for help. Let them find out what kind of pediatrician they see and collect opinions about them from mothers waiting in front of the office. Ask your friends. Maybe they have their own pediatrician and are satisfied with them.
You can also look for help on regional internet forums – mothers often exchange experiences this way and recommend specific specialists. You are no longer restricted to your area, so consider pediatricians across the city, but think about travel logistics. Private pediatricians are also an option to explore.
Extensive knowledge is necessary, but in the case of pediatrics, an appropriate approach to the child plays an essential role. Children in the doctor's office often cry, are moody and uncooperative. Force and coercion are certainly not good ways to convince a baby that there is nothing to be afraid of. On the contrary, they only arouse more stress and resistance so that the next time, the child may start protesting before going to the doctor.
A good pediatrician will be characterized by patience, kindness, gentleness, and intuition because a little patient cannot always describe what is wrong with them. It is also worth paying attention to the appearance of the office. It is best if it is pleasant for children – colorful with decorations that will appeal to little patients. Many doctors also arrange a small corner with toys in their office, where the child can sit and play while their parents talk to the doctor. All this helps alleviate the child's stress and encourages them to visit the pediatrician further.

You cannot feel embarrassed in the office. It is better to avoid doctors who create a formal atmosphere, react impatiently to your probing questions, and those who make you feel rushed. The visit should not last less than 15–20 minutes. During this time, the pediatrician should provide comprehensive information about the baby's health condition, clarify all doubts, and inform you how and when to administer medications.
A pediatrician does not necessarily need to be a professor, but having experience and staying updated with current knowledge is significant. You can look for signs of this in their office, like completion certificates of relevant training. However, the real measure of their competence will be their ability to provide successful treatment. If your child is still unwell after a week of medication and the pediatrician seems dismissive, it may be wise to seek another opinion. Do the same if you need to confirm each of their diagnoses with a different doctor or keep prescribing the same medications.
Toddlers often start getting sick at night. Therefore, contact with a doctor must be possible 24 hours a day. The pediatrician should not only provide you with telephone numbers at which they will be available (cell, home, or work) but also encourage you to call them at any time if necessary. And if they travel often, they should also give you the telephone numbers of other doctors who can cover for them.
The distance to the doctor is also significant. If you don't have a car, check whether the doctor will be able to get to you if necessary, or whether you can call a taxi to get to the office. And of course – how much will you pay for a home visit?
If you don't have a car, check if the doctor can make home visits or if you can easily access the office by taxi if needed. Also, consider the cost of home visits.
The first check-up visit to the pediatrician, also known as a patronage visit![]() , typically occurs within the baby's first six weeks. This visit can be scheduled at the medical center where the child was born or at the clinic where the parents registered their baby. During the patronage visit, the doctor inspects the newborn, evaluates their physical and neurological development, checks for jaundice by observing its skin color, examines the fontanelle, and conducts a hip dysplasia assessment, which may involve ordering a hip joint ultrasound.
, typically occurs within the baby's first six weeks. This visit can be scheduled at the medical center where the child was born or at the clinic where the parents registered their baby. During the patronage visit, the doctor inspects the newborn, evaluates their physical and neurological development, checks for jaundice by observing its skin color, examines the fontanelle, and conducts a hip dysplasia assessment, which may involve ordering a hip joint ultrasound.
The doctor also records the child's weight, body length, and head circumference measurements. During the visit, the doctor also offers guidance on child care, vaccinations, and recommended health check-ups.
The patronage visit plays a crucial role in promptly identifying any developmental abnormalities in the baby. It is the foundation for immediate intervention and treatment if any issues are detected.
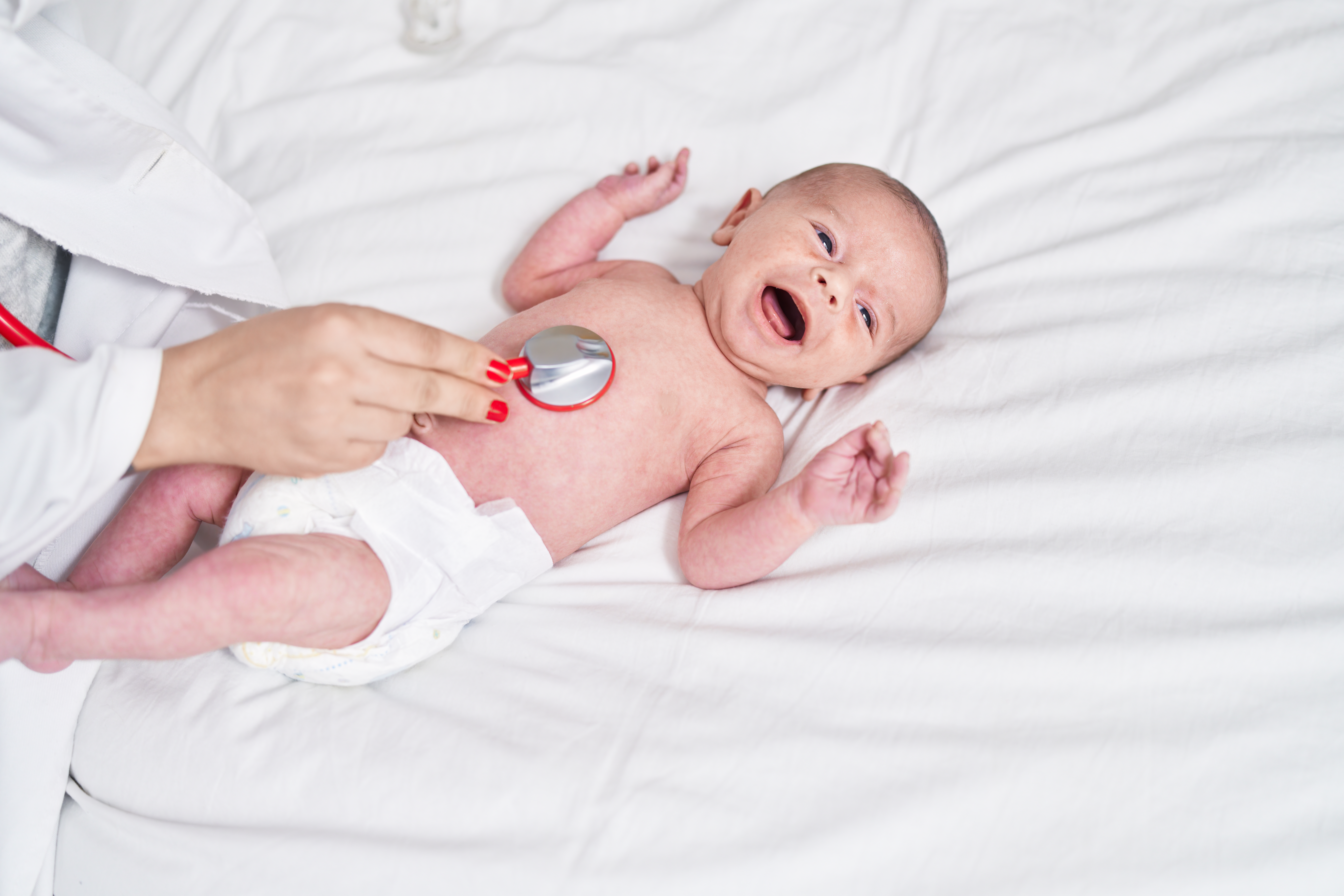
A follow-up visit to a pediatrician is intended to check whether the newborn's adaptation to extrauterine life is progressing properly. The pediatrician assesses the child's health, checks the effectiveness of feeding and care, and discusses the vaccination plan with the parents. The visit should be between the first and fourth weeks of the baby's life.
Ensuring a comprehensive newborn assessment is the foundation of every well-baby visit. It is crucial because a baby's body works differently during the first few weeks of life. Consequently, it is challenging to evaluate the health of a newborn using the same standards that we apply to older children. Some subtle signs may go unnoticed by parents who are not well-versed in newborn care. A baby's body, still adjusting to life outside the womb, has limited capacity to react to stimuli, making it less adept at regulating temperature, hunger, and thirst. A newborn may not run a fever even when experiencing an infection, cry despite hunger, or awaken despite thirst.
A professional assessment of the baby's well-being by a pediatrician or midwife allows for quick detection of abnormalities or symptoms of illness and immediate reaction.
Observation of the child's and parents' behavior is the first and most valuable assessment of the psychosomatic well-being of the entire family. Then the doctor becomes acquainted with the child's perinatal documentation, i.e., the discharge letter from the neonatal ward, the health booklet, and the vaccination card. You sometimes need to go back to the course of pregnancy and the mother's documentation. It is worth preparing the necessary documents in advance.
The pediatrician then starts examining the child. They check their response to stimuli, appearance, and skin color. They also evaluate the firmness of the skull bones, the size of the soft spots on their head, and their tension. Measuring the head circumference is an important part of the assessment. The doctor then examines the reaction to light, the external ear canals, and the nostrils. As part of the throat examination, they check the sucking reflex by inserting a gloved finger into the child's mouth and assessing the palate for any cleft signs. The neck, collarbones, and armpits are also examined for enlarged lymph nodes, which might appear after tuberculosis vaccination but should not be painful or red.
The pediatrician listens to the newborn's heart, lungs, and abdomen. They also examine the abdomen by gently pressing to check for pain or bloating. It is crucial to inspect the diaper area to evaluate the normality of the genital organs, the anal area, and the skin. The pediatrician should guide proper care for the intimate areas of both girls and boys. With the diaper removed, the hip joints are also examined. Next, newborn reflexes and muscle tone should be assessed.
If the examination shows no significant deviations, the final stage is the body weight and gain assessment. If the baby is gaining properly, assessing the effectiveness of feeding is a formality. However, the technique, efficiency, and feeding frequency should be carefully monitored if the weight gain is too low.
The last significant element of the patronage is the discussion of vaccinations. The doctor notifies parents about vaccinations applicable.
The patronage visit should end with an entry in the health book, which will serve as a reference point for subsequent periodic assessments of the baby's health.
Please book a patronage visit with a doctor and midwife after your child is discharged. Notify the primary care clinic you have selected by submitting a completed declaration of your chosen doctor, nurse, and midwife, either electronically or in paper form.
This visit presents a great opportunity to discuss with a midwife and pediatrician about caring for your child, their development, and feeding. The medical staff will try to dispel the parents' doubts in their new life situation.
During the visit, it is worth showing the process of feeding the baby. This way, you can get practical tips on lactation and feeding the newborn. In case of problems with feeding and lactation, the mother may be referred to a lactation clinic.
During the patronage visit, Parents will be guided on newborn care, vitamin administration, bathing, and umbilical cord care. Discussing vaccinations with your doctor, including mandatory and recommended vaccines, is also essential.
You do not need to prepare specially for a visit to the pediatrician. Remember to dress your baby warmly when going outside (in the first weeks of life, the baby has not yet developed proper immunity) and to take all documentation received in the hospital ward after birth.
Preparing for a care visit with a midwife and a pediatrician is a key element in ensuring effective health care for the newborn and support for the parents. Although you should not stress about them additionally, it is worth thinking about all the questions you would like to ask the midwife or doctor before your patronage visit.