An itchy scalp is a tiring symptom that makes everyday life difficult. An unpleasant and persistent feeling forces you to constantly scratch a given place. It is all because the sensory receptors that cause itching have been irritated. They then transmit information to the brain. The organ processes the data and sends a warning signal, manifesting as an itchy scalp.
The causes![]() of itchy scalp
of itchy scalp![]() are diverse – from improper care to various types of diseases:
are diverse – from improper care to various types of diseases:
If itching of the scalp persists for a long time and is accompanied by disturbing skin symptoms (including seborrhea, scalp flaking, redness, papules, or pustules), you should immediately consult a specialist. If the cause of the itchy scalp is a dermatological disease, they require professional treatment. Below is an overview of the most popular health problems that cause scalp itching.

Seborrheic dermatitis![]() is a chronic and recurrent condition. This skin inflammation affects areas where sebaceous glands are accumulated, such as the scalp, chest, and back. The causes, apart from excessive work of the sebaceous glands, include the accumulation of fungi of the Malassezia genus (as in the case of dandruff) and the incorrect process of epidermal cell renewal, leading to accelerated keratinization.
is a chronic and recurrent condition. This skin inflammation affects areas where sebaceous glands are accumulated, such as the scalp, chest, and back. The causes, apart from excessive work of the sebaceous glands, include the accumulation of fungi of the Malassezia genus (as in the case of dandruff) and the incorrect process of epidermal cell renewal, leading to accelerated keratinization.
The appearance of erythematous and exfoliative lesions in a given area can diagnose seborrheic dermatitis. The disease manifests with skin redness, peeling off the epidermis, and twitching. Factors like stress or sweat may intensify the urge to scratch. An itchy scalp and scratching the irritated area can lead to thinning of the hair on the head.
Seborrheic dermatitis is treated primarily with shampoos and antifungal medications. Usually, a few weeks of treatment at home allows you to control the disease on the scalp. To prevent recurrence of the disease, it is recommended to use these measures prophylactically. Moreover, because seborrheic dermatitis can result from an inappropriate diet, it is worth looking closely at what we eat and modifying our diet.
Psoriasis![]() is a chronic, autoimmune inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by specific skin changes resulting from excessive keratinization of the epidermis. Fungi of the genus Malassezia also cause the skin condition to deteriorate.
is a chronic, autoimmune inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by specific skin changes resulting from excessive keratinization of the epidermis. Fungi of the genus Malassezia also cause the skin condition to deteriorate.
The disease is related to the improper functioning of the immune system. The normal process of producing subsequent layers of skin takes 28 days. New cells are created, mature, and die during this time, exfoliating naturally. When we suffer from psoriasis, our immune system sends a signal to work much earlier, which shortens the entire process to a few days. Then, new cells develop very fast, and the old ones cannot keep up with the epidermis peeling. It generates a thick layer of dead cells to form on the body in the formation of scales.
The primary symptom of psoriasis is red, scaled, scratchy inflammatory patches on the skin. Moreover, there are lesions covered with silvery scales. Eventually, the scales fall off in thin flakes, revealing the shiny surface of the skin.
Psoriasis is often confused with dandruff, but they are separate, independent diseases. Lesions can be observed all over the body (mainly on the elbows, knees, hands, feet, and torso), but they also often appear on the scalp. Characteristic places are the hairline above the forehead, the skin behind the ears, and the back of the neck.
We still cannot heal this condition. Moreover, it tends to go into remission. For this reason, treatment mainly involves alleviating the symptoms of psoriasis. Specialists suggest using products that allow the removal of the excess layer of scales and prevent the excessive production of new epidermal cells. This effect is achieved by salicylic acid and urea used in medicinal dermo-cosmetics, as well as ichthyol, which additionally relieves itchy scalp.
You cannot forget about intensively moisturizing and greasing the scalp, which will prevent micro-damage to the skin. During treatment, many people also use antifungal and antibacterial shampoos. Importantly, using appropriate cosmetics helps soothe active changes. Moreover, it has a prophylactic effect, prolongs the periods between disease relapses, and alleviates their course.
Dandruff![]() is a small-scale flaking of the epidermis of the scalp. The symptoms are caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, which naturally lives on the scalp. When appropriate conditions exist for its multiplication, it causes dandruff.
is a small-scale flaking of the epidermis of the scalp. The symptoms are caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, which naturally lives on the scalp. When appropriate conditions exist for its multiplication, it causes dandruff.
The Malassezia fungus![]() is a lipophilic species, which means it uses the lipids in human sebum as an energy source for growth. During the breakdown of triglycerides, metabolites irritate the epidermis and cause inflammation. It accelerates the exfoliation of dead layers of the epidermis. Then, white scales appear on the scalp and fall off like flakes.
is a lipophilic species, which means it uses the lipids in human sebum as an energy source for growth. During the breakdown of triglycerides, metabolites irritate the epidermis and cause inflammation. It accelerates the exfoliation of dead layers of the epidermis. Then, white scales appear on the scalp and fall off like flakes.

Dandruff is a recurrent disease. It is based on various endogenous (internal) factors, such as hormonal disorders or genetic predispositions. Other causes include lifestyle issues, including excessive and long-term stress, alcohol abuse, and an incorrect diet. Dandruff may also occur due to exogenous (external) factors, such as:
Once you detect dandruff, it is usually enough to conduct home treatment with an anti-dandruff shampoo. Choosing products containing active substances with antifungal and keratolytic properties is best. It is also worth choosing cosmetics that soothe itchy scalp and moisturize the irritated scalp.
It is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory skin disease. It manifests with severe itching and the characteristic appearance of the resulting lesions. It usually has an allergic origin, but genetic factors also influence its occurrence. The cause of this disease may also be the proliferation of fungi of the Malassezia species. It is a condition commonly identified in children but can also manifest in adults. The condition can last a lifetime, but the disorder disappears by school age in most circumstances.
Atopy leads to excessive production of immunoglobulin E (IgE) and the development of an immediate-type allergic reaction in response to and contact with a minimal amount of an allergen, often commonly found in the environment. In the skin of people with atopic dermatitis, the metabolism of epidermal lipids is also disturbed, which leads to an abnormal structure of the hydrolipid coat.
In atopic dermatitis![]() , the skin becomes dry, rough and itchy. Redness, little lumps, and thickened scales appear on the head. For this reason, preventing the development of atopic dermatitis symptoms is based on proper skin care. It means frequent body moisturizing with specialized dermatological products that do not contain potentially irritating or sensitizing substances. It is worth avoiding long, hot baths. Use towels and clothes made of soft, natural materials. They reduce the risk of skin irritation and abrasion. You should also pay attention to using household chemicals that are free of allergenic agents.
, the skin becomes dry, rough and itchy. Redness, little lumps, and thickened scales appear on the head. For this reason, preventing the development of atopic dermatitis symptoms is based on proper skin care. It means frequent body moisturizing with specialized dermatological products that do not contain potentially irritating or sensitizing substances. It is worth avoiding long, hot baths. Use towels and clothes made of soft, natural materials. They reduce the risk of skin irritation and abrasion. You should also pay attention to using household chemicals that are free of allergenic agents.
Lice![]() is a disease caused by human lice – an arthropod that feeds on human blood. There are three types of the disease – head lice, clothing lice, and pubic lice.
is a disease caused by human lice – an arthropod that feeds on human blood. There are three types of the disease – head lice, clothing lice, and pubic lice.
Head lice and clothing lice are spread mainly through close, direct contact with an infected person and pubic lice – through sexual contact. Head lice can also be spread by sharing combs, brushes, headgear, or hair accessories. The disease spreads easily in nurseries, kindergartens, and schools, facilitated by children's typical behavior and play. Head lice, unlike clothing lice, are not directly related to poor hygiene.
Symptoms of lice are the result of bites from the parasite. The skin is severely itchy. Skin eruptions also appear in papules, erythema, or urticaria. In the case of head lice, lesions are present on the scalp, behind the ears, and on the back of the neck. Sometimes, the disease also affects eyebrows, eyelashes, and facial hair. Due to scratching, the lesions may ooze and become crusted or become infected with bacteria. Lice eggs (nits) can also be seen on the hair of an infected person. Live individuals are harder to spot.
To get rid of an itchy scalp, you must always find the cause of the problem and focus on removing it. If you observe disturbing symptoms that may suggest that you suffer from health problems, consult your doctor and start appropriate treatment![]() .
.
Usually, however, itchy scalp can also be remedied with methods that can be successfully applied at home. It mainly happens in the case of ailments caused by improper head care. However, regularity and preventive actions are necessary here. It is the only way to get rid of the problem and avoid its recurrence.
If cosmetics caused the problem, you should look closer at your cosmetics bag. In the case of an itchy scalp, the substances contained in the shampoo may be too intense or chemical and cause an allergic reaction, so if the problem started after changing the product, it is better to return to the previous cosmetic.

An exemplary way to soothe irritated skin is to choose a gentle cleanser. It should also be noted that the conditioner is intended to condition the hair, not the scalp. For this reason, it is not worth applying it at the roots but only along the length of the strand. It is also particularly significant to rinse the cosmetics thoroughly. Avoid hot and hard water because it dries out the hair. Instead, rinse your hair with cool water.
You should always choose the type of cosmetics according to your scalp and hair type needs. We will use different products for dry and damaged hair, and oily hair will require different ones.
It is also worth taking care of your lifestyle![]() , e.g., diet. Vitamin A stimulates hair follicles to grow. In case of its deficiency, the hair becomes dry, brittle, and susceptible to split ends. Scalp changes may also occur, including hyperkeratosis, manifested by thickening and calluses on the scalp's surface.
, e.g., diet. Vitamin A stimulates hair follicles to grow. In case of its deficiency, the hair becomes dry, brittle, and susceptible to split ends. Scalp changes may also occur, including hyperkeratosis, manifested by thickening and calluses on the scalp's surface.
Vitamin C improves circulation in the scalp and, as a strong antioxidant, prevents the damaging effects of free radicals generated by, among others, stress and environmental pollution. Vitamin C deficiency does not cause direct hair loss but worsens the functioning of the hair bulbs, where the protein keratin is produced – an extremely important building block of hair. Vitamin C deficiency disturbs the production of keratin proteins, which causes their defective structure and, consequently, hair brittleness and splitting.
Vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), and B6 (pyridoxine) play an essential role in the production of amino acids – the building blocks of hair. They partake in energy production procedures, thanks to which the reproductive cells of the hair matrix can start the hair shaft growth.
Vitamin B7 (biotin) can gather sulfur molecules replenished with food and transport it to the hair-building matrix. Strong and flexible bonds are created in the matrix between sulfur molecules, which connect the hair shaft along its entire length. Even slight biotin deficiencies cause hair loss. In addition, vitamin B7 normalizes fat metabolism, which prevents seborrhea and dandruff.
The most significant microelements responsible for the hair condition include zinc, copper, and iron. Zinc deficiency causes skin hyperkeratosis and increases hair loss. Copper deficiency causes structural changes in the hair and discolors it, and too little iron in women causes baldness.
The human organism consists of up to 60% water – about 20% of which is in the skin. Water largely determines the proper functioning of the skin and the protective barrier of the epidermis – if it is damaged, the risk of recurrence of dandruff increases, and the skin begins to itch and flake. Water penetrates the epidermis from the dermis based on the difference in osmotic concentration (it is “pushed” towards the outer layers), then continuously evaporates. If the barrier is damaged, the skin dries out faster. That's why it's so important to replenish its reserves from the inside. Drink 2 liters of water a day.
Proper protection of the scalp is also critical. Frost, heat, and dry air deteriorate the condition of the scalp. Therefore, you should protect yourself from the sun's rays in summer and from low temperatures in winter by wearing a hat.
If a disease causes an itchy scalp, it should be treated to alleviate or eliminate it. Then, specialists recommend the use of pharmacological agents. Medications for itchy scalp can be used topically and systemically.
Table of Contents

Lice are ectoparasites, so they live outside the body of their host, in this case the human. What symptoms do… read more »
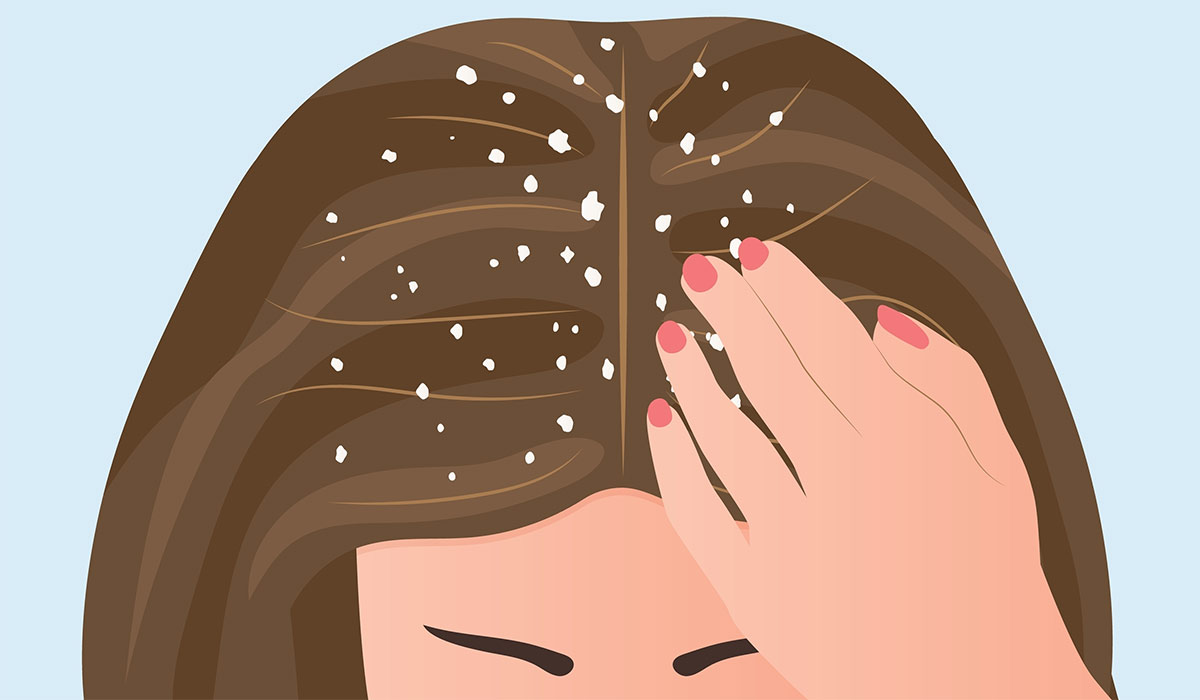

Dandruff is the result of excessive skin exfoliation, overproduction of sebum, or the presence of Malassezia yeast on the skin.… read more »
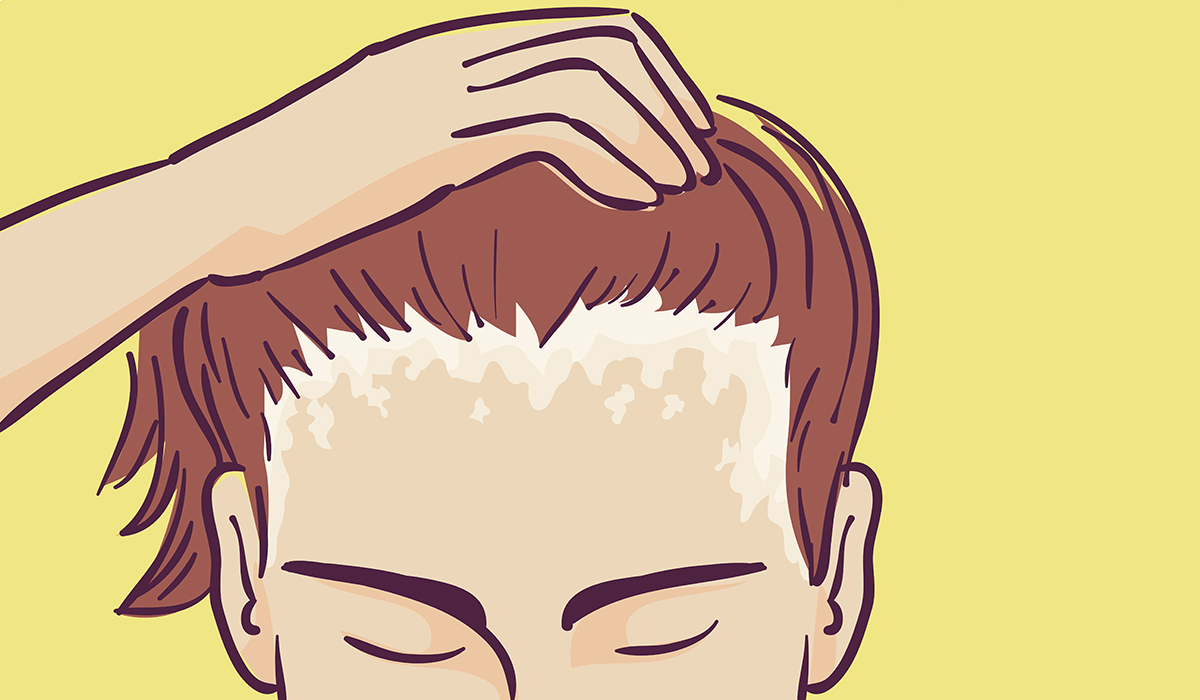

Dry scalp is a condition characterized by the scalp skin becoming dry, irritated, and flaky. It often results in itching… read more »
Eczema flare-ups are usually related to specific triggers. Learning how to avoid specific to your eczema triggers, can be a… read more »
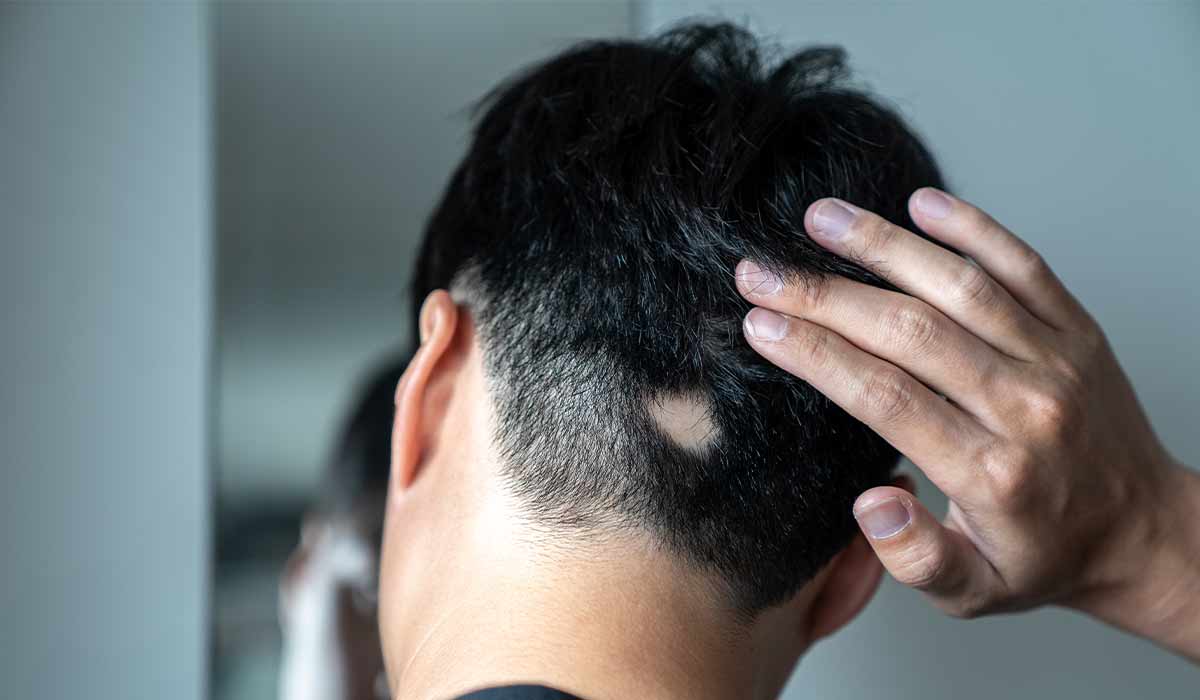

Alopecia is a disease that manifests itself in various ways, including thinning or loss of hair. What are the causes… read more »

Psoriasis is characterized primarily by skin lesions that result from impaired epidermal regeneration. Learn about all types and signs of… read more »

The term typhus encompasses three main types of typhus – epidemic typhus, endemic typhus, and scrub typhus. Each one of… read more »
Folliculitis is a skin disease that appears very often. What are its causes and symptoms? What is the treatment for… read more »

Itchy skin, or pruritus, is a bothersome feeling that encourages you to scratch. This itchiness acts more like a sign… read more »