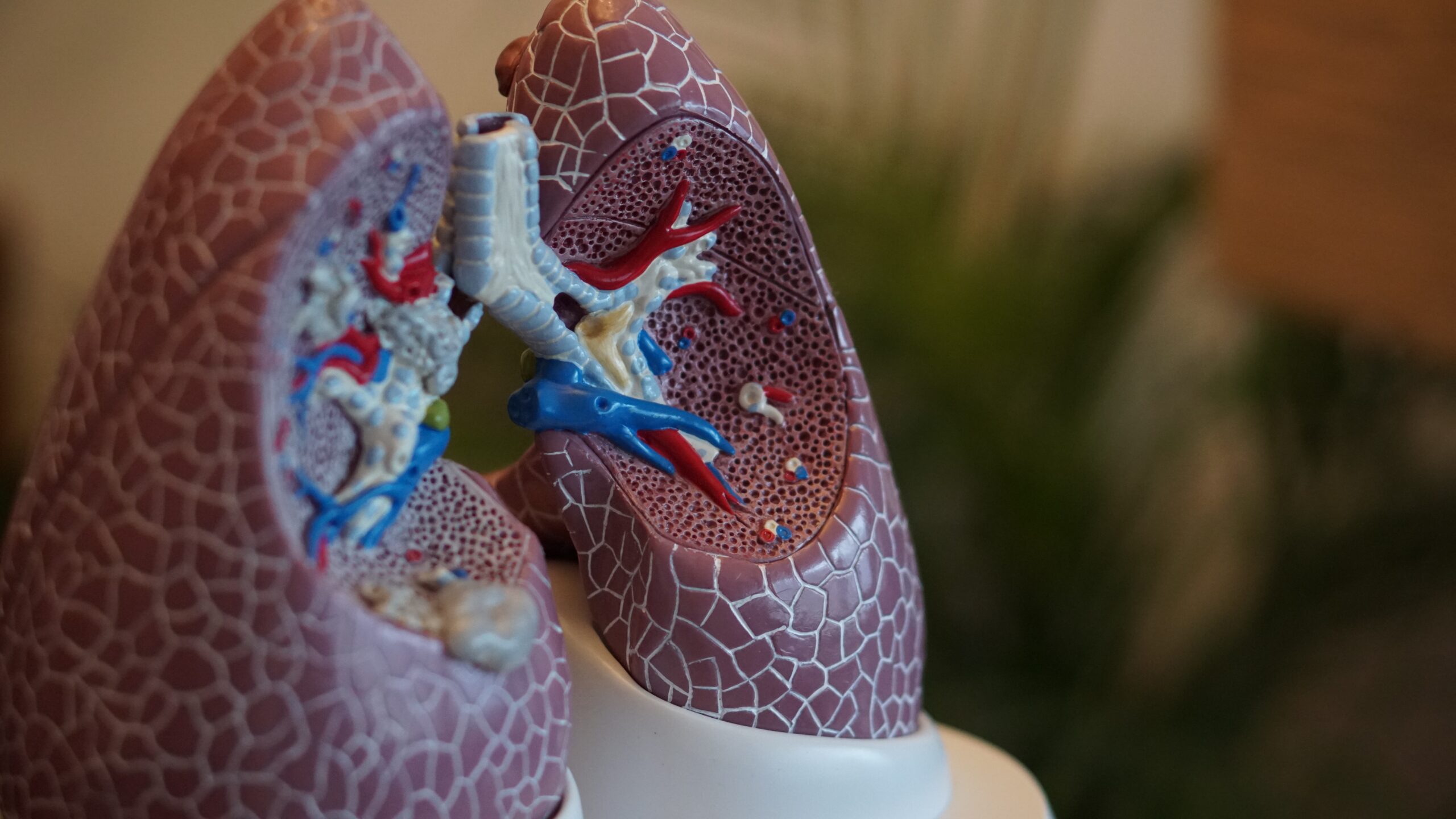
Atelectasis is a lung condition in which parts of the alveoli, tiny air sacks in the lung, lose air. When it develops, oxygen levels in the bloodstream decrease, affecting the ability to breathe.
To breathe in and out correctly, lungs must have the ability to inflate and deflate. But if there is a pressure on the lungs or something blocks the airways, they can't perform their functions as they should, which may result in atelectasis.
Continue reading to learn more about atelectasis, including its two types: obstructive and non-obstructive atelectasis.
Causes of atelectasis are different for obstructive and non-obstructive atelectasis. Obstructive atelectasis![]() occurs due to a blocked airway, while non-obstructive atelectasis develops due to pressure from outside the lung.
occurs due to a blocked airway, while non-obstructive atelectasis develops due to pressure from outside the lung.
When airways get blocked, air can't get to the alveoli, leading to the collapse of the lung and the development of atelectasis. It can have various causes, including:
Surgeries, particularly procedures that prevent you from coughing, are the most common cause of mucus plug. Moreover, some drugs ordered after surgery may cause weak breathing, making mucus more likely to accumulate in the airways. This is why healthcare specialists perform lung suctioning to get rid of the build-up. But in some cases, the mucus may still accumulate, leading to atelectasis.
Atelectasis that does not lead to blocked airways is referred to as non-obstructive atelectasis![]() . The causes of this type of atelectasis include surgery, pneumothorax, injury, pleural effusion, chest tumor, lung scarring, and surfactant deficiency.
. The causes of this type of atelectasis include surgery, pneumothorax, injury, pleural effusion, chest tumor, lung scarring, and surfactant deficiency.
Surgeries that may lead to non-obstructive atelectasis often require from the patients to:
These factors may make an individual's breath weak and less likely to cough, which increases the risk of non-obstructive atelectasis. The inability to breathe deeply and cough may cause parts of the alveoli to collapse. Because of that, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional before the procedure to learn how to reduce the risk of developing atelectasis after the surgery.
Pneumothorax, also known as collapsed lung, is a condition sometimes confused with atelectasis. It develops when the air enters the pleural space (space around the lungs). Some of its characteristic symptoms include low blood pressure, anxiety, fatigue, stabbing pain in the chest, and shortness of breath.
Pneumothorax is similar to pleural effusion because it also blocks the airways. However, while fluid is responsible for blockage in pleural effusion, pneumothorax involves a build-up of air. This may lead to lung collapse and the development of atelectasis.
Like pneumothorax, pleural effusion may cause atelectasis due to the build-up in the pleural cavity, a space between two thin membranes surrounding the lungs. These two structures are typically very close to each other but can be separated when the air accumulates in the space between them. As a result, pleural effusion may result in non-obstructive atelectasis and the following symptoms:
Chest tumors and growths that put pressure on the lung may cause non-obstructive atelectasis. This happens because tumors can force the air out of the alveoli and deflate them.
Also referred to as pulmonary fibrosis, lung scarring is a lung disease that causes respiratory problems such as difficulty breathing and coughing when alveoli become damaged. Lung scarring usually develops due to infections and prolonged exposure to irritants such as smoke or toxins.
Alveoli can stay open thanks to a substance called surfactant. If there is not enough of it, alveoli can collapse, potentially leading to atelectasis. Surfactant deficiency![]() is most often observed in infants.
is most often observed in infants.
Some people are more likely to develop atelectasis than others. Factors that increase the risk of this condition include the following:

The number of issues and severity of symptoms caused by atelectasis vary from person to person. How an individual experiences it depends on how much of the lung is affected, how fast it progresses, and whether complications have developed.
The following symptoms are the most likely to appear in a typical case of atelectasis:
Atelectasis that affects a lot of alveoli may cause low blood oxygen and lead to the following symptoms:
If pneumonia develops as a complication of atelectasis, you may also experience these health issues:

While atelectasis is not a severe health condition, it may lead to several serious complications. Some of the most often observed include the following:
Diagnosis of atelectasis encompasses physical examination, medical history review, lung diseases and surges, and tests. If your doctor suspects a lung condition after the initial assessment, they may order the following tests:
In rare cases, atelectasis requires a surgical removal of a small lung area. Healthcare professionals recommend it as a last resort if other treatment strategies are unsuccessful or if there is permanent lung scarring. In other scenarios, treatment usually involves one or a combination of the following therapies and procedures:
Damage caused by atelectasis is usually reversible![]() once the cause is identified and treated. Most people don't develop severe complications and recover quickly. However, individuals who are struggling with chronic atelectasis may require further treatment and management strategies to relieve the symptoms.
once the cause is identified and treated. Most people don't develop severe complications and recover quickly. However, individuals who are struggling with chronic atelectasis may require further treatment and management strategies to relieve the symptoms.
It is possible to reduce the risk of lung conditions, including atelectasis, by following a healthy lifestyle and applying good practices for general health. Here are some ideas that would particularly benefit people with atelectasis:
It's important to note that these general recommendations can only help you reduce the risk of developing lung conditions or manage their symptoms better. Still, they can't replace conventional treatment strategies. Remember to always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice based on your medical history and current health status. If you experience symptoms of atelectasis, such as difficulty breathing or chest pain, seek medical as soon as possible.
Atelectasis is a lung condition characterized by the partial collapse of alveoli, leading to decreased oxygen levels in the bloodstream and affected breathing. There are two types of atelectasis: obstructive and non-obstructive.
Obstructive atelectasis results from blocked airways, often caused by tumors, foreign bodies, or mucus plugs. Non-obstructive atelectasis occurs due to external pressure on the lung and can result from various causes, including surgery, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, chest tumors, lung scarring, and surfactant deficiency.
Symptoms range from coughing, shallow breathing, and chest pain to more severe issues like fever, rapid heart rate, and low blood oxygen levels. Complications may include pneumonia, respiratory failure, and bronchiectasis.
Treatment options include chest physiotherapy, incentive spirometry, bronchodilators, oxygen therapy, airway suction, and addressing underlying conditions like pneumonia or tumors. Surgical intervention is rare and considered a last resort.