Cryotherapy, or cryo stimulation, is a stimulus, short (1-5 minutes) application of very low temperatures (from -35⁰C to -195⁰C) to the surface of the whole body or its fragment. Such stimulation triggers beneficial physiological changes in the body. Cold has many effects:
It is significant to consult with a specialist before undergoing cryotherapy. The most common indications for cryotherapy![]() are:
are:
Cold therapy has a beneficial effect![]() on the above ailments – due to the effect of therapeutic cold. These are:
on the above ailments – due to the effect of therapeutic cold. These are:
The use of cryotherapy in rehabilitation and biological regeneration has contributed to a significant improvement in health among people using it. This only confirms the growing benefits of using low temperatures.
The result of effectively reducing the unpleasant sensations associated with injuries by applying cold is well known. Cryostimulation therapy takes advantage of the fact that when exposed to extremely low temperatures, nociceptors (sensitive pain receptors) experience a functional shutdown, which also inhibits their connections with proprioceptors. Furthermore, the intense conditions of the therapy slow down the transmission of impulses through sensory neurons![]() .
.
Cryogenic temperatures also affect the muscles![]() , which during stimulation reduce their tension – by slowing down neuronal transmission and limiting the excitability of peripheral nerve endings. Interestingly, muscle tissue after cryotherapy significantly increases its strength, and the therapy itself is safe for it – the activity of creatine kinase remains unchanged.
, which during stimulation reduce their tension – by slowing down neuronal transmission and limiting the excitability of peripheral nerve endings. Interestingly, muscle tissue after cryotherapy significantly increases its strength, and the therapy itself is safe for it – the activity of creatine kinase remains unchanged.
Low temperatures have a two-pronged anti-inflammatory effect![]() . Firstly, they reduce biochemical markers of inflammation read from the blood (levels of CRP proteins, fibrinogen, immunoglobulins, and pro-inflammatory interleukins). They also regulate the oxidative economy and inhibit the release of lysosomal enzymes from the body's cells.
. Firstly, they reduce biochemical markers of inflammation read from the blood (levels of CRP proteins, fibrinogen, immunoglobulins, and pro-inflammatory interleukins). They also regulate the oxidative economy and inhibit the release of lysosomal enzymes from the body's cells.
The first systemic treatment with the use of cold causes an imbalance in the antioxidant-prooxidant balance, but each subsequent session leads to adaptive changes in the body. The activity of antioxidant proteins is increased, as a result of which the plasma copes better with free radicals and markers of oxidative stress![]() decrease. This effect is used as protection for the body during high physical exertion and as support for anti-inflammatory processes.
decrease. This effect is used as protection for the body during high physical exertion and as support for anti-inflammatory processes.
Cryostimulation has a strong effect on microcirculation![]() . This is because the precapillary sphincters of the skin contract, which returns oxygenated blood to the large veins and the right ventricle of the heart muscle. Once the small vessels expand, there is an increased blood supply to the body's tissues, which brings along oxygen and nutrients to the organs.
. This is because the precapillary sphincters of the skin contract, which returns oxygenated blood to the large veins and the right ventricle of the heart muscle. Once the small vessels expand, there is an increased blood supply to the body's tissues, which brings along oxygen and nutrients to the organs.
Currently, science does not have reports confirming the importance of systemic cryotherapy for large blood circulation. However, that pacing does not affect the rhythm of work and myocardial ischemia or blood pressure. Cryostimulation treatments allow for the reduction of the concentration of LDL cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein; “bad cholesterol”) in the blood plasma, and, interestingly, increase the amount of HDL fraction (high-density lipoprotein; “good cholesterol”).
Whole-body cryotherapy treatments increase the length of time in the physical effort that the body can undertake. It also has a positive effect on the strength and anaerobic capacity of skeletal muscles. This relationship is often used in sports![]() – especially when speed or strength is required.
– especially when speed or strength is required.
Local cryotherapy used in periarticular edema![]() supports capillary blood filtration. Lowering the temperature to cryogenic levels can enhance the movement of lymph in the lymphatic vessels, which are responsible for draining the spaces between cells. This is achieved by improving the openness of the vessels.
supports capillary blood filtration. Lowering the temperature to cryogenic levels can enhance the movement of lymph in the lymphatic vessels, which are responsible for draining the spaces between cells. This is achieved by improving the openness of the vessels.
Systemic cryotherapy![]() involves applying temperatures below -100⁰C to the entire human body for 1 to 3 minutes. The treatment takes place in a cabin filled with liquid nitrogen. The patient needs to keep walking during the procedure. It is recommended to repeat sessions daily for 10-15 days.
involves applying temperatures below -100⁰C to the entire human body for 1 to 3 minutes. The treatment takes place in a cabin filled with liquid nitrogen. The patient needs to keep walking during the procedure. It is recommended to repeat sessions daily for 10-15 days.
Local cryostimulation![]() is a treatment only within the area of pain. To perform the procedure, the medical worker tilts the cryotherapy device towards the part of the body to be treated and then stimulates the area with cold gas from a distance of 15-30 cm. The procedure is short – it lasts up to 5 minutes, and during it, you feel only cold – there is no pain. Local stimulation is usually repeated once a day for 10-20 days.
is a treatment only within the area of pain. To perform the procedure, the medical worker tilts the cryotherapy device towards the part of the body to be treated and then stimulates the area with cold gas from a distance of 15-30 cm. The procedure is short – it lasts up to 5 minutes, and during it, you feel only cold – there is no pain. Local stimulation is usually repeated once a day for 10-20 days.
The most popular and cheapest form of cryotherapy is cold baths![]() . As with exposure to cold air, cool water causes an immediate decrease in skin temperature and vasoconstriction, which in turn can lead to less muscle soreness and faster recovery after training. The body's response to a cold bath will vary depending on whether it is a cold shower after a sauna, swimming, or swimming in cold water.
. As with exposure to cold air, cool water causes an immediate decrease in skin temperature and vasoconstriction, which in turn can lead to less muscle soreness and faster recovery after training. The body's response to a cold bath will vary depending on whether it is a cold shower after a sauna, swimming, or swimming in cold water.
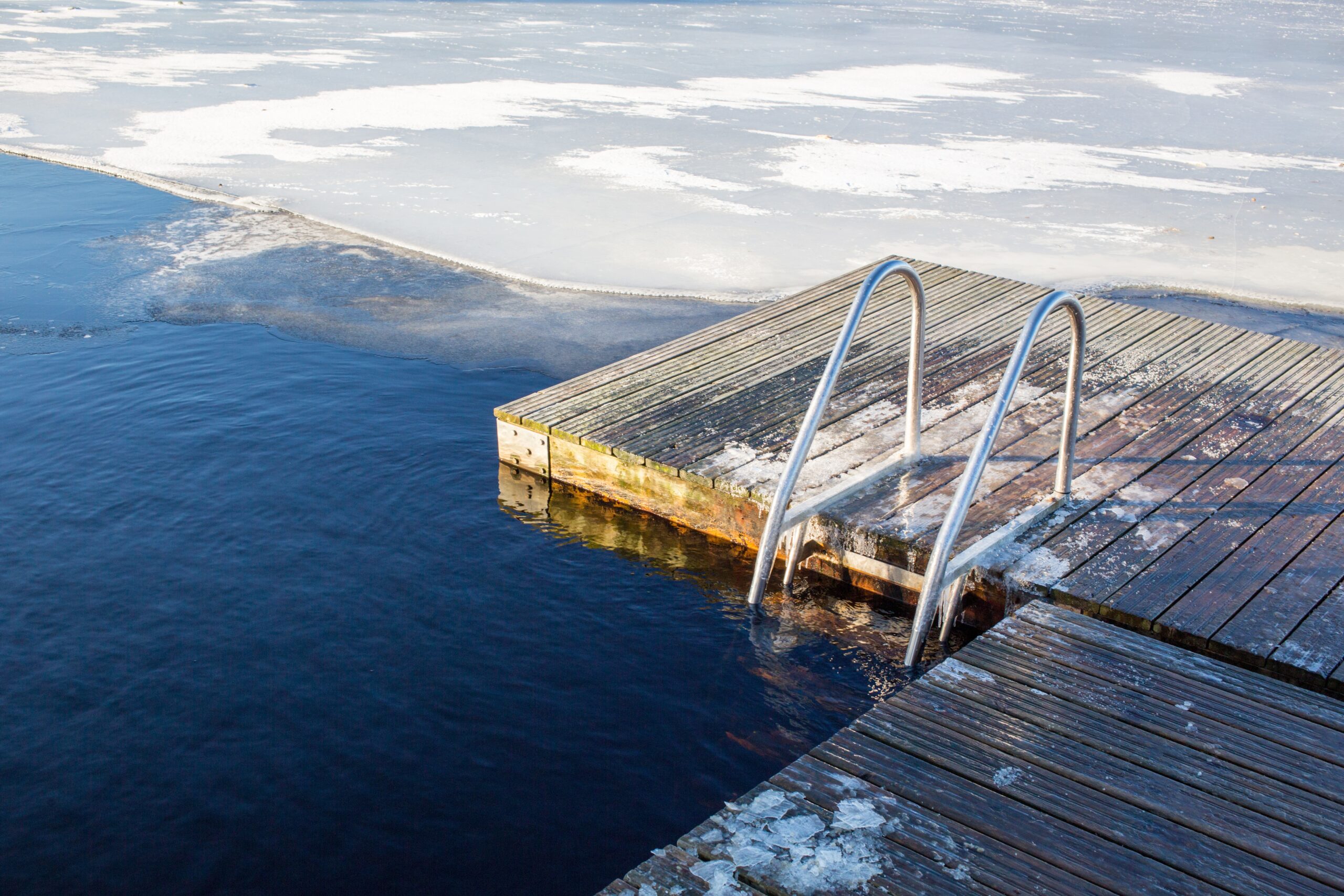

However, when using cold baths, one must not forget about the rapid cooling of the body and the increased risk of hypothermia. There is not enough strong evidence to support the use of cold baths, similar to dry cryotherapy. Despite common beliefs, cold baths do not significantly enhance immune response or stimulate the production of leukocytes.
Cryostimulation is often used in:
The treatments allow for a faster return to fitness after injuries and surgeries![]() , reduce pain after intense physical exercise and accelerate recovery, also improve the appearance of the skin – improving microcirculation makes the skin radiant and cellulite disappears.
, reduce pain after intense physical exercise and accelerate recovery, also improve the appearance of the skin – improving microcirculation makes the skin radiant and cellulite disappears.
The use of cold therapy is especially worth considering in the case of people who suffer from diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Pathological conditions within soft and hard tissues, rheumatoid arthritis, and metabolic and neuromuscular syndromes are special indications for the use of treatments. Quick pain relief will allow a patient to improve their daily functioning.
If you are experiencing mood disorders![]() , anxiety, or chronic stress, cryostimulation may be a beneficial option to consider. The body's constant movement can cause chronic inflammation, but cold therapy can help alleviate this issue. Scientists have documented the beneficial effect of cryotherapy on the psyche – it helps to fall asleep and maintain sleep, relaxes, improves mood, and reduces tiredness and fatigue.
, anxiety, or chronic stress, cryostimulation may be a beneficial option to consider. The body's constant movement can cause chronic inflammation, but cold therapy can help alleviate this issue. Scientists have documented the beneficial effect of cryotherapy on the psyche – it helps to fall asleep and maintain sleep, relaxes, improves mood, and reduces tiredness and fatigue.

Treatments using a cryo chamber, thanks to the ability to regulate the oxidative economy, rejuvenate, support the removal of toxic metabolic products from the body, reduce cellulite, facilitate fat loss, and firm the skin.
While cryotherapy has many benefits for the body, it is not advisable for all patients. There are some contraindications to cryotherapy![]() treatments. These include, among others:
treatments. These include, among others:
The decision whether a person will be admitted to the procedure is made each time by the doctor. Then, the parameters of the method and the type of kinesitherapy are individually selected. Before cryotherapy, the patient's arterial blood pressure is measured and recorded on the treatment card.
Depending on the indications, cryotherapy can be referred by, among others: a neurologist, rheumatologist, doctor specializing in motor rehabilitation, orthopedist, or dermatologist. Before undergoing therapeutic cryotherapy, it is significant to consult with a doctor to ensure that there are no contraindications and to discuss the procedure in detail with the patient.
The patient undergoes the procedure in underwear or a swimsuit![]() . The parts of the body most sensitive to cold must be correctly covered and protected:
. The parts of the body most sensitive to cold must be correctly covered and protected:
To ensure the best results from a cryo chamber session, patients need to wash off any creams or lotions from the skin beforehand because they can interfere with the distribution of the low temperature. Additionally, before the procedure, it's necessary to remove outer clothing, jewelry, watches, and glasses. The body should also be dried in areas that are prone to sweating to prevent the risk of frostbite.

Before entering, physiotherapists provide patients with instructions on proper breathing techniques. This is crucial for safety, as extremely cold air can cause breathing difficulties due to increased volume in the alveoli. We recommend taking short breaths through the nose to warm the gases before they reach your lungs and exhaling slowly through the mouth.
After putting on appropriate protective clothing, the patient and the physiotherapist enter the vestibule of the chamber, where adaptation to low temperatures takes place. The temperature is approximately -60⁰C![]() and the residence time is 30 seconds. Then the patient begins to breathe according to the previously given instructions and goes to the appropriate cryo chamber. The patient has to walk slowly and repeatedly in the cryo chamber. It is important not to touch the skin during the procedure.
and the residence time is 30 seconds. Then the patient begins to breathe according to the previously given instructions and goes to the appropriate cryo chamber. The patient has to walk slowly and repeatedly in the cryo chamber. It is important not to touch the skin during the procedure.
The duration of the procedure and the temperature are determined by the doctor, taking into account the individual needs, capabilities, and resistance to cold of the patient. When the patients come out of the cryo-chamber, they are asked to put on sports clothes and exercise shoes. The next step is kinesitherapy![]() – treatment with movement under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
– treatment with movement under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
Cryotherapy is a comprehensive method supporting the treatment of diseases and ailments originating from the musculoskeletal system. High efficiency, low invasiveness, and easy accessibility mean that more and more people choose this type of help in rehabilitation. The use of physiological processes occurring in the body with cold stimulation reduces the risk of health complications.
Cryotherapy – price, number of treatments, and duration of treatment depend on the general health of the patient and the type of ailments. Usually, local cryotherapy is applied in the form of a series of treatments, and the frequency and duration of each treatment are determined by a doctor or physiotherapist. If the treatments bring the expected effect, it is worth repeating them after a few months to maintain the treatment effect.
Improperly used cold therapy can lead to local frostbite of the tissues. The most common complications of cryotherapy![]() are allergic reactions, burns, and intolerance/pain. There are also episodic cases of superficial neuropathy after applying ice to muscle fatigue and acute contusions. Although these types of cold shocks are temporary, they can last from a few hours to several months.
are allergic reactions, burns, and intolerance/pain. There are also episodic cases of superficial neuropathy after applying ice to muscle fatigue and acute contusions. Although these types of cold shocks are temporary, they can last from a few hours to several months.
Cryotherapy, despite its high popularity and easy availability, is not the only and necessary method in the treatment of muscle pain or injury. There is still no hard scientific evidence confirming the effectiveness of this type of practice, and it is currently discouraged to use ice on fresh injuries, as it can lead to slower tissue healing. After a lot of physical effort, to reduce the level of markers of tissue reaction to stress (skeletal troponins or keratin kinase) or to reduce the subsequent DOMS pain (delayed onset muscle soreness), warm baths at a temperature of approx. 38⁰C work much better than cold.
Table of Contents

Moles are common skin moles that can be harmless or indicative of disease. Read the article and increase your knowledge… read more »

Trigger finger is a condition that impairs daily functioning. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms.… read more »

Lipoma, made from fat tissue and regularly called a fatty lump, ordinarily feels delicate once you touch it. Take note… read more »
Warts are skin lesions resulting from infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). What are the symptoms? What is the diagnosis… read more »
Muscle strain occurs when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn. This can happen due to excessive force, overuse, or sudden… read more »

A common cold is a set of symptoms associated with inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose, throat and… read more »

Liposuction is a surgical procedure with the goal of getting rid of excess fat. Learn about the indications and contraindications… read more »

Cold feet are usually harmless symptoms caused by the body's reaction. However, it can also be a warning sign that… read more »
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat joint problems. When is it done? What to… read more »