Trigger finger is characterized by difficulty bending and straightening a finger, most commonly the thumb, ring finger, and little finger. It is a chronic condition that affects one or more tendons in the hand.
The state makes daily functioning much more complicated since, in addition to pain, tenderness, and difficulty in doing movements, the biggest problem is the limitation of hand function.
The causes of the condition are not fully known. It may be a congenital disability, a slip-limiting nodular thickening of the flexor tendons. Typical symptoms of snapping and crackling in the fingers result from reduced space in the tendon sheath caused by inflammation. Treatment of snapping fingers depends on the level of the lesions.
Trigger finger is a disease of the musculoskeletal system characterized by inflammation of the synovial membrane and tendon sheath![]() . It can affect one or more fingers at the same time. The leading cause of snapping fingers is repetitive strain and micro-injury of the tendons of the fingers' superficial and deep flexor muscles. These tendons are located in the tendon sheath, which holds the tendons in place and facilitates their sliding. Persistent inflammation causes constriction, tightening of the sheaths, and thickening of the flexor tendons, which causes them to slide more difficulty during finger movement and causes pain, stiffness of the joint, and the jumping feeling described by patients.
. It can affect one or more fingers at the same time. The leading cause of snapping fingers is repetitive strain and micro-injury of the tendons of the fingers' superficial and deep flexor muscles. These tendons are located in the tendon sheath, which holds the tendons in place and facilitates their sliding. Persistent inflammation causes constriction, tightening of the sheaths, and thickening of the flexor tendons, which causes them to slide more difficulty during finger movement and causes pain, stiffness of the joint, and the jumping feeling described by patients.

Causes of trigger finger include:
Overload – The primary cause of the trigger finger is repetitive strain caused by performing repetitive hand movements. Repetitive strain occurs when tendons and muscles are excessively used, leading to fatigue, pain, and possible injury. As a result, trigger finger commonly affects individuals whose occupation or hobby involves precise hand movements and continuous manual labor.
Diseases – Trigger finger can develop due to certain diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation that affects joints and various organs. Its most characteristic symptom is pain and swelling in the joints of the hands and feet, but inflammation can also affect other joints. Joint disease is also associated with diabetes. It is probably due to a change in the structure of collagen, the main component of tendons, which binds to glucose. Joint changes are often the cause of persistent pain and can also impair mobility.
Injuries – Trigger finger can also occur due to trauma to the hand, such as a contusion or fracture of the fingers, or by injuries to the flexor muscles. The flexor muscles of the upper limb include all the muscles that flex the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and phalanges. Muscle and tendon pain that does not go away for the long term may be a symptom of muscle damage. Such injuries are common, especially in athletes and people who insufficiently warm up before exercise or do dynamic and sudden movements.
Trigger finger is characterized by pain and a distinctive snap when bending or straightening the finger. While it primarily affects the ring finger and thumb, it can impact any finger. It's more prevalent in the right hand and tends to affect the dominant hand more frequently. The snapping sensation can make everyday tasks like writing, buttoning shirts, unlocking doors, or driving challenging.
Symptoms of trigger finger include:

Chronic finger pain – The main symptom is pain in the finger area when bending, causing tenderness![]() in the hand. The pain is usually experienced in the morning after a night of little movement. This discomfort makes it difficult to flex and extend the fingers.
in the hand. The pain is usually experienced in the morning after a night of little movement. This discomfort makes it difficult to flex and extend the fingers.
Finger stiffness – Stiffness![]() in the finger joints can be particularly intense in the morning, causing limited mobility and pain. This may be accompanied by difficulty straightening the fingers and a distinct snapping sound. Often, the patient has to untangle the snapping finger with the other hand. In advanced conditions, complete contracture of the finger may occur.
in the finger joints can be particularly intense in the morning, causing limited mobility and pain. This may be accompanied by difficulty straightening the fingers and a distinct snapping sound. Often, the patient has to untangle the snapping finger with the other hand. In advanced conditions, complete contracture of the finger may occur.
Finger snapping feeling – Squeaking and clicking![]() the finger during bending is also a characteristic symptom. Inflammation of the tendon of the fingers of the hand causes a reduction in the space in the tendon sheath and increased friction between the tendons. It generates a problem with flexion and extension of the fingers, and the characteristic sound of the tendon skipping against the tendon is described by patients as a snapping, crackling sound.
the finger during bending is also a characteristic symptom. Inflammation of the tendon of the fingers of the hand causes a reduction in the space in the tendon sheath and increased friction between the tendons. It generates a problem with flexion and extension of the fingers, and the characteristic sound of the tendon skipping against the tendon is described by patients as a snapping, crackling sound.
Lumpy finger – In the trigger finger, a palpable small lump![]() may appear near the base of the affected finger. Nodules on the hands are often the result of osteoarthritis. It does not necessarily mean that you have acquired a severe condition. A common abnormality is Heberden's and Bouchard's nodules, which should be distinguished from a nodule caused by a trigger finger.
may appear near the base of the affected finger. Nodules on the hands are often the result of osteoarthritis. It does not necessarily mean that you have acquired a severe condition. A common abnormality is Heberden's and Bouchard's nodules, which should be distinguished from a nodule caused by a trigger finger.
Swelling of the finger – Inflammation can cause characteristic symptoms. One of them is swelling![]() , which may be accompanied by skin redness. Swollen toe joints are an unpleasant condition that can also result from fluid accumulation or a reaction to excess salt in the body.
, which may be accompanied by skin redness. Swollen toe joints are an unpleasant condition that can also result from fluid accumulation or a reaction to excess salt in the body.
Redness of the finger – The sign is associated with long-term inflammation. Inflammation of the finger gives characteristic symptoms like redness, limited mobility, and increased skin temperature within the inflamed area. In addition to this, the erythema may be caused by local irritation.
Trigger finger is diagnosed based on the history and the symptoms the patient reports. Sometimes, additional tests are used to confirm the diagnosis.
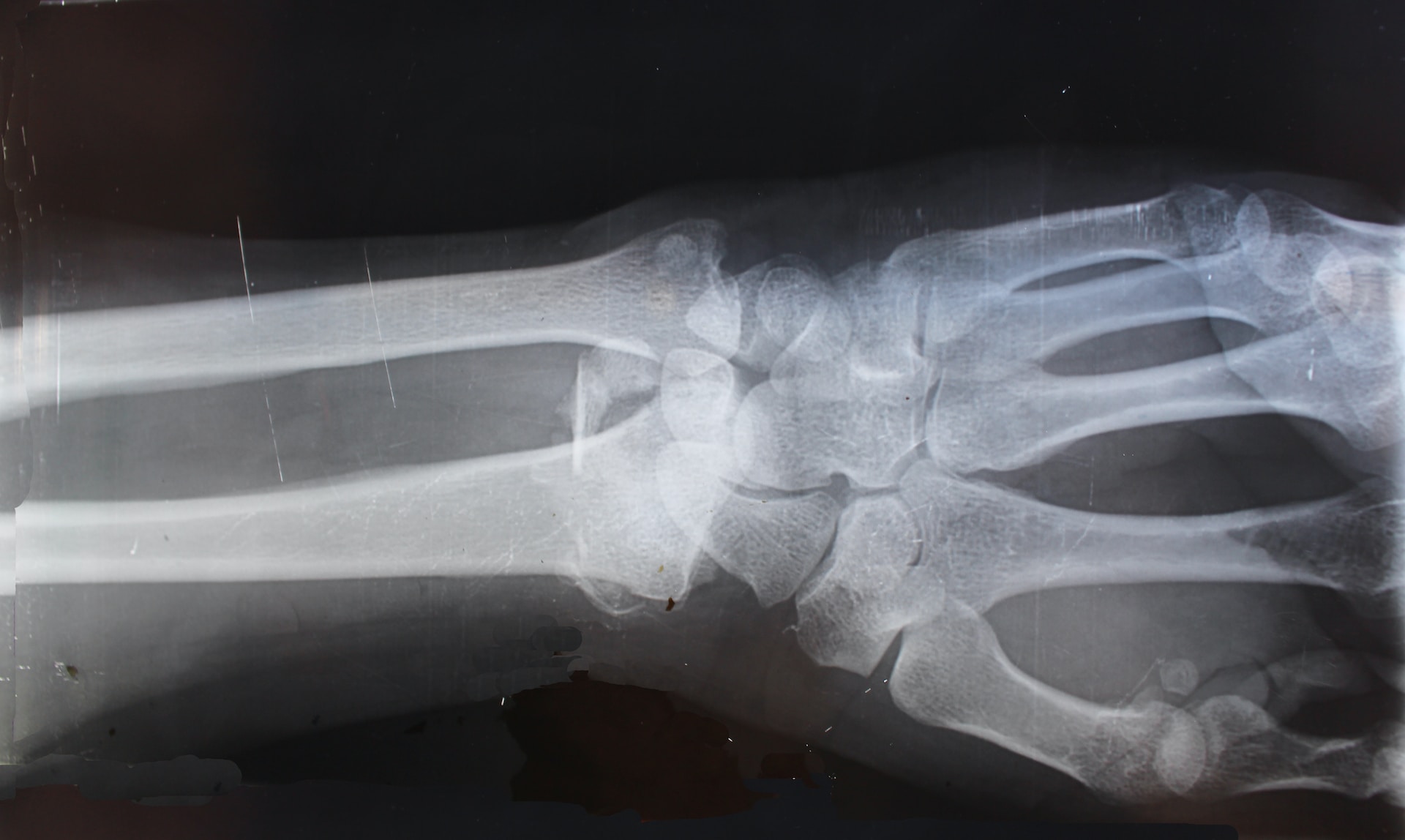
Examinations – An ultrasound is used, which images the inflamed tendon and the exact location of the area causing the patient's discomfort. In the case of past injuries and fractures, it is advisable to take an X-ray to localize the site of the problem.
Symptoms and differentiation for symptoms originating in the thumb are significant. Thumb trigger finger is an affliction affecting the tendons of the hand's first finger. However, a cracked thumb can sometimes be confused with de Quervain's syndrome![]() .
.
De Quervain's syndrome – Is an inflammation of the extensor and extensor tendons of the thumb![]() . The trigger thumb, in this case, will cause pain with the movement of bending the wrist of the wrist to the side. The trigger finger is treated similarly to what de Querwain's syndrome mentioned earlier, but the location of the problem is different. Sometimes, both disease entities co-occur. Recognizing the proper place of the problem is crucial to the effectiveness of the treatment procedures carried out.
. The trigger thumb, in this case, will cause pain with the movement of bending the wrist of the wrist to the side. The trigger finger is treated similarly to what de Querwain's syndrome mentioned earlier, but the location of the problem is different. Sometimes, both disease entities co-occur. Recognizing the proper place of the problem is crucial to the effectiveness of the treatment procedures carried out.
Treatment of the trigger finger varies depending on its severity and duration. Various therapies used for trigger finger affliction include:
Anti-inflammatory drugs – In the initial stages, treatment consists of anti-inflammatory agents![]() , namely NSAIDs. Various types of drugs can be used, including pills and ointments. However, it should be noted that home treatment applied to a snapping finger in the form of generally available salves or poultices will not ensure getting rid of the problem, and postponing professional help may only exacerbate it. Untreated snapping finger causes the finger to become blocked and permanently stiffens the joint.
, namely NSAIDs. Various types of drugs can be used, including pills and ointments. However, it should be noted that home treatment applied to a snapping finger in the form of generally available salves or poultices will not ensure getting rid of the problem, and postponing professional help may only exacerbate it. Untreated snapping finger causes the finger to become blocked and permanently stiffens the joint.
Rehabilitation – It is adjusted on a case-by-case basis. Rest is recommended. Patients should avoid work that requires repetitive and prolonged manual activities until symptoms resolve. In addition, physiotherapy has very effective anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving treatments to offer. There are various physiotherapy methods![]() used to treat trigger fingers. Physiotherapy treatments for trigger fingers reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
used to treat trigger fingers. Physiotherapy treatments for trigger fingers reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
Steroid injections – Steroid injections![]() are a highly effective treatment for tendon sheath inflammation. By injecting therapeutic substances directly into the affected muscle, such as corticosteroids and local anesthetics like m****************e acetate, lidocaine, or b*********e, inflammation can be reduced and tissue regeneration stimulated. These injections are often combined with physical therapy treatments for optimal results.
are a highly effective treatment for tendon sheath inflammation. By injecting therapeutic substances directly into the affected muscle, such as corticosteroids and local anesthetics like m****************e acetate, lidocaine, or b*********e, inflammation can be reduced and tissue regeneration stimulated. These injections are often combined with physical therapy treatments for optimal results.
Orthoses – To ease discomfort, it is recommended to wear the correct orthosis that keeps the finger properly aligned. Wearing a splint helps relieve pressure on the tendon and commonly involves keeping the finger upright. However, this approach is no longer used due to the risk of finger stiffness and unsatisfactory outcomes.
Surgery – Surgery becomes necessary in more severe cases of snapping finger where conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. Studies have shown that surgical interventions![]() on the affected tendon sheaths and tendons yield the highest success rates. Fortunately, there are now minimally invasive techniques available that effectively treat the condition, allowing for a quick return to full hand function. During surgery, the inflamed tendon sheath is carefully cut to restore normal finger movement. It's important to note, however, that not everyone is a suitable candidate for surgical treatment of snapping finger. Contraindications for the procedure include systemic infections, skin lesions, cardiac arrhythmias, unregulated hypertension, and inflammation of soft tissues.
on the affected tendon sheaths and tendons yield the highest success rates. Fortunately, there are now minimally invasive techniques available that effectively treat the condition, allowing for a quick return to full hand function. During surgery, the inflamed tendon sheath is carefully cut to restore normal finger movement. It's important to note, however, that not everyone is a suitable candidate for surgical treatment of snapping finger. Contraindications for the procedure include systemic infections, skin lesions, cardiac arrhythmias, unregulated hypertension, and inflammation of soft tissues.

Rehabilitation of the trigger finger is the basis of treatment. It includes various methods adapted depending on the case. Rehabilitation is also essential in post-surgical patients. Then, its task is mainly to relax tense tissues, make the incision scar more flexible, and strengthen muscles. A physiotherapist can also give tips on preventing the recurrence of ailments by modifying the workstation and daily habits. Rehabilitation methods used for trigger finger include:
Kinesitherapy, or properly selected exercises![]() for the snapping finger, is helpful. They mainly do gentle passive, active-passive, and general mobility exercises. Their task is primarily to increase the range of motion in the hand, stretch the hand and forearm muscles, and relax the entire upper limb. Massage and rubbing of the painful tendon relieve pain by congestion and better nutrition of the tissues.
for the snapping finger, is helpful. They mainly do gentle passive, active-passive, and general mobility exercises. Their task is primarily to increase the range of motion in the hand, stretch the hand and forearm muscles, and relax the entire upper limb. Massage and rubbing of the painful tendon relieve pain by congestion and better nutrition of the tissues.
Topical cryotherapy![]() is a treatment that utilizes a specialized device to produce liquid nitrogen vapor. It is commonly used to alleviate pain in arthritic joints or bruised muscles. During the initial stage of local cryotherapy, blood vessels and tissues contract rapidly, followed by rapid dilation and increased blood circulation. While cryotherapy is generally safe, it may not be suitable for everyone. It is important to inform your healthcare specialist about any existing medical conditions before undergoing this therapy.
is a treatment that utilizes a specialized device to produce liquid nitrogen vapor. It is commonly used to alleviate pain in arthritic joints or bruised muscles. During the initial stage of local cryotherapy, blood vessels and tissues contract rapidly, followed by rapid dilation and increased blood circulation. While cryotherapy is generally safe, it may not be suitable for everyone. It is important to inform your healthcare specialist about any existing medical conditions before undergoing this therapy.
Ultrasound therapy![]() is a treatment that uses ultrasound waves to penetrate the skin and reach deeper structures in the body. Its primary goals are to provide pain relief and stimulate cellular repair processes by inducing different physiological responses, both thermal and athermal. In physical therapy, a stationary ultrasound machine is used as the source of ultrasound waves.
is a treatment that uses ultrasound waves to penetrate the skin and reach deeper structures in the body. Its primary goals are to provide pain relief and stimulate cellular repair processes by inducing different physiological responses, both thermal and athermal. In physical therapy, a stationary ultrasound machine is used as the source of ultrasound waves.
By setting the appropriate parameters and following proper treatment methodology, indications, and contraindications, therapists can effectively carry out this therapeutic procedure. While ultrasound therapy has several positive therapeutic effects, it's important to be aware of potential side effects as well.

Laser therapy refers to medical procedures that utilize specialized devices known as medical lasers. These lasers emit a focused beam of light in a single color, and they offer numerous therapeutic benefits. Laser therapy has been found to have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-edema effects. Additionally, it promotes healing and stimulates microcirculation. As a result, laser therapy is highly regarded for its ability to provide relief for both acute and chronic conditions.
Most commonly, a combination of various therapeutic procedures is used. The treatment can be used in children. However, it requires particular caution and adherence to all the processes involved in the course of escapement to laser light. The use of lasers in medicine and rehabilitation also has its contraindications. Among others, this method should not be used by pregnant women.
Shockwave therapy![]() is a non-invasive physical therapy method that uses acoustic wave energy to treat medical conditions. The result of shock wave therapy is an analgesic effect, acceleration of tissue regeneration processes, intensification of collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis, i.e., creation of new blood vessels.
is a non-invasive physical therapy method that uses acoustic wave energy to treat medical conditions. The result of shock wave therapy is an analgesic effect, acceleration of tissue regeneration processes, intensification of collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis, i.e., creation of new blood vessels.
The advantage is the relatively short therapy, compared to other forms of treatment, which sometimes take several months. The result can most often be observed after the first treatment. Like each type of treatment, shock wave treatments can not be used for all patients. Furthermore, great caution should be exercised when treating people after heart attacks.
Magnet therapy is a commonly used physical therapy method. Use magnets to heal tissues by stimulating them with magnetic fields. The device for doing magnetotherapy is a magnetron. Magnetic field treatments help reduce pain and inflammation, reduce swelling, and accelerate healing. Without contraindications to magnetic field treatments and when the correct dose is set, the treatment has many measurable benefits. It mainly improves metabolism and shortens the recovery period and wound healing. Magnetic field treatment can be combined with many different rehabilitation methods.
If conservative treatments and injections have not been effective, surgery may be recommended by the doctor. Surgery is typically considered when the disease affects multiple fingers, the inflammation is chronic and persistent for several months, and the patient also has other conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. The surgical process![]() can be categorized based on different techniques used.
can be categorized based on different techniques used.

Open – A small incision is made near the base of the affected finger to perform the procedure. The surgeon carefully removes the constricted portion of the tendon sheath. This technique has been in practice for longer and may be preferred by surgeons because it provides better visibility during surgery.
Percutaneous – Percutaneous procedures are performed using local anesthesia. This involves inserting a needle into the affected area to separate the sheath from the tendon, allowing for smoother movement. This technique is less invasive and may be preferred by patients due to its shorter duration.
Following the process, rehabilitation![]() is necessary to promote healing and recovery. The primary goals of rehabilitation include relieving tissue tension, enhancing flexibility in the surgical scar, and strengthening muscles. In the initial phase, focus is placed on wound care and reducing pain, swelling, and inflammation. Subsequently, rehabilitation aims to restore full range of motion and functionality to the hand. This may involve incorporating physiotherapy treatments.
is necessary to promote healing and recovery. The primary goals of rehabilitation include relieving tissue tension, enhancing flexibility in the surgical scar, and strengthening muscles. In the initial phase, focus is placed on wound care and reducing pain, swelling, and inflammation. Subsequently, rehabilitation aims to restore full range of motion and functionality to the hand. This may involve incorporating physiotherapy treatments.
The likelihood of finger triggers is higher in certain groups at risk for this condition. Trigger finger is sometimes a problem for pregnant women, what with the increased effect of hormones. But the most significant threat is from diseases such as:

It is a autoimmune chronic disease that primarily affects the medium and small joints of the arms and legs, causing significant pain. The inflammation![]() targets not only the synovial membrane but also the surrounding areas like bursae and tendon sheaths. One of its main symptoms is symmetrical joint pain along with irreversible deformity changes, contractures, or even muscle atrophy.
targets not only the synovial membrane but also the surrounding areas like bursae and tendon sheaths. One of its main symptoms is symmetrical joint pain along with irreversible deformity changes, contractures, or even muscle atrophy.
The main treatment goal is to reach remission by suppressing symptoms, relieving discomfort, and temporarily halting disease progression. This approach helps prevent further joint damage and improves long-term functional outcomes for patients.
Diabetes is not just one disease; it encompasses a group of metabolic diseases that are characterized by chronic high blood sugar levels. Either insulin secretion disorders or dysfunction can cause this elevated blood sugar. The long-term consequences of this constant high blood sugar![]() include damage to nerves, blood vessels, and various organs. Musculoskeletal disorders in diabetes mellitus can vary depending on the type of diabetes, duration of the disease, average blood glucose levels, and the treatment used.
include damage to nerves, blood vessels, and various organs. Musculoskeletal disorders in diabetes mellitus can vary depending on the type of diabetes, duration of the disease, average blood glucose levels, and the treatment used.
These complications can also arise from other related conditions often seen with diabetes, such as lipid metabolism disorders, calcium-phosphate metabolism issues, obesity, and hypertension. Diagnosis of diabetes is typically based on fasting blood sugar tests that show higher than normal glucose levels. Treatment approaches for diabetes will depend on the specific type diagnosed.
Gout is arthritis caused by the deposition of sodium urate crystals in joint fluid and other tissues. The testimony of calcium urate crystals occurs because of elevated levels of the body's uric acid. An increase in uric acid concentration alone is not conclusive of the disease. The cause of hyperuricemia is excessive urate production or insufficient urate excretion in the urine.
Improper treatment of hyperuricemia can cause a chronic character of gout, in which deposited deposits cause the destruction of cartilage and bone epiphyses, leading to joint deformity and disability. Gout attacks can affect ankle joints, knee joints, upper limb joints, and, most commonly, the metatarsophalangeal joint of the 1st big toe.
Amyloidosis![]() is a chronic condition characterized by the buildup of insoluble proteins known as amyloid in various tissues of the body. The severity and scope of the disease can vary, with some cases affecting a single organ while others impact multiple tissues. The disease develops slowly over many years, and its early symptoms can be hard to notice.
is a chronic condition characterized by the buildup of insoluble proteins known as amyloid in various tissues of the body. The severity and scope of the disease can vary, with some cases affecting a single organ while others impact multiple tissues. The disease develops slowly over many years, and its early symptoms can be hard to notice.
The symptoms vary depending on the affected organs. Dialysis causes pain, swelling in joints, and carpal tunnel syndrome. In primary amyloidosis, the key treatment approach involves targeting and eliminating cells that produce antibody light chains.
It is a condition characterized by insufficient production of hormones, which are essential for the body's proper functioning. The symptoms of hypothyroidism arise from the inadequate stimulation of cells by these hormones. In many cases, symptoms may be mild, unnoticed, or have low severity.
Decreased levels of thyroid hormones![]() in the body can lead to a decline in muscle strength and flexibility, making patients hesitant to engage in physical exercise. This condition also accelerates muscle tissue breakdown. Treatment with l***********e is often necessary for most patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism.
in the body can lead to a decline in muscle strength and flexibility, making patients hesitant to engage in physical exercise. This condition also accelerates muscle tissue breakdown. Treatment with l***********e is often necessary for most patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism.
Carpal tunnel syndrome![]() falls under a category of conditions known as compression neuropathies, where pressure is exerted on peripheral nerves. The main signs of this state are pain in the wrist and numbness or tingling sensations in the hand.
falls under a category of conditions known as compression neuropathies, where pressure is exerted on peripheral nerves. The main signs of this state are pain in the wrist and numbness or tingling sensations in the hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome arises from swelling around the structures surrounding the median nerve, commonly due to prolonged strain caused by work activities. Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome doesn't always require surgery; it can involve pharmacological interventions combined with physiotherapy approaches.
It is a condition that causes the palmar tendon to scar, resulting in a flexion contracture of the fingers. While the exact causes of this disease are not fully understood, genetic factors and soft-tissue trauma or strain are often cited as possible contributors. The main symptom of Dupuytren's contracture![]() is restricted finger extension and limited mobility in the hand, which can significantly impact everyday activities. To improve finger extension and restore hand function, early management, and treatment are recommended before severe changes that significantly impair hand function.
is restricted finger extension and limited mobility in the hand, which can significantly impact everyday activities. To improve finger extension and restore hand function, early management, and treatment are recommended before severe changes that significantly impair hand function.
Trigger finger is a chronic condition that most commonly affects the thumb, ring finger, and little finger, leading to difficulty bending and straightening. This condition significantly complicates daily functioning by causing pain, tenderness, limited mobility, and hand function impairment. The exact causes of trigger finger are still not fully understood, but it could be attributed to congenital disabilities or nodular thickening of the flexor tendons. Snapping and crackling sensations in the fingers are typical symptoms, resulting from inflammation-induced reduced space in the tendon sheath.
To diagnose trigger finger, doctors rely on patient history and reported symptoms. Sometimes, additional tests are used for confirmation. Treatment options vary based on the severity and duration of symptoms. They can range from anti-inflammatory drugs to rehabilitation exercises, steroid injections, or surgery. There are certain groups at higher risk for developing trigger finger. Pregnant women may experience this condition due to increased hormonal effects; however, the most significant risk factor is underlying diseases or medical conditions.