Spondylosis is a pathological lesion involving bony and disc structures within the spine. The lesions affect the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, the cartilage and joint structures of the spine, and its ligamentous system. Due to dehydration, the intervertebral discs lose their elasticity and reduce their height. As a result of these changes, the spine loses its stability, which causes discopathy.
These changes can sometimes cause complications. Three types of spondylosis are categorized, and in addition to these, unspecified spondylosis of idiopathic origin is also distinguished. Spondylosis of the spine is a degeneration that develops as a result of the aging process following mechanical trauma or congenital disabilities. Various methods are observed in the mechanism of its formation. The symptoms of the disease cause severe pain and stiffness, making it difficult to function normally.
Spondylosis diagnoses include a detailed patient history, diagnostic tests, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Spondylosis treatment mainly consists of slowing down the development of degenerative changes, thus preventing irreversible damage to the spine. Therefore, diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential here. Pharmacotherapy and rehabilitation are used.
Spondylosis is a degenerative spinal disease that causes damage to the intervertebral cartilage and bone cartilage and changes in the shape of the spinal canal and intervertebral openings.
Spinal degeneration develops gradually. Spondylosis causes changes that result in pressure on the spinal nerves and spinal cord. One of the fastest-onset pathological changes is discopathy![]() . It causes degeneration of the intervertebral discs that protect the vertebrae from rubbing and subsequent degradation.
. It causes degeneration of the intervertebral discs that protect the vertebrae from rubbing and subsequent degradation.
Another pathological process is dehydration![]() , i.e., reduced ability to bind water molecules. Thus, this condition causes a loss of elasticity and the ability of tissues to regenerate. Spondylosis lesions cause processes such as a decrease in the cross-sectional area of the spinal canal and narrowing of the intervertebral openings.
, i.e., reduced ability to bind water molecules. Thus, this condition causes a loss of elasticity and the ability of tissues to regenerate. Spondylosis lesions cause processes such as a decrease in the cross-sectional area of the spinal canal and narrowing of the intervertebral openings.
Spondylosis can be primary or secondary. The primary type has no reasonable cause. In contrast, the secondary type can have various causes, which include:
Spondylosis of the spine is a degeneration that can develop following mechanical trauma. Closed spinal injuries cause bone and connective tissue damage due to energy dissipation. A spinal injury can be a fracture without displacement, a fracture with displacement, or a dislocation. The causes of spinal injuries can be various. They very often occur during traffic accidents. Injuries also appear due to a fall from a height, an impact, or lifting a heavy object. Spinal injuries can result from weakening bone structures by osteoporosis or cancerous lesions.
Sometimes, spondylosis develops as a result of congenital disabilities. Many types of congenital disabilities of the spine can be distinguished that increase the risk of spondylosis. Congenital malformations of the spine can be in congenital scoliosis, congenital spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine, hemiplegia in various spine sections, and congenital muscle abnormalities in torticollis. Congenital malformations of the spine develop during intrauterine life. The most risky period for their formation is the second month of pregnancy.
A postural abnormality is an abnormal, non-physiological posture that can cause discomfort. Abnormal posture can increase the risk of spondylosis. Working at a desk for many hours at a time, lack of physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle, long-term time spent at the school desk or too heavy backpacks for children, or poor postural habits. It can all lead to postural defects. The affliction is most often noticeable when a postural deformity occurs.
Little or no physical activity is becoming an increasingly common cause of back pain. It is caused by the current lifestyle of an increasing number of people involving sedentary work and car travel. Avoiding physical activity results in gradually weakening the muscles that cannot support the spine. In summary, it increases the risk of spondylosis.

Both inactivity and not being careful during physical activity can lead to spondylosis. Overload syndromes are chronic injuries resulting from repeated stress on the musculoskeletal system without adequate rest. Excessive training, hard training ground, reduced flexibility, muscle strength, and incorrect limb positioning result in injuries. Physical activity is essential, but you must exercise moderately and follow your body's needs.
Metabolic and endocrine disorders can cause spondylosis. For example, a higher risk of spinal pain has been observed in people with type 2 diabetes![]() . With type 2 diabetes, the structure of the intervertebral discs, the so-called discs, is damaged. They become less flexible and distribute energy less well. Also, people affected by hormonal imbalances very often experience back pain. One of the most common causes of spinal degeneration is hormonal disorders.
. With type 2 diabetes, the structure of the intervertebral discs, the so-called discs, is damaged. They become less flexible and distribute energy less well. Also, people affected by hormonal imbalances very often experience back pain. One of the most common causes of spinal degeneration is hormonal disorders.
Spinal conditions and defects such as kyphosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and chiropractic can cause spondylosis. Also, rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of spondylosis. Rheumatoid arthritis![]() is an inflammatory condition, a chronic disease that involves various joints and various organs. Its most characteristic symptoms are pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints of the hands and feet, but inflammation can also affect other joints.
is an inflammatory condition, a chronic disease that involves various joints and various organs. Its most characteristic symptoms are pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints of the hands and feet, but inflammation can also affect other joints.
With time, the structures of the musculoskeletal system become worn out. Wearing intervertebral discs become dehydrated and flattened and gradually perform their cushioning function less well. Advanced spondylosis also means wear and tear of the bony elements. Changes in the spine's structure are a natural process that intensifies after age 50. Additional factors can contribute to an increased risk of spondylosis and its intense course.

Various types of spondylosis are distinguished depending on the location of the degenerative changes.
Spondylosis can be located in each section of the spine, including the thoracic spine![]() . Admittedly, this type of spondylosis is relatively rare. Thoracic spondylosis most often occurs in people with scoliosis or Scheuermann's disease. It manifests itself with pain, restricted range of movement, and intercostal neuralgia.
. Admittedly, this type of spondylosis is relatively rare. Thoracic spondylosis most often occurs in people with scoliosis or Scheuermann's disease. It manifests itself with pain, restricted range of movement, and intercostal neuralgia.
Lumbar spondylosis is a type of spondylosis that is burdened by degenerative changes. It is most common in men over 50 who do heavy physical work. It is the most common type of spondylosis, the symptoms of which are severe pain. Spondylosis pain usually radiates from the lumbar region![]() to the buttocks, thighs, and knees.
to the buttocks, thighs, and knees.
Cervical spondylosis refers to changes in the cervical vertebrae![]() . This type of spondylosis is also referred to as spondylarthrosis. Cervical spondylosis causes many bothersome symptoms. The disease manifests with frequent headaches in the occipital region, radiating to the shoulder, arm, and elbow, and there may also be dizziness and limitations of mobility in the spine.
. This type of spondylosis is also referred to as spondylarthrosis. Cervical spondylosis causes many bothersome symptoms. The disease manifests with frequent headaches in the occipital region, radiating to the shoulder, arm, and elbow, and there may also be dizziness and limitations of mobility in the spine.

Spondylosis causes several bothersome symptoms. Symptoms usually reach their most incredible intensity in the morning, becoming milder as the day progresses. Their localization mainly involves the back. However, the symptoms' location can vary depending on the type of spondylosis. Usually, spondylosis of the spine does not produce any symptoms. This is especially true in the early stages of the condition. In the advanced stages, the first symptoms of spondylosis usually appear between the ages of 40 and 50![]() .
.
Symptoms of spondylosis include:

When the spinal canal becomes narrowed, the patient starts to hurt. In cervical spondylosis, there are headaches, dizziness, and neck stiffness. In thoracic spondylosis, pain radiating to the shoulder blades and ribs predominates. In contrast, lumbar spondylosis is characterized by neck, shoulder, buttocks, and lower limb pain. Spinal pain often prevents mobility.
In spondylosis, there is a reduction in the mobility of the spine. Patients have compensatory abnormalities around the axis of the spine. It causes problems with walking and general mobility. Spondylosis is a dysfunction that impairs the spine's architecture, affecting the spine's biomechanics and function when participating in sports or doing everyday activities.
Bony outgrowths are observed in spondylosis, which can press on nerve structures. This, in turn, can cause discomfort like numbness in the limbs, muscle weakness, or the stabbing pain described above. Muscle weakness is the feeling of decreased normal muscle strength.
Depending on the nerve structure being compressed, spondylosis can cause bowel and bladder dysfunction. Patients may experience an embarrassing symptom like urinary incontinence, thus an involuntary leakage of urine through the urethra. There is also fecal incontinence, which is the involuntary leakage of liquid or solid stools or bowel gases.

In its initial phase, spondylosis is challenging to detect. Patients present to the doctor when pain symptoms appear, which already indicates an advanced stage of spondylosis. Diagnosis of spondylosis includes a detailed patient history, tests, and examinations, which include:
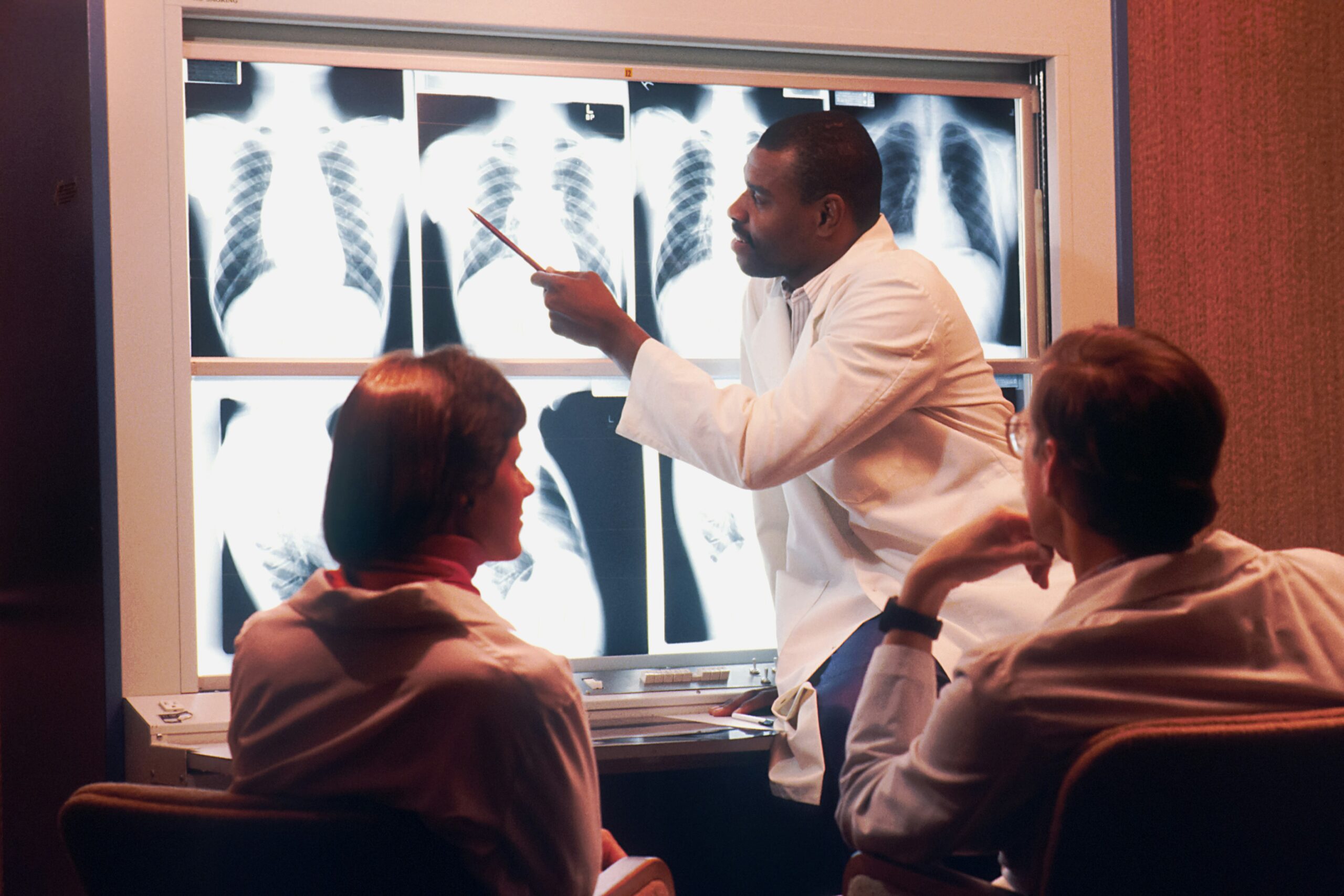
In the diagnosis of spondylosis, an X-ray of the spine![]() is done. The examination involves X-rays of the area in question. X-rays help clear pathologies of the skeletal system and possible sites of previously sustained injury.
is done. The examination involves X-rays of the area in question. X-rays help clear pathologies of the skeletal system and possible sites of previously sustained injury.
Magnetic resonance![]() imaging of the spine is functional when complaints indicate pressure on a nerve. The examination allows the most precise imaging of all its anatomical structures. MRI is also helpful in detecting disc pathologies. The assessment is also performed if the patient is experiencing neurological symptoms.
imaging of the spine is functional when complaints indicate pressure on a nerve. The examination allows the most precise imaging of all its anatomical structures. MRI is also helpful in detecting disc pathologies. The assessment is also performed if the patient is experiencing neurological symptoms.
An accurate assessment of the joints, the contents of the spinal canal, and other bone structures can be obtained by carrying out a CT scan![]() . The examination makes it possible to take a series of detailed spine scans in which the most minor structures are visible. Computed tomography is a frequently performed examination in the diagnosis of spondylosis. In addition, it is a painless and non-invasive examination.
. The examination makes it possible to take a series of detailed spine scans in which the most minor structures are visible. Computed tomography is a frequently performed examination in the diagnosis of spondylosis. In addition, it is a painless and non-invasive examination.
Unfortunately, the degenerative changes of spondylosis cannot be fully reversed, but with the proper treatment, we can influence the intensity of their sensation and slow down their development. Spondylosis treatment aims to slow down the developing degeneration of the spine, thus preventing irreversible damage to the spine. Treatments for spondylosis include:
First, analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)![]() improve the patient's quality of life. In addition to it, muscle relaxants are used. Taking appropriate supplements may be helpful to regenerate joint cartilage.
improve the patient's quality of life. In addition to it, muscle relaxants are used. Taking appropriate supplements may be helpful to regenerate joint cartilage.
Steroid injections![]() are used to treat spondylosis. Epidural steroid injections can help people with a herniated disc, a common complication of spondylosis. Steroid injections have a potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Hence, they are mainly used when persistent inflammation occurs in the musculoskeletal region.
are used to treat spondylosis. Epidural steroid injections can help people with a herniated disc, a common complication of spondylosis. Steroid injections have a potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Hence, they are mainly used when persistent inflammation occurs in the musculoskeletal region.
Rehabilitation is of great importance in the treatment of spondylosis. Exercises are used to strengthen the muscles of the back, abdomen, neck, and buttocks to increase spinal stabilization. Relaxing massages are also done to relieve muscle tension. Ice packs or different cooling compresses may be helpful. Manual treatments are being done to increase the spine's range of movement.
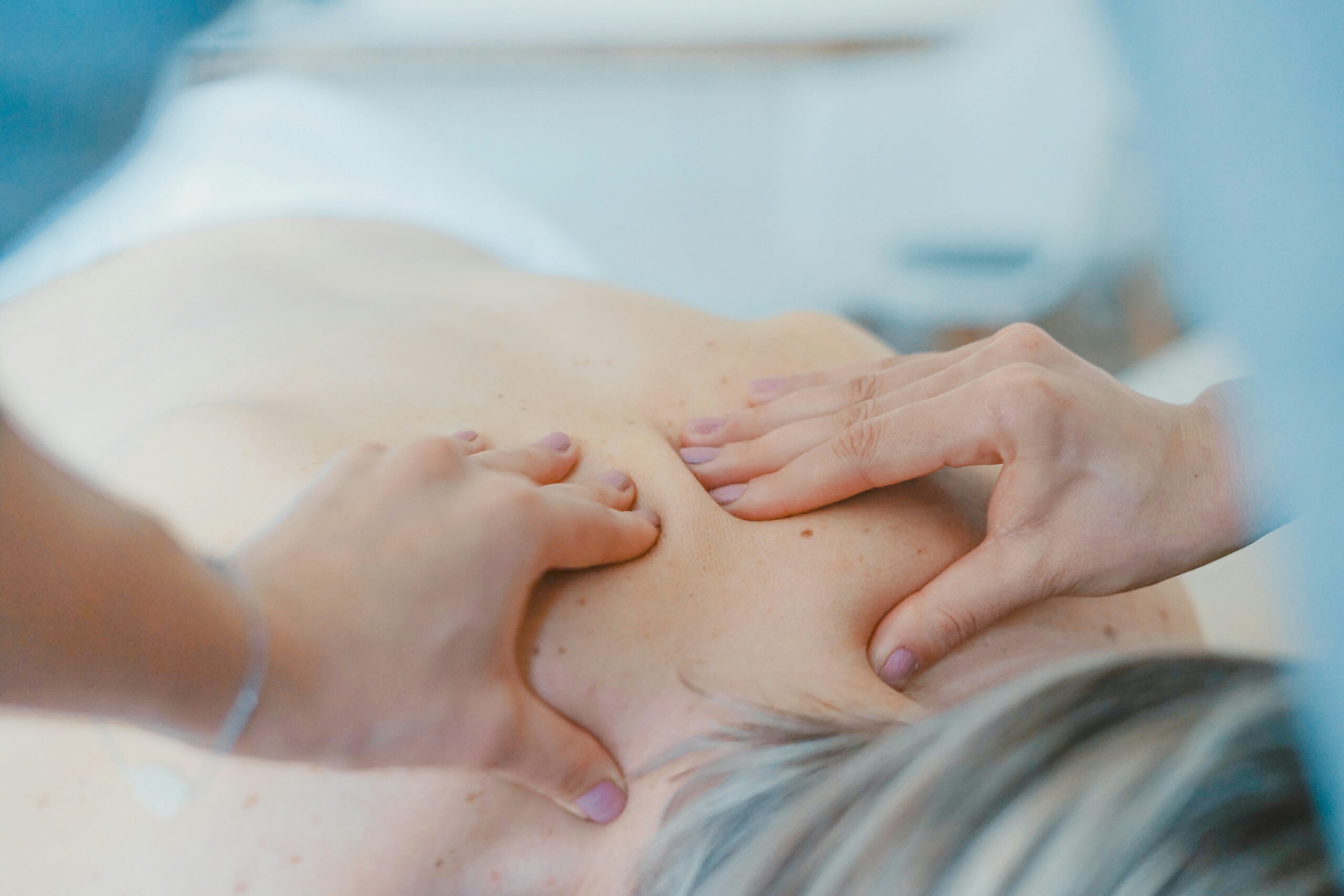
It is imperative to achieve a neutral spinal position as soon as possible to reduce the load on the affected area. It is possible by incorporating physiotherapy. Exercises address the muscles surrounding the painful area, improving its stability.
Various neuromuscular techniques can be used. Once the stability of the affected area has been achieved, protecting it exercises to improve muscle strength and functional activity training are used.
The physiotherapy program must include postural control training and teach the patient to maintain correct posture when sitting, standing, standing up, lifting, and lying down. It is estimated that with the proper course of therapy, the comeback time to total physical activity is more than five months.
With spondylosis, it may be necessary to change unhealthy habits that exacerbate symptoms. The patient should take care to be physically active. Regular gymnastics will be beneficial in reducing the stiffness and symptoms associated with lumbar spondylosis. Care should also be brought to ensure correct posture, not overloading the spine, and maintaining a healthy weight.

There are surgical treatments for severe spondylosis, including spinal fusion![]() and laminectomy, which reduces pressure on the spinal nerves or disc replacement. The operation is dedicated to the most severe cases of spinal degeneration with associated instability. Thanks to technological advances, this operation can also be done using minimally invasive techniques with microsurgical access routes to the spine.
and laminectomy, which reduces pressure on the spinal nerves or disc replacement. The operation is dedicated to the most severe cases of spinal degeneration with associated instability. Thanks to technological advances, this operation can also be done using minimally invasive techniques with microsurgical access routes to the spine.
Various treatment methods are often used to assist the process. Doctors recommend that patients wear belts, cords, corsets, or orthoses to protect the lower spine. Most often, these items are used after surgery and also for conservative treatment of cases that do not qualify for surgery. Bracing for the lower spine is not a substitute for working the strong muscles of the spine.
In addition, various treatments can be applied. Exposure to pulsed magnetic fields, laser therapy, or hydromassage are used for this goal. Degenerative changes of the spine and intervertebral joints respond very well to spa treatment. Sulfur baths, mud packs, and baths or brine baths are mainly used here. Home remedies for spondylosis include using poultices, infusions, and drinking cures with anti-inflammatory effects.

Untreated spondylosis can cause a severe condition called stenosis![]() . A spinal stenosis is a critical constriction of the luminal space of the spinal channel, resulting in compression of the spinal cord. It affects the abnormal functioning of the nervous system, causing neurological symptoms. Stenosis is a condition that significantly impairs quality of life. The condition can cause neurological disorders affecting the upper and lower limbs.
. A spinal stenosis is a critical constriction of the luminal space of the spinal channel, resulting in compression of the spinal cord. It affects the abnormal functioning of the nervous system, causing neurological symptoms. Stenosis is a condition that significantly impairs quality of life. The condition can cause neurological disorders affecting the upper and lower limbs.
In stenosis, there is also a symptom like sciatica. It is an intense pain radiating to the buttock or lower limb. Thus, severe pain symptoms significantly impair the quality of life and mobility. Symptoms of spinal cord compression in the lumbar region are exacerbated when walking.
Suppose there is no improvement, and the condition worsens when there is already critical spinal canal stenosis. In that case, the doctor may refer for surgery, which involves removing the structures compressing the spinal cord and stiffening the spinal segment. The health risks associated with spinal canal stenosis are high, so it is advisable to contact specialists quickly to start treatment and manage the deterioration of this spinal cord disease as early as possible.
Spondylosis is a syndrome of progressive degenerative changes of the spine. Due to dehydration, the intervertebral discs lose their elasticity and decrease in height. Depending on the location of the degenerative changes, various types of spondylosis are distinguished. Spondylosis can be primary or secondary. The primary type has no reasonable cause. The secondary type, on the other hand, can be caused by past trauma or spinal defects.
Changes in the spine often occur after the age of 50. Spondylosis causes a range of bothersome symptoms. If spinal canal narrowing occurs, the patient begins to experience pain and different, annoying symptoms. In its early stages, spondylosis is challenging to detect. Various tests are used in its diagnosis to indicate changes in the spine.
Spondylosis treatment mainly consists of slowing down the development of degenerative changes, thus preventing irreversible damage to the spine. Therefore, diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential here. The lesions can sometimes lead to stenosis, i.e., a critical narrowing of the spinal canal lumen, causing spinal cord compression. It affects the abnormal functioning of the nervous system, causing neurological symptoms.