The pumpkin, classified in the Cucurbitaceae family, encompasses 130 genera and over 800 species, including watermelons and cucumbers. Pumpkins come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from just a few centimeters to much larger sizes. They can be spherical, cylindrical, or pear-shaped.
When you cut open a pumpkin, you'll discover its valuable flesh and seeds, which can be used in cooking and medicine. The pumpkin plant has distinct heart-shaped leaves with jagged edges, serving as vital protection and nourishment for the plant. Its bell-shaped flowers are usually yellow, adding a delightful touch to its overall charm. Some varieties even have long stems. It's worth noting, however, that not all pumpkins are edible.
Moreover, there are edible varieties of pumpkin that are not only safe but also healthy. Interestingly, dogs can also consume pumpkin. However, it is advisable to include pumpkin in a dog's diet in moderation and as an occasional snack, rather than as the main component of a meal.

While some are cultivated for their culinary versatility, others exist purely for their decorative appeal. Consuming edible pumpkin varieties can provide a rich source of vitamins, minerals, carotenoids, and other health-promoting substances. Therefore, this appetizing gourd is widely used in various culinary creations, offering a diverse and flavorful range of possibilities.

The pumpkin is a type of seed plant grown in many parts of the world. The range of natural occurrence of these plants covers all continents. The pumpkin is native to South America and was cultivated as early as 3000 BC. The pumpkin is an annual plant. Although it is commonly consumed as a vegetable, botanically speaking, pumpkin belongs to the same category as melons and watermelons – it is a fruit.
The pumpkin season typically occurs during autumn, spanning from July to November. And because Halloween falls within this period, pumpkins are frequently utilized in various ways. You can often spot hollowed-out pumpkins adorning houses as decorations for the holiday celebrated on the last day of October.
Additionally, dishes and desserts made from pumpkins, like pumpkin pie, are quite popular among many individuals. Therefore, pumpkin is now associated with the autumn season, and people who enjoy this season will again taste the well-known Pumpkin Spice flavored coffee.
There are many species of pumpkin. Some of them are more popular and widespread. These belong to, among others:

Common pumpkin – (Cucurbita pepo) is an annual crop in the Cucurbitaceae family. There are a great many varieties of common pumpkin, including both ornamental and edible varieties. The common pumpkin produces fruits with orange, cream, and yellow, primarily thick shells. Inside is flesh and a seed nest with oval seeds. The common pumpkin is used in dishes, salads, soups, and stews, as well as in cakes and preserves.
Giant pumpkin – The giant pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima) is famous for its vibrant orange skin and impressive size. Varieties like the Atlantic Giant can produce fruits weighing up to 100 kg. The flesh of giant pumpkins is commonly used in dishes such as soups, pies, and purees. Additionally, the edible flowers of the pumpkin plant are also enjoyed by many.
Musk pumpkin – (Cucurbita moschata) This type of pumpkin reaches a smaller size and has an unusual oblong shape. The skin is quite thick, which makes the pumpkin long-lasting; the color is bright orange, and the flesh is intensely orange. It is an edible pumpkin, valued chiefly for its distinctive nutty flavor. Its flesh has no fibers and is much sweeter than other pumpkin varieties. It is, therefore, ideal for making dishes for children.
Fig-leaf pumpkin – (Cucurbita ficifolia) It is a unique green-colored pumpkin. Its fruit bears some resemblance to a watermelon, while its leaves resemble those of a fig tree. The most favored variety features green skin with white spots, snow-white flesh, and black seeds. This exquisite specimen blooms throughout the year. Its sprouts, flowers, and leaves are commonly consumed raw. Additionally, processed fruit is utilized in various food productions such as sweets, soft drinks, and alcoholic beverages.

Different pumpkin varieties may require specific growing conditions. However, here are some recommended general growing procedures for common pumpkin types.
Space Requirements – Growing pumpkins requires a larger area due to their long stems. However, if you don't have a large garden, you can still grow smaller varieties. Keep in mind that pumpkins do not thrive in marshy areas and require a sunny location.
Soil – Soil plays a crucial role in the successful growth of pumpkins. While they can tolerate different soil types, pumpkins thrive in well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter and nitrogen. If you opt for seeds, make sure to sow them at the right depth and spacing in the soil.
Seeds – Growing pumpkins can be done using either seeds or cuttings. If you opt for seeds, it's important to sow them in the ground at the appropriate intervals. For a successful harvest, pumpkin seeds should be planted indoors early in the year as these plants have a longer growing season.
Temperature – Pumpkins thrive best in temperatures around 25 degrees Celsius or 77 degrees Fahrenheit. If the weather conditions deviate from this ideal range, there's no need to worry. You can cover the plant with agricultural fleece to protect it from wind and colder temperatures.
Watering – Proper watering is essential for keeping your pumpkin plants healthy. It's important to water them deeply once a week, increasing the frequency to twice a week during hot and dry weather conditions. When watering, make sure to focus on soaking the soil rather than directly wetting the leaves to prevent fungal diseases.
Time – When growing pumpkins, it's important to consider their growing season, which typically ranges from 75 to 120 days. If you want to increase the yield, one strategy is to prune the shoots. This helps promote the quicker development of fruiting side shoots.
Problems – One problem that pumpkins can face is powdery mildew. It is a disease of fungi that results in white powdery marks on the leaves and can stunt plant growth when it becomes severe. This disease is more likely to affect plants during drought conditions, making them more susceptible. Powdery mildew poses a threat to pumpkin cultivation.

Pumpkin is a versatile ingredient to incorporate into autumn and winter dishes. It can serve as the base of a dish or be used as an addition to enhance flavor. When preparing pumpkin for cooking, it is recommended to start by slicing it in half or cutting it into larger pieces. This will provide easy access to the inside, where the seeds can be removed using a spoon for other purposes.
Certain pumpkin varieties, like those with thin skin, can be eaten without peeling. However, thicker-skinned pumpkins, such as musk pumpkins, may require peeling before consumption.
The pumpkin is an incredibly versatile ingredient that opens up countless culinary possibilities. It can be used in a variety of dishes, ranging from soups and pies to chops and both hot and cold preparations. There are numerous cooking methods available for pumpkin, including roasting, frying, boiling, or whichever method suits the recipe and desired outcome.
There are several compelling reasons to include pumpkin in our diet due to its numerous positive effects on human health. Pumpkin has a lot of vitamins, making it a valuable addition to our meals. Additionally, its seeds provide a good source of unsaturated fatty acids and dietary fiber.
In terms of protein, amino acids, aspartic and glutamic acids, and arginine are particularly important components found in pumpkin. The bright colors of vegetables like pumpkins, such as vibrant orange, yellow, or red, indicate that they are rich in carotenoids, particularly beta-carotene. These compounds have been shown to provide protection against cancer and promote healthy skin.

Pumpkins contain the following beneficial ingredients:
Vitamin A – Pumpkins come in various types and are rich in vitamin A, which offers numerous health benefits. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision, strengthening the immune system, preventing cancer, promoting red blood cell production, and keeping the skin, hair, and nails healthy.
Vitamin B – Pumpkin is a rich source of vital B vitamins. These nutrients are essential for various bodily functions, including energy metabolism, maintaining a healthy nervous system, producing red blood cells, and promoting healthy skin and mucous membranes.
Vitamin C – Pumpkin is rich in Vitamin C, which acts as a strong antioxidant in the body. It helps protect against harmful free radicals and reduces cell damage that can be associated with diseases and aging. Additionally, Vitamin C plays a role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
Vitamin E – Pumpkin is a rich source of vitamin E, which offers numerous health benefits. Vitamin E aids in reducing LDL bad cholesterol levels and minimizing plaque buildup in arteries. Additionally, it helps to lower the risk of blood clots.
Vitamin K – Pumpkin is also a good source of vitamin K, which plays a key role in the production of blood clotting factors. This helps prevent excessive bleeding and makes pumpkin beneficial for preventing hemorrhages. Additionally, vitamin K is important for bone health and helps regulate calcium levels in the body.

Potassium – Potassium is an essential mineral found in pumpkin that has several important roles in the body. It helps regulate cell pH levels, aids in nerve impulse conduction, and supports proper functioning of the nervous system and brain.
Magnesium – Magnesium is a vital material found in pumpkin. Magnesium plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. It also influences nerve conduction, supports cardiovascular health, and aids muscle contraction. In addition, magnesium helps regulate glucose and insulin levels and promotes healthy bone metabolism.
Calcium – Calcium is an essential mineral for the human body, particularly important for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. While pumpkin contains small amounts of calcium, it does contribute to supporting normal bodily functions. Moreover, this mineral also acts as a catalyst for various enzymes involved in the process of blood clotting.
Zinc – Pumpkin seeds are a great source of zinc, a mineral that plays an important role in regulating blood pressure, promoting bone health, and ensuring the proper functioning of internal organs like the pancreas. Zinc also supports normal insulin levels in the body.
Iron – Iron is another important nutrient found in pumpkin seeds. It plays a crucial role in delivering oxygen to our organs and muscles, supports our immune and nervous systems, and provides antioxidant effects. Adding pumpkin seeds to your diet can help ensure you're getting an adequate intake of iron along with other essential minerals.
Phosphorus – Phosphorus is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in multiple bodily functions. It is involved in energy production, as well as the development and functioning of bones, muscles, and the nervous system. Additionally, phosphorus helps maintain the body's acid-base balancebeta
Despite its high glycaemic index, pumpkin is low in calories. Healthy people losing weight do not have to, and should not, give up pumpkins. In addition, individuals following a reduced diet will benefit from the high fiber and potassium content. Fiber helps alleviate digestive issues and provides a sense of fullness. Potassium aids in the elimination of excess water from the body, reducing swelling. However, it is worth noting that pumpkin seeds are more calorific compared to the flesh of the pumpkin.

Although dried pumpkin seeds contain calories, they actually have fewer calories compared to other sources of fat like sunflower seeds or walnuts. The specific calorie content may vary based on the type and variety of pumpkin used. Calorific value also increases with heat treatment. Roasted pumpkin has a higher energy value than raw pumpkin. How much depends on the amount of water evaporated.
Regular consumption of pumpkin is recommended for the prevention of many diseases. Pumpkin is a fruit worth eating during the autumn season and beyond. Here are some health benefits of pumpkin:

Lowering blood cholesterol – The beta-carotene found in pumpkins can help lower bad cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cholesterol buildup in artery walls. This can prevent conditions like atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes. In addition, pumpkin regulates blood pressure levels.
Positive effects on brain function – Adding pumpkin to your diet can have positive effects on brain function. Pumpkin is a nutrient-rich food that contains lecithin and unsaturated fatty acids, which are known to support memory and concentration. Eating pumpkin regularly can also help reduce stress levels, thereby positively impacting overall mental health.
Protecting your eyesight – Eating pumpkins can also benefit your eye health by providing important nutrients like carotenoids and vitamin A that support optimal eyesight. Including vegetables in your diet can help protect against common eye issues like night blindness and macular degeneration.
Anti-cancer effects – Carotenoids provide important benefits in fighting cancer and maintaining skin health. As powerful antioxidants, they offer protection against premature aging and help shield the skin from the harmful effects of the sun.
Not only the flesh of the pumpkin fruit is edible, but the seeds are also a delicious and nutritious option. Roasting pumpkin seeds brings out their best flavor. These seeds make for a healthy snack as they contain magnesium, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, and B vitamins. You can add them to soups, salads, or even desserts. Roasting pumpkin seeds is simple enough that you can easily do it yourself at home.
Roasting pumpkin seeds step by step:
You can enjoy the pumpkin seeds as a snack or add them as a delicious topping to salads and sandwiches. For the best taste, it's recommended to consume them while they're still slightly warm, within about half an hour after roasting.
If you're wondering what to cook with pumpkin, we have some delicious and reliable recipes for you. Pumpkin is a versatile ingredient that can be used in various dishes and desserts. It offers a delightful flavor that works well in both sweet and savory recipes. Explore different ways to prepare pumpkin and savor its unique taste while enjoying its health benefits.
A delicious pumpkin cream soup with the addition of potatoes. It is delicately spiced with ginger, turmeric, and garlic. Light and mild, it is also suitable for children.

Start by peeling and dicing the potatoes. In a larger pot, sauté the chopped onion and garlic in butter. Add the pumpkin and potatoes, then season with salt and spices. Sauté everything together, stirring occasionally for about 5 minutes. Next, pour in the stock, cover the pot, and bring it to a boil. Let it cook for 10 minutes. Finally, transfer everything to a blender and blend until smooth, adding milk as needed to achieve your desired consistency.
These cookies are a great choice for a Halloween party. They have a soft and fluffy texture and the spices used in the recipe give them a delicious gingerbread flavor. For an extra special touch, try adding icing or chocolate on top!
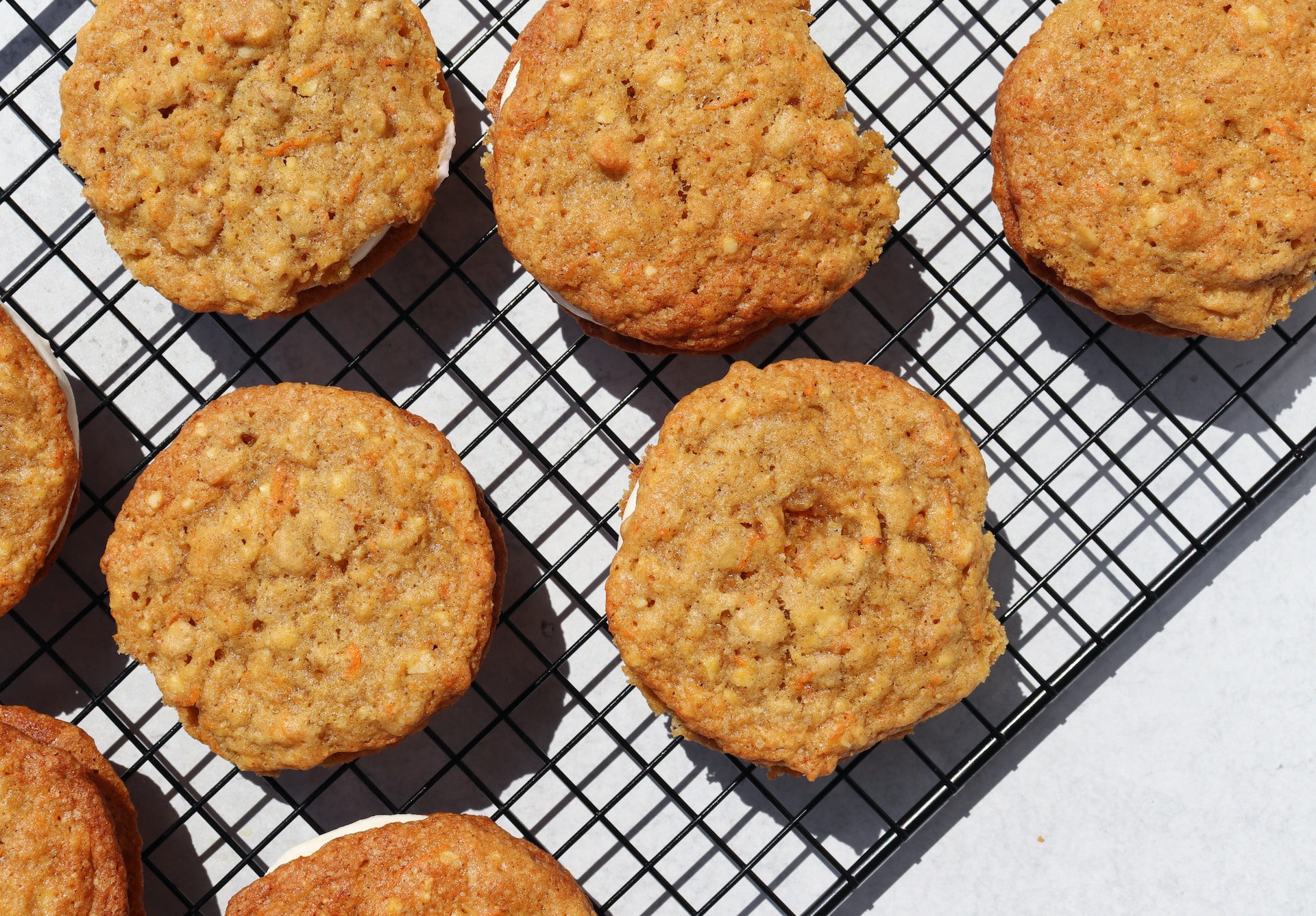

Cream or mix the butter and sugar until a light and fluffy butter mixture is formed. In a mixing bowl, combine the egg with the pumpkin puree until well blended. Gradually add in the flour, spices, and salt, stirring until a soft and sticky dough forms. Line a flat cake tin with baking paper. Using a spoon, scoop portions of the dough onto the prepared tin. Bake the pumpkin cookies at 180ºC for approximately 10 minutes or until they turn golden brown.
Table of Contents

Strawberries are a beloved fruit, known not only for their delicious taste but also for their abundance of vitamins. Let's… read more »
Lychee is a fruit known for its exceptional flavor. Discover the health benefits of incorporating lychee into your diet, and… read more »

The cucumber is a popular vegetable. If you want to learn about its health effects then read our article. We… read more »

Dragon fruit is an exotic fruit that combines the taste of kiwi, pear, and citrus. It's known for its red… read more »

Papaya, a fruit cherished for its flavor and health benefits, offers a variety of culinary options for incorporating it into… read more »

The Paleo diet is a way of eating inspired by the diet of our ancestors living in prehistoric times. What… read more »

Healthier heart, lungs and kidneys. Black cumin oil is a plant product known for its many health benefits. Find out… read more »

Almonds are a delicious snack that also have many health properties. It works well for the heart and more. But… read more »

Jicama is a vegetable that offers various health benefits. Let's explore the nutrients present in jicama and discover some simple… read more »