The nervous system is a complex structure that can be divided into various parts. The system is divided into subsystems that work together with each other and with the different parts of the body. Two essential structures of the nervous system can be distinguished: the peripheral and central nervous systems. Every part of the nervous system has vital functions. The brain's functions include thought processing, memory, reactions, emotions, and control of the body and its reflexes.
The nervous system, protected by the skull, cerebrospinal fluid, and meninges, consists of nerve cells communicating with the outside world. Nerve impulses send signals as electrical impulses, causing specific reactions and reflexes. The operation of the nervous system is essential for human functioning and enables survival. Therefore, the nervous system's proper functioning is critical, but various types of disease and damage can also compromise it.
Abnormalities related to the nervous system can manifest themselves in an extensive range of symptoms, as the system controls the entire human body. Therefore, prevention is essential for the nervous system. Even if some diseases can be prevented, it is through prevention that you can significantly improve your functioning. Increase your knowledge of the nervous system.

The brain is an organ that is divided into left and right hemispheres![]() that communicate with each other. Although closely linked, the hemispheres are responsible for different functions and have specific roles in acting and thinking. The left hemisphere is responsible for most people's understanding and creation of language and is also dominant in mathematical abilities. In contrast, the right hemisphere is predominant in artistic and musical skills.
that communicate with each other. Although closely linked, the hemispheres are responsible for different functions and have specific roles in acting and thinking. The left hemisphere is responsible for most people's understanding and creation of language and is also dominant in mathematical abilities. In contrast, the right hemisphere is predominant in artistic and musical skills.
The cerebral hemispheres contain billions of nerve cells called neurons![]() . Neurons and their extensions receive and transmit signals. The nervous system can also be separated into the CNS
. Neurons and their extensions receive and transmit signals. The nervous system can also be separated into the CNS![]() and the PNS
and the PNS![]() . The central nervous system includes the nerves in the spinal cord and brain. On the other hand, the peripheral nervous system consists of the rest of the nerves. The different parts of the nervous system that perform specific functions include the following sections:
. The central nervous system includes the nerves in the spinal cord and brain. On the other hand, the peripheral nervous system consists of the rest of the nerves. The different parts of the nervous system that perform specific functions include the following sections:

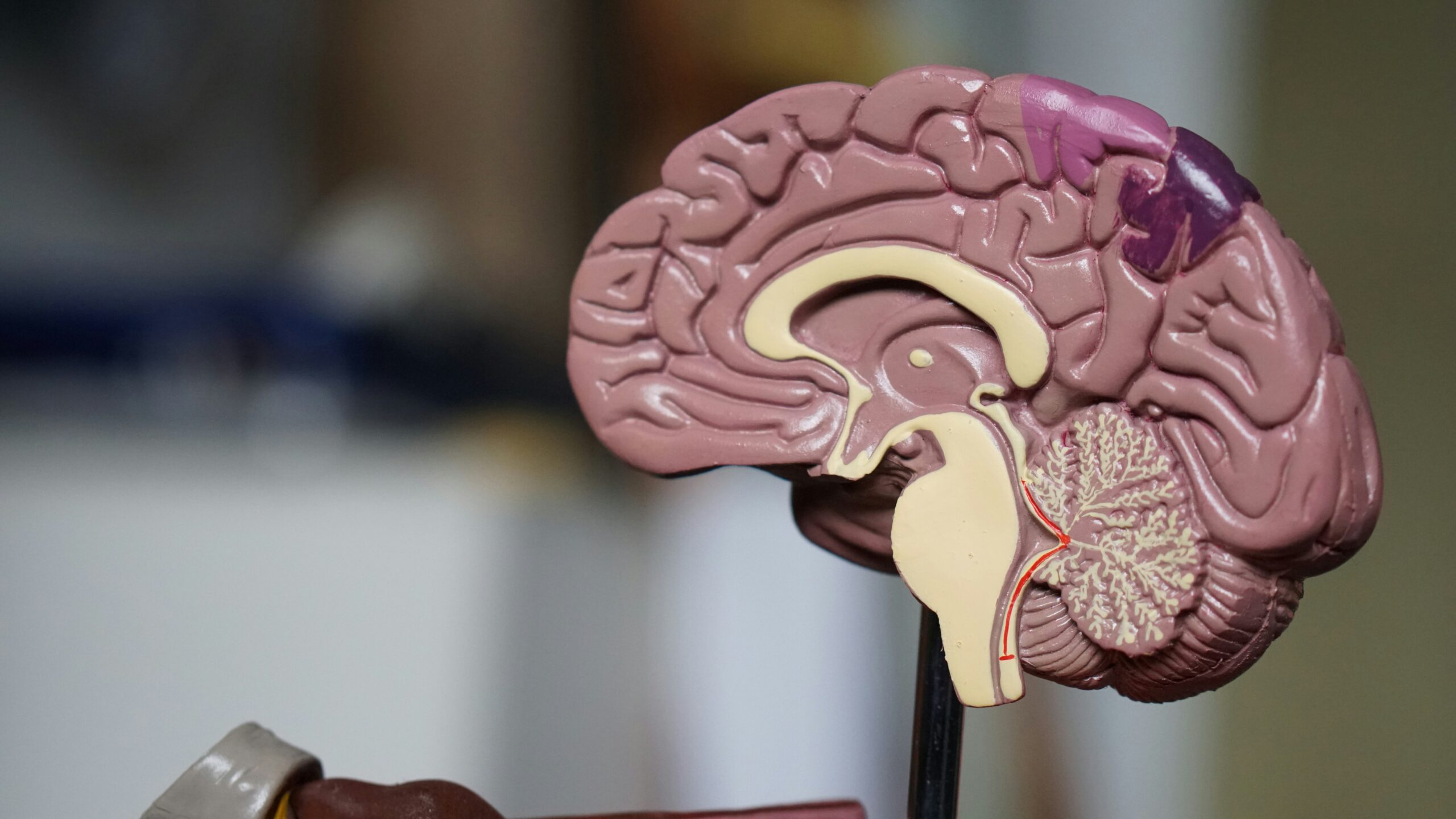
The cerebral cortex is crucial in the nervous system, forming the brain's outer layer. It is undulating and made of grey matter. The outer part of the brain can be divided into four different areas: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Each lobe of the cerebral cortex has specific functions. The brain's frontal lobe is mainly responsible for motor functions, as it contains the motor cortex.
In addition, its functions can include skills such as memory, attention, and language. Broca's area![]() is also located in its area. The parietal lobe contains the somatosensory center, i.e., its functions include processing information through touch. The occipital lobe, on the other hand, contains the visual cortex, meaning that it receives and interprets visual stimuli. The temporal lobe, on the other hand, contains the auditory cortex area, analyzing sounds and impulses. In addition, Wernicke's area
is also located in its area. The parietal lobe contains the somatosensory center, i.e., its functions include processing information through touch. The occipital lobe, on the other hand, contains the visual cortex, meaning that it receives and interprets visual stimuli. The temporal lobe, on the other hand, contains the auditory cortex area, analyzing sounds and impulses. In addition, Wernicke's area![]() is active in speech comprehension.
is active in speech comprehension.
The thalamus is an important area that receives impulses from sensory receptors. Receptors are located throughout the body and transmit information. Therefore, the thalamus supports the proper functioning of the cortex lobes. In addition, the thalamus has a consciousness control function, meaning that it influences sleep regulation.
The hypothalamus is a small area of the nervous system that connects to the endocrine system![]() . Therefore, the hypothalamic area is responsible for general body functions such as cardiovascular function, appetite control, and body temperature. The hypothalamus causes the release of hormones, which have many essential roles in the body. The hypothalamus also produces hormones, which include oxytocin
. Therefore, the hypothalamic area is responsible for general body functions such as cardiovascular function, appetite control, and body temperature. The hypothalamus causes the release of hormones, which have many essential roles in the body. The hypothalamus also produces hormones, which include oxytocin![]() . The hormone secreted into the bloodstream influences socialization, sexual function, and emotions.
. The hormone secreted into the bloodstream influences socialization, sexual function, and emotions.
These parts of the nervous system are responsible for controlling motor activity. The caudate nuclei, globus pallidus, and corpus callosum are involved in involuntary and voluntary movements, thus condition motor skills and coordination. The nuclei send projections to the cortex, thalamus, and brainstem.

The medulla oblongata is located in the brainstem's lower part. It is attributed to many roles, including the autonomic functions necessary for survival. This part of the nervous system controls the amount of oxygen in the blood and the respiratory rate. The respiratory center regulates the rhythm of breathing and stimulates the muscles of the respiratory system. The medulla also influences the cardiovascular system, regulating heart contractions and blood pressure. In addition, the medulla oblongata is responsible for activating necessary reflexes such as swallowing, vomiting, coughing, and sneezing. Centers in the spinal cord are also responsible for the secretion of saliva and sweat.
The cerebellum is an area that communicates with other parts of the brain. Thus, it enables voluntary movements of the arms and legs and is responsible for the functions of balance and posture. This part of the nervous system sends signals that activate voluntary muscle contractions with a specific force and momentum. The cerebellum also receives information about the position of the body in space. Thanks to the cerebellum, people can move smoothly and maintain motor coordination.
This part is located within several parts of the central nervous system. The limbic system includes many vital areas. The pyramidal cortex![]() is associated with the sense of smell. The hippocampus
is associated with the sense of smell. The hippocampus![]() , which belongs to the limbic system, is responsible for various memory functions. In addition, it influences learning and the ability to orient oneself in space. The hippocampus also has many connections to other areas of the body.
, which belongs to the limbic system, is responsible for various memory functions. In addition, it influences learning and the ability to orient oneself in space. The hippocampus also has many connections to other areas of the body.
The amygdala![]() has many essential functions related to emotions. It influences the emotional sphere, building memory based on emotional associations and negative emotions. This part of the limbic system also allows for recognizing emotions and regulating stress responses. In threatening situations, the amygdala takes over for protective purposes.
has many essential functions related to emotions. It influences the emotional sphere, building memory based on emotional associations and negative emotions. This part of the limbic system also allows for recognizing emotions and regulating stress responses. In threatening situations, the amygdala takes over for protective purposes.
Several types of nucleus accumbens connect the different areas and enable the transmission of information between them. Other parts of the limbic system are also responsible for functions such as the sensation of pleasure, having to do with addictions.
This part of the brain conducts nerve impulses between the cerebrum and the peripheral nervous system. The spinal cord forms a bidirectional pathway between the brain and the body. It makes all motor activities possible. The spinal cord runs through an almost complete channel in the middle of the spine, inside the vertebrae. The spinal nerves comprise millions of individual nerve fibers that control muscle movements and conduct stimuli from peripheral sensory nerve endings. All stimuli are felt thanks to the spinal cord, and vital activities can be performed. If the spinal cord is severed, the entire body stops functioning properly.
There are diseases and disorders related to the nervous system. Problems that may indicate diseases of the nervous system should not be ignored, as untreated conditions can be life-threatening. Symptoms of nervous system problems can be various depending on the disease. Observation of symptoms should prompt patients to seek medical attention. Neurologists carry out various diagnostic tests that can detect pathological conditions. Diseases associated with abnormalities in the nervous system include:
Aphasia is the term used to describe a lack of language ability in various ranges. Broca's aphasia is a type of motor-motor aphasia. The condition refers to problems with verbal expression related to general speech comprehension. Patients have difficulty naming and repeating things, even though they know and understand what they want to communicate. This type of aphasia can have various causes, including brain injuries and tumors or strokes, where oxygen does not reach Broca's part of the brain.
This type of aphasia is characterized by problems in understanding heard speech. This is due to the inability to distinguish and identify the heard speech sounds. Patients do not understand sentences spoken to them; in more severe cases, they have problems understanding short commands and words. Voices sound very similar, so they cannot combine and analyze them. Patients can speak, but the audience may not understand their message because of the difficulty in understanding language. Wernicke's aphasia has various causes, which include ischaemic and hemorrhagic strokes.

Strokes can cause problems with the nervous system due to inadequate oxygenation of various symptoms. Hypoxia can even cause the death of brain tissue with permanent complications. There are also transient strokes, which are temporary conditions. However, the symptoms of strokes can vary widely, depending on where the blood clot has occurred. Symptoms may include slurred speech, breathing problems, or paralysis. The intensity of the symptoms is related to how much the clot cuts off oxygen to the brain.
It is a type of condition that occurs when brain activity is disrupted by trauma. Mechanical injuries can occur during physical activity or a car accident. Various symptoms occur depending on the severity of the injury. Initially, there is usually a concussion, which causes dizziness and disruption of consciousness. In contrast, a severe brainstem contusion is associated with the risk of coma and permanent neurological damage. As a result of the injury, blood in the brain builds up from ruptured vessels, increasing intracranial pressure. Autonomic functions can be severely impaired or even lost when this condition occurs.
When a spinal cord injury occurs, symptoms usually involve sensory stimuli causing paralysis. Depending on where the injury occurs, paralysis can involve various muscles. Among other things, paraplegia![]() may occur. It is the term used to describe paralysis of the lower limbs. It can also be exclusively in the upper limbs, but these situations occur less frequently. Paralysis may involve partial paresis or complete absence of sensation and movement.
may occur. It is the term used to describe paralysis of the lower limbs. It can also be exclusively in the upper limbs, but these situations occur less frequently. Paralysis may involve partial paresis or complete absence of sensation and movement.
One nervous system disease is Parkinson's disease, which is based on a decrease in dopamine levels. The decrease in the hormone causes characteristic symptoms that include reduced motor coordination and tremor. Bradykinesia, or motor slowing and rigidity, are other symptoms of this condition. This type of nervous system disorder progresses over time, increasing the intensity of the symptoms. Treatment consists solely of symptom control, but research is still ongoing to invent an effective treatment for Parkinson's disease.

Huntington's disease is another disease of the nervous system. It has a genetic basis, and its main symptoms are involuntary, jerky movements of the limbs, especially the hands. This disease also progresses over time, increasing the intensity of the motor symptoms and cognitive impairment. Huntington's disease has an unfavorable prognosis, as it eventually causes patients to die. No causal treatment has been developed, and movement therapy treats movements that reduce symptoms.
The following disease related to the nervous system is Alzheimer's dementia, in which there is a gradual degeneration and death of neurons. Scientists have discovered that dementia is caused by an abnormal accumulation of proteins in and around brain cells. The disease causes deterioration of various brain functions, such as memory and cognitive function. Patients within the hippocampus and parietal cortex show lower neuronal activity, which causes symptoms. Current treatment is only symptomatic, i.e., it does not eliminate the cause of the disease but only combats or alleviates the symptoms.
Nervous system problems can also have an autoimmune basis. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin proteins of the central nervous system attack the body, damaging the communication between the brain and the body. Symptoms of the disease include various discomforts, such as general weakness and pain, loss of coordination, and reception of different external stimuli. Treatment also involves controlling the symptoms by inhibiting the intense response of the immune system.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a Lou Gehrig's disease in which the neurons responsible for movement are destroyed. The control of voluntary and involuntary movements is impaired, resulting in speaking, swallowing, and breathing difficulties. Scientists are still working to discover the cause and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Viral infections![]() can also cause issues with the nervous system. Poliomyelitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the spinal cord. The Polio virus spreads between people and destroys neurons. Symptoms mainly include paralysis. Poliovirus causes a pathological condition that involves damage to the spinal cord and brainstem neurons, mostly motor neurons. It causes paralysis, paresis, and even death. You must receive the appropriate vaccinations to protect yourself against this nervous system disease.
can also cause issues with the nervous system. Poliomyelitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the spinal cord. The Polio virus spreads between people and destroys neurons. Symptoms mainly include paralysis. Poliovirus causes a pathological condition that involves damage to the spinal cord and brainstem neurons, mostly motor neurons. It causes paralysis, paresis, and even death. You must receive the appropriate vaccinations to protect yourself against this nervous system disease.