The classical Mediterranean diet, known in today's terminology, refers to the eating habits found in Greece, particularly in Crete, and southern Italy, mainly in Naples. Its core principle emphasizes consuming seasonal foods with high nutritional value and minimal industrial process.
This diet primarily relies on vegetable fats, fish, seafood, and vegetables. A Mediterranean Diet Pyramid has been created, which specifies the intake of a particular group of products for an adult. However, physical activity is at the pyramid's base, which was also high in Mediterranean people.
People may eat differently depending on where they live. Geographical conditions determine the availability of local products, although nowadays, thanks to well-developed infrastructure, delivering high-quality food to different places on earth is possible. Therefore, the Mediterranean diet gained great popularity when people from other parts of the world noticed the benefits of the ways of eating of Italians and Greeks.
Inspired by the traditions of the Mediterranean countries, UNESCO![]() staff included the Mediterranean diet on the Heritage of Humanity list in 2010. The concept of the Mediterranean diet has been introduced and studied by many nutritionists and specialists. Studies conducted have shown that the Mediterranean diet can have beneficial effects on health.
staff included the Mediterranean diet on the Heritage of Humanity list in 2010. The concept of the Mediterranean diet has been introduced and studied by many nutritionists and specialists. Studies conducted have shown that the Mediterranean diet can have beneficial effects on health.

The principles of this diet refer to a dietary model inspired by a diet typical mainly of the people of Italy and Greece in the 1960s![]() . The choice of this geographical area and historical period is based on scientific and epidemiological arguments. Back then, it was observed in those areas that life expectancy was one of the highest in the world.
. The choice of this geographical area and historical period is based on scientific and epidemiological arguments. Back then, it was observed in those areas that life expectancy was one of the highest in the world.
The incidence of various diseases was lower than in other parts of the world. Interestingly, these health statistics persisted despite the high percentage of smokers in those regions, the low level of socioeconomic development, and the poor state of health care.
Countries in the Mediterranean have access to local food, so it has been assumed that it is the diet that has such a beneficial effect on the health of these residents. The Mediterranean diet has many variations. Significant differences depend on the region. The diet and gastronomic traditions of the countries bordering the Mediterranean vary significantly due to cultural, religious, and economic differences.
Like any other dietary approach, the Mediterranean diet is based on certain principles about which foods to consume regularly and which to avoid. However, it's not just about food choices – non-nutritional factors inherent in the Italian and Greek way of life are also significant. By adopting the Mediterranean lifestyle, we embrace their eating habits and imitate their overall way of living.
The Mediterranean diet is based on the following types of food:
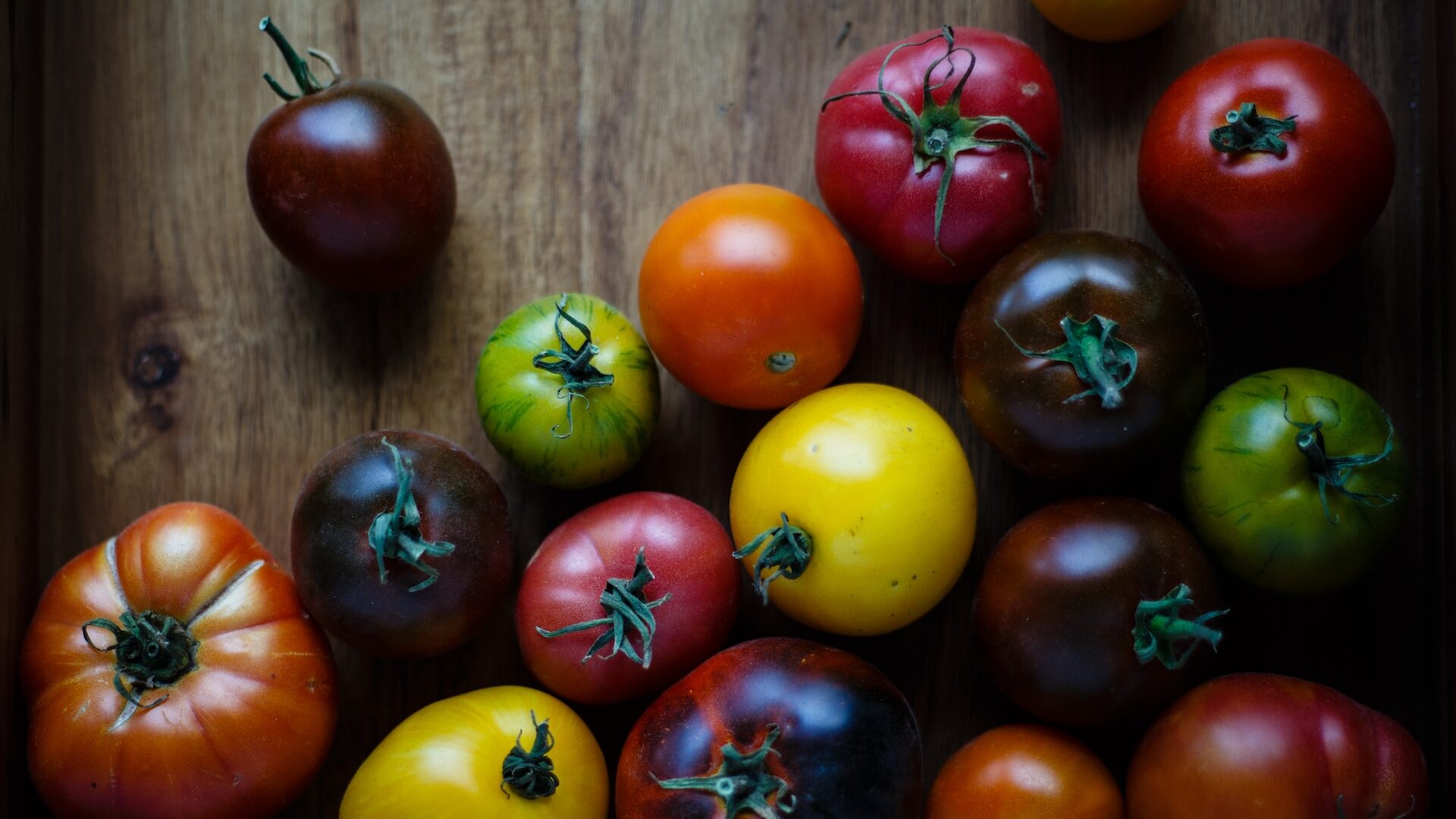

Vegetables and fruits are vital components of the Mediterranean diet, highly recommended by nutritionists. They offer a wide range of essential minerals and vitamins, providing the body with nourishment in every meal. Mediterranean cuisine often includes salads featuring various vegetables as their nutritious base.
This diversity allows for many meal options, including tomatoes, garlic, olives, zucchini, and asparagus. Additionally, fruits are commonly enjoyed fresh instead of traditional desserts. Avocados, oranges, apricots, cherries, and many other fruits contribute to the healthful benefits provided by this diet.
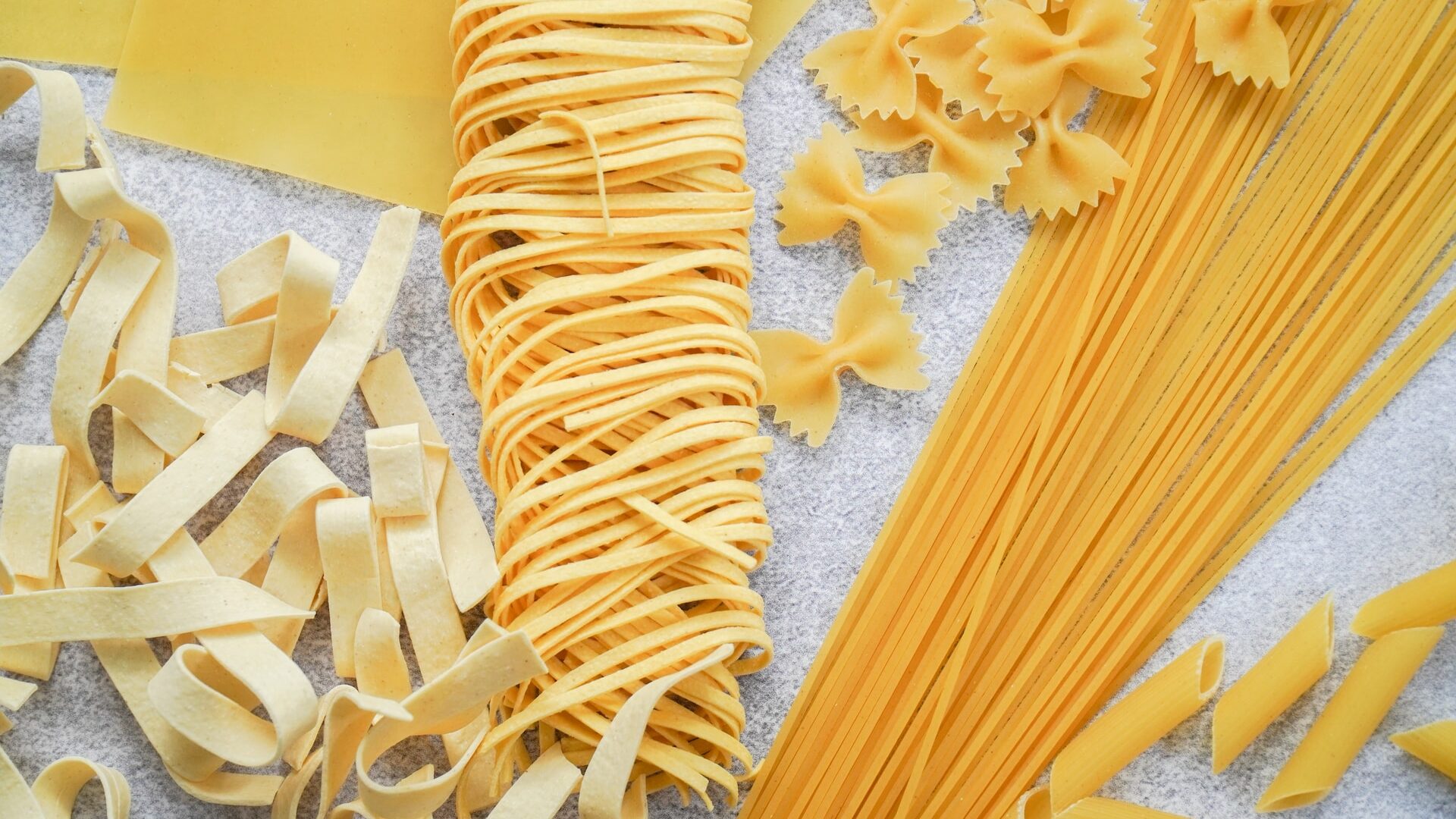

The Mediterranean diet centers around various plant-based foods, focusing on incorporating cereal products. These products serve as the foundation or accompaniment to dishes like salads. Cereal products provide essential carbohydrates for sustaining energy and vital minerals, vitamins, and fiber.
This category includes whole-grain bread, low-processed flour pasta, brown rice, and a variety of groats that can add diversity to the Mediterranean diet. However, it is advised to avoid highly processed grain products such as wheat bread and white rice in this dietary approach.

Legumes are commonly found in the Mediterranean diet, serving as versatile side dishes or ingredients. Lentils, chickpeas, beans, and peas offer abundant protein, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. These legumes can be effortlessly substituted for meat in various dishes like cutlets or spreads to accompany bread. The essence of the Mediterranean diet lies in incorporating fruits, vegetables, and grains into every meal along with protein sources like legumes.

In the Mediterranean diet, dairy products serve as another source of protein. They offer complete protein, easily digestible calcium, and phosphorus. A well-liked option is thick natural yogurt, commonly used in desserts or salads. Italian and Greek cuisines particularly showcase cheeses like mozzarella or feta.
However, it is advised to limit saturated fatty acids in eggs and dairy to plant-based fats instead. Therefore, excessive consumption of dairy products should be avoided. Opting for low-fat dairy products is also recommended.

The Mediterranean diet gives excellent importance to vegetable fats![]() . These fats can be found in various forms, such as olive oil, nuts, almonds, and seeds. Olive oil is widely used by Mediterranean people for cooking meat, fish, and vegetables. It not only provides antioxidants that help prevent cancer but also contains monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial for lowering cholesterol levels.
. These fats can be found in various forms, such as olive oil, nuts, almonds, and seeds. Olive oil is widely used by Mediterranean people for cooking meat, fish, and vegetables. It not only provides antioxidants that help prevent cancer but also contains monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial for lowering cholesterol levels.
Avocados, walnuts, hazelnuts, cashews, Brazil nuts, almonds, and different types of seeds added to salads are excellent sources of monounsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E. However, consuming these products in moderation is essential due to their high caloric content. Olive oil is the most commonly used type among all the choices of vegetable fats in the Mediterranean diet.

In the Mediterranean diet, it is advised to consume animal fats in smaller quantities compared to vegetable fats. The main emphasis should be on fish and occasionally lean meat and poultry. Fish, particularly fatty fish, contain omega-3 fatty acids, which offer various health benefits.
Seafood is also included in the diet. Instead of dairy or legumes, meat can serve as a source of protein, but it should be low in saturated fats that contribute to atherosclerosis. However, meat and eggs are not considered the core components of the Mediterranean diet; they are rather consumed as side dishes.

Herbs play a crucial role in Mediterranean cuisine, infusing it with enticing flavors. These aromatic condiments, such as garlic, marjoram, basil, thyme, nutmeg, tarragon, oregano, cumin, rosemary, and sage, not only enhance taste but also possess antioxidants that exhibit anti-cancer effects. Opting for these herbs instead of excessive salt can be beneficial for maintaining a healthy diet. Moreover, dishes seasoned with spices are known to promote easy digestion.
In the Mediterranean diet, you won't find any forbidden foods. However, certain foods should be consumed very rarely. These include:
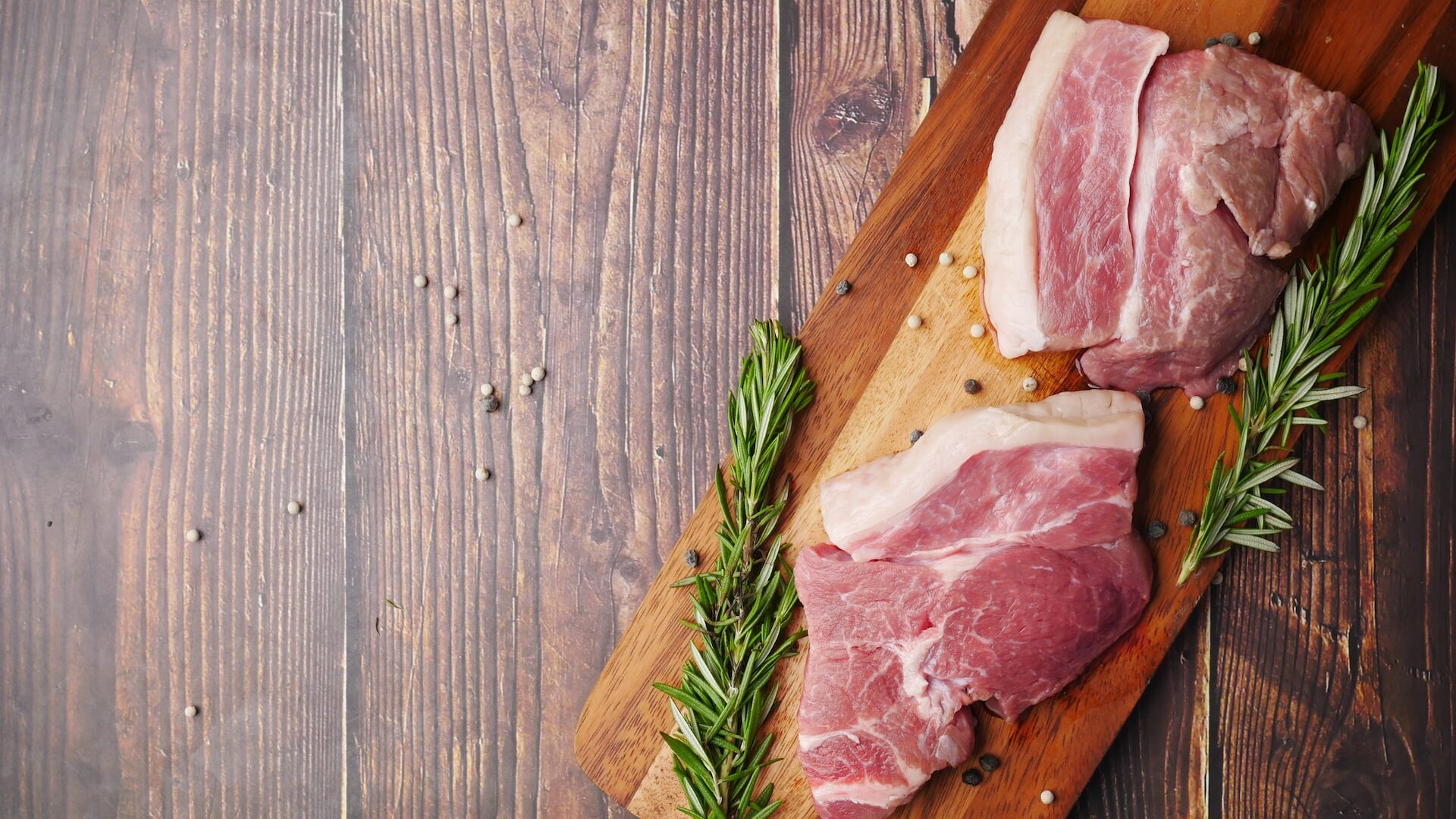

In the Mediterranean diet, meat is only a supplement, not the base of the diet. Red meat![]() , on the other hand, should be especially avoided. It has adverse effects on health. Statistics confirm that people who eat high amounts of pork and beef are more likely to develop cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and cancer. Although red meat is a good source of vitamins and minerals, it should be eaten infrequently due to the dangers of regular consumption. Such meats include beef or pork, among others.
, on the other hand, should be especially avoided. It has adverse effects on health. Statistics confirm that people who eat high amounts of pork and beef are more likely to develop cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and cancer. Although red meat is a good source of vitamins and minerals, it should be eaten infrequently due to the dangers of regular consumption. Such meats include beef or pork, among others.
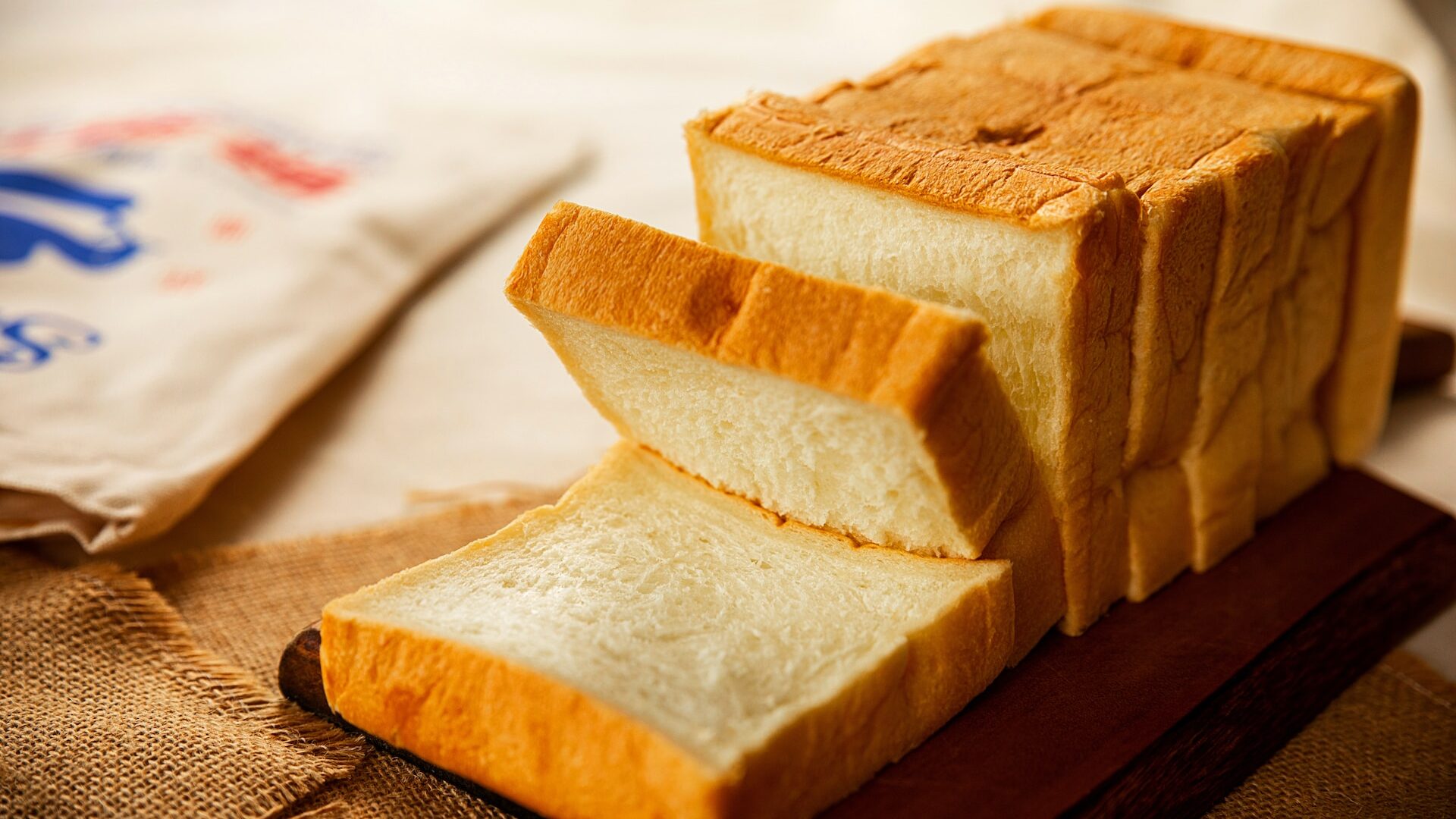

This group of products includes white pasta, white rice, and white bread, among others. Whole-grain types of these foods are recommended instead. Excessive consumption of white bread, rice, or pasta contributes to weight gain, insulin resistance, and many chronic diseases, including osteoporosis.
These foods have a lot of calories, so it is recommended to avoid them, especially if you want to lose weight. Highly processed foods include instant meals, bought in markets and ready to reheat in the microwave. Instead of such dishes, it is better to prepare wholesome meals. Also, limit salty snacks such as crackers and chips, which are highly processed foods.
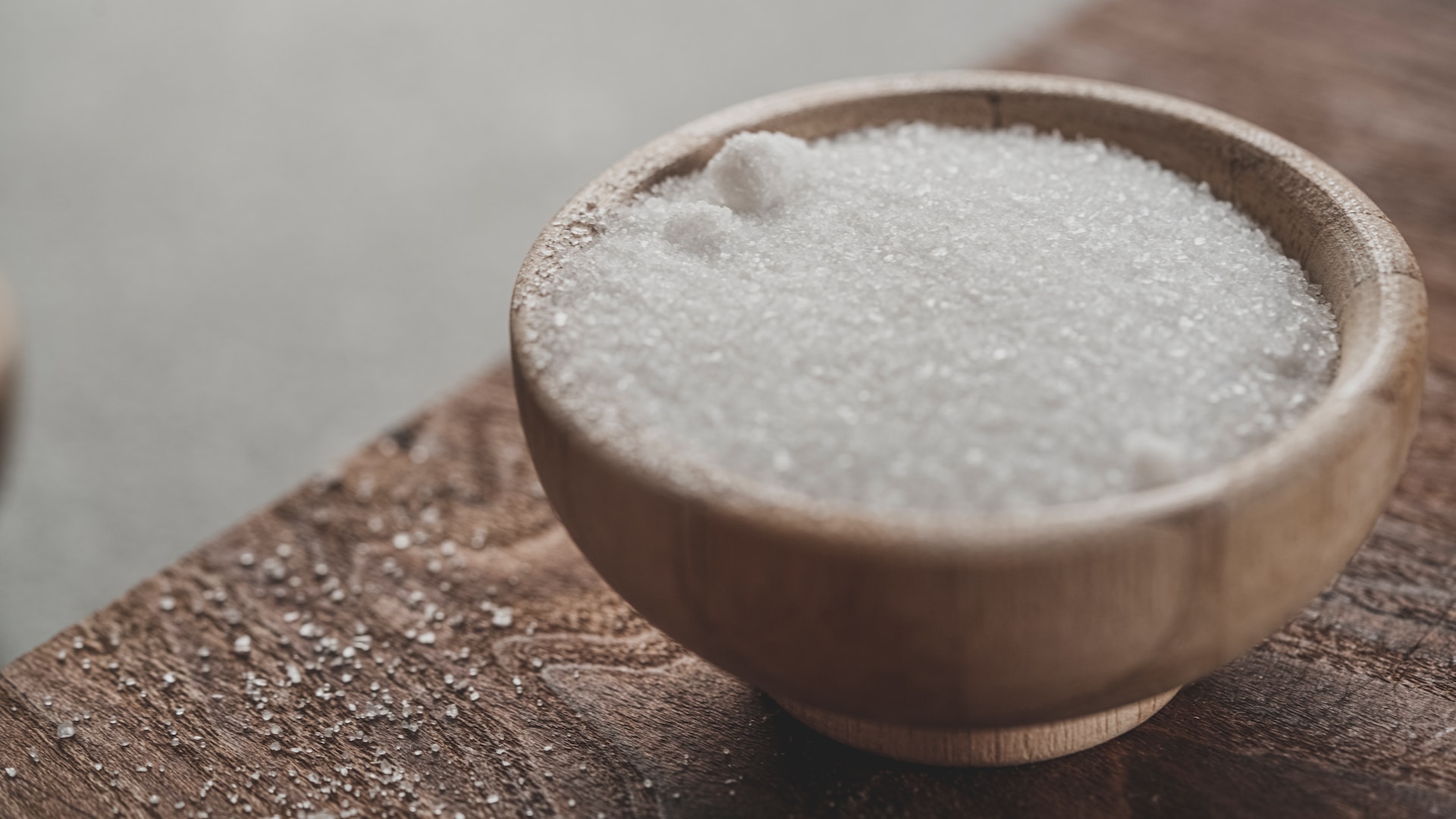

In the Mediterranean diet, it is crucial to limit salt intake as excess consumption can harm our health. Overloading the kidneys, salt is believed by scientists to contribute to stomach cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, strokes, and nervous system irritability.
Additionally, it extracts calcium from the body and maybe a contributing factor to osteoporosis. While table salt enhances the taste of prepared foods, caution should be exercised. The Mediterranean diet offers various spices such as herbs![]() , oils, and nuts that add flavor to meals.
, oils, and nuts that add flavor to meals.
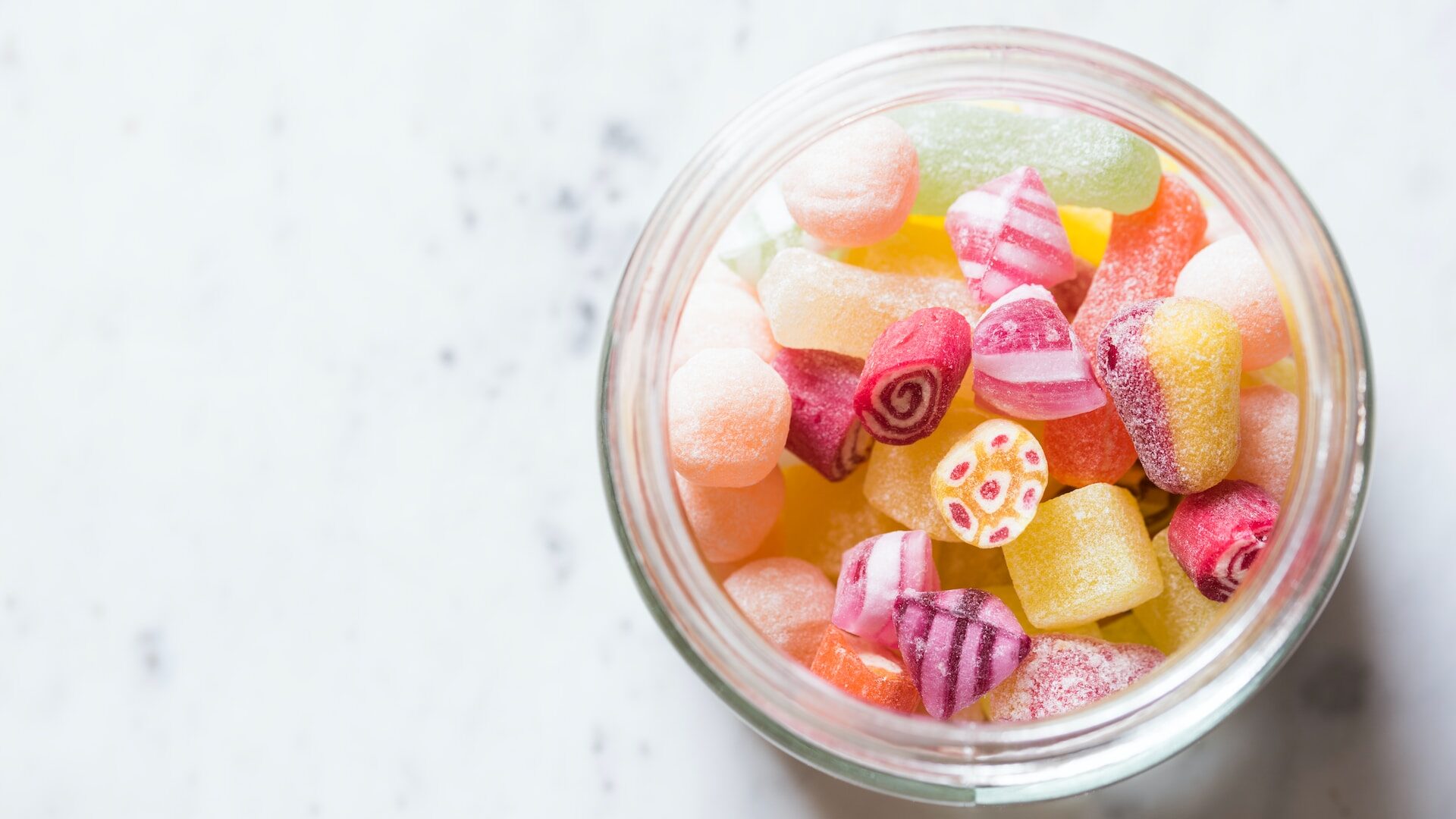

In the Mediterranean diet, desserts can be enjoyed occasionally. Italian and Greek cuisine often includes fresh fruit as a healthier dessert option that promotes well-being. Additionally, honey, nuts, and yogurt are commonly used in Greek desserts, offering additional nutrients alongside the natural sugars.
However, excessive consumption of sweets can contribute to weight gain and obesity due to their high energy content. In addition, eating sweets such as candy bars and cookies causes tooth decay, increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis, and raises cholesterol levels.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy dietary model. Many scientific studies have shown its numerous health benefits. The main nutritional principles of the Mediterranean diet are:
Nutrition is based mainly on vegetables, including legumes, fruits, herbs, nuts, whole grains, and healthy fats – primarily olive oil![]() . The Mediterranean diet mainly revolves around the consumption of fish and seafood, with occasional inclusion of poultry, eggs, or cheese. However, it is advised to prioritize fermented dairy products like yogurt. Red meat and sweets should be limited in the diet.
. The Mediterranean diet mainly revolves around the consumption of fish and seafood, with occasional inclusion of poultry, eggs, or cheese. However, it is advised to prioritize fermented dairy products like yogurt. Red meat and sweets should be limited in the diet.
Vegetables and fruits sourced locally are key components of every meal in the Mediterranean diet. Instead of relying on salt for flavoring, natural herbs are preferred during meal preparation. Cooking methods such as steaming, baking in foil, and grilling are recommended, while deep frying is avoided.
In addition to nutrition, non-nutritional factors like physical activity and positive social relationships play a significant role in promoting health within the context of the Mediterranean diet.
The Mediterranean eating style requires frequent drinking of pure water and herbal teas. The basis, therefore, is to drink plain water or with the addition of lemon or mint. Other drinks are also allowed, as the Mediterranean diet is not strict. However, be aware that juices and sodas contain large amounts of sugar.

However, when it comes to alcohol, it is allowed in the Mediterranean diet. Alcohol should also be consumed in moderation. A popular choice for Italians and Greeks is to drink a glass of wine with a meal. In addition to its taste, red wine![]() also has health benefits.
also has health benefits.
Red wine has ten times the polyphenol content of white wine, and this difference is the result of the fermentation of red wine grape must. Higher polyphenol content is associated with more substantial health-promoting properties.
The antioxidants in red wine slow down free radicals, which are responsible for accelerating the aging process in the body. Red wine also has a positive effect on the human circulatory system. In addition, drinking red wine with a meal facilitates digestion.
The Mediterranean diet does not have restrictive calorie rules. It is recommended to adjust to a calorie that suits individual needs. According to the general calorie criteria, the calories consumed are 2500 kcal for men and 2000 kcal for women. In summary, the amount of calories resulting from the meals consumed should be, at most, the metabolic demand resulting from the scale of physical activity practiced.
The Mediterranean diet is ideal for people who care about improving their well-being, health, and long life. It is based on healthy eating habits and a satisfying lifestyle. Not related to food, the principles of the Mediterranean diet also include regular physical activity and healthy social relationships.
Research affirms that adhering to the principles of the Mediterranean diet and engaging in regular physical activity can effectively mean of maintaining a healthy body weight. Furthermore, when combined with the Mediterranean diet, physical activity confers positive benefits on the cardiovascular system, guarding against cardiovascular disease![]() .
.
Moreover, regular physical activity enhances immune function and overall fitness while acting as a preventive measure or delay tactic against various health conditions. It is crucial to tailor physical activity according to individual requirements. For health, moderate physical activity is more beneficial. Aerobic workouts like slow jogging, marching, or yoga stimulate the body to do extra work but do not strain it.
The Mediterranean diet pyramid also maintains social relationships![]() at its base. The people of the countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea ate meals with family and friends and spent their free time doing physical activity together. It has been repeatedly proven that satisfying social contacts promotes mental and physical health.
at its base. The people of the countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea ate meals with family and friends and spent their free time doing physical activity together. It has been repeatedly proven that satisfying social contacts promotes mental and physical health.
This is because they protect us from loneliness and stress, give us a sense of competence and belonging, bring joy, and encourage movement. So, they are worth taking care of at every stage of life. Contact with other people is one of the basic human needs and affects overall health. Therefore, good relationships with family and friends can be a factor in supporting diet's health benefits.

The Mediterranean diet can be confidently categorized as a model diet to base your eating habits. Following the recommendations of the Mediterranean diet and getting surprisingly positive results from the change in diet results from a diet low in saturated fats and sugar and rich in plant products and fish, including oils high in mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids. The health advantages of the Mediterranean diet are as follows:
Help with weight loss – A high probability of short-term weight loss and long-term maintenance also characterizes this type of diet. The Mediterranean diet is not a standard diet to weight loss, while it is possible to lose weight on this diet if you follow a negative caloric balance. The low intake of animal fats in the Mediterranean diet helps you lose weight. In addition, regular exercise is another factor that causes weight reduction.
Regulation of blood sugar – The American Diabetes Association![]() recommends the Mediterranean diet for both preventing and treating diabetes. Studies have shown that this diet improves glycemic control in diabetic patients. People with diabetes should incorporate complex carbohydrates into their meals, such as whole grains and vegetables while avoiding sweets and white bread. Dietitians often endorse this approach to manage or prevent diabetes.
recommends the Mediterranean diet for both preventing and treating diabetes. Studies have shown that this diet improves glycemic control in diabetic patients. People with diabetes should incorporate complex carbohydrates into their meals, such as whole grains and vegetables while avoiding sweets and white bread. Dietitians often endorse this approach to manage or prevent diabetes.
Positive effects on the cardiovascular system – The research-backed Mediterranean Diet offers positive effects on the cardiovascular system, making it a practical approach to prevent and treat cardiovascular disease. Combining this diet with regular exercise further reduces the risk of such conditions. Moreover, a proper diet plays a crucial role in addressing issues related to poor blood circulation. Insufficient intake of necessary nutrients leads to inadequate oxygen supply to the body's cells, resulting in compromised blood circulation.
Stronger immune system – A stronger immune system is vital for optimal health. It relies on a well-balanced and nutritious diet, such as the Mediterranean diet. This diet offers a variety of nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. By following the Mediterranean diet, individuals can ensure they obtain these essential nutrients that contribute to improved immunity![]() . Moreover, this dietary approach helps protect against infections and diseases by bolstering the immune system.
. Moreover, this dietary approach helps protect against infections and diseases by bolstering the immune system.
Support for the digestive system – Supporting digestive health involves following a diet low in fat and fiber. By excluding fatty foods found in the Mediterranean diet, such as meat, one can positively impact their digestive system. Conversely, incorporating vegetables into the diet provides ample fiber content, which aids in proper stomach function.
Support for brain function – A Mediterranean diet, abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, has been found to enhance brain function. Specifically, it improves memory![]() , learning abilities, and the excitability of neuronal membranes. These essential fatty acids also facilitate the growth of nerve cells in the hippocampus and increase receptors and neurotransmitters. Additionally, incorporating nuts, vegetables, and vegetable fats into one's diet positively impacts brain function.
, learning abilities, and the excitability of neuronal membranes. These essential fatty acids also facilitate the growth of nerve cells in the hippocampus and increase receptors and neurotransmitters. Additionally, incorporating nuts, vegetables, and vegetable fats into one's diet positively impacts brain function.
Provision of nutrients – The Mediterranean diet, when followed correctly, can provide all the necessary minerals and vitamins for proper bodily functions. This is achieved through a significant intake of vegetables containing essential nutrients. Additionally, the healthy properties of vegetable fats contribute positively to overall health.

Following the Mediterranean diet model is recommended for people with various health problems. Due to certain health benefits, the Mediterranean diet is recommended for the following groups:
The Mediterranean diet is recommended for people who want to care for their health with a varied and balanced menu. First, this diet, in a non-rigorous way, helps people struggling with excessive body weight and, with the help of balanced nutrition, want to shed excess weight and reduce body fat.
Also, people with abnormal fasting glucose levels, insulin resistance, or type 2 diabetes can follow the Mediterranean diet. Then, the menu should include only whole-grain cereal products while excluding refined ones, which are acceptable in the traditional diet model.
Also, patients who have elevated levels of total blood cholesterol and the so-called bad LDL cholesterol or have a diagnosed or high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, i.e., atherosclerosis, hypertension, and coronary artery disease, can benefit from the Mediterranean diet.
The Mediterranean diet, like any diet, has its advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, before changing your diet, it is worth considering the following penalties:
Availability of food products – In some regions, the availability of food products may pose a challenge for adhering to the Mediterranean diet. This diet heavily relies on fresh vegetables, fruits, and other locally sourced items, which might be limited in certain parts of the world. It's important to consider that these specific products could have higher prices when scarce, requiring adequate financial provision. In such instances, it becomes crucial to shift our focus towards utilizing the foods that are readily accessible within our respective areas.
High fiber in the diet – High fiber has its considerations. While it benefits many, confident individuals, such as those recovering from acute pancreatitis, should be cautious. Special pancreatic diets with lower fiber and fat content are recommended.
On the other hand, the advantages of the Mediterranean diet include:
Easy to follow – The diet is a diet that is easy to implement. Products are usually widely available, or you can use substitute local products. It is also not a restrictive diet, so it can be carried out quickly over time without requiring unpleasant sacrifices. In addition, the meals of the Mediterranean diet are delicious, which positively affects the perception of this diet.
Low risk of complications – The Mediterranean diet poses a low risk of complications. It is quickly followed, reducing the chances of improper adherence and potential deterioration of health. Importantly, this diet is not associated with the risk of inadequate nutritional status or deficiencies in specific nutrients like minerals and vitamins. Hence, it is widely appreciated for its safety.
The concept of the Mediterranean diet has garnered attention from numerous nutritionists and specialists, who have extensively studied its effects on health. Research indicates that following a Mediterranean diet can yield various health benefits. The dietary principles of this approach are inspired by traditional eating habits predominantly observed in Italy and Greece during the 1960s.
At its core, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes consuming seasonal, minimally processed foods with optimal nutritional value. The main components include vegetable fats, fish, seafood, and vegetables. A Mediterranean Diet Pyramid has been devised to guide adults on specific food group intake. However, physical activity forms the foundation of this pyramid as it was also an integral part of Mediterranean lifestyles.
The predominant protein sources in a Mediterranean diet encompass fish, seafood, and infrequently poultry or cheese. Fermented dairy products like yogurt are encouraged, while red meat and sweets should be consumed sparingly. Fresh vegetables and fruits play an indispensable role in every meal within this diet, and they are often sourced locally.
Preparing meals incorporates minimal salt usage in favor of natural herbs, while cooking techniques such as steaming, foil baking, or grilling are preferred over deep frying practices to enhance health benefits. Besides nutrition-related factors, elements like physical activity and positive social relationships significantly contribute to overall well-being within the context of a Mediterranean lifestyle.
Research supports the effectiveness of the Mediterranean diet for preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases—an ideal choice for individuals focusing on improving their well-being and longevity through dietary choices characterized by balance variety.
Moreover, this regimen offers particular assistance to people looking to manage excessive body weight or reduce body fat through balanced nutrition instead of strict restrictions severe measures. Likewise, those grappling with abnormal fasting glucose levels and insulin resistance can find adopting the principles embodying characteristics inherent to following patterns beneficial and impactful.
Table of Contents

The DASH diet is a diet ideal for improving hypertension. In addition, it also has many other benefits. Learn about… read more »

Olive oil is a delicious and healthy addition to dishes. Discover the many benefits of it. It is worth reading… read more »

Vegan food comes in many different forms and types. With new products, a vegan diet can be more varied. Learn… read more »

Do you know what to put in your diet to lower your cholesterol? Learn about 15 foods that effectively affect… read more »
There are a number of natural high-protein foods that you can introduce into your diet. Learn about animal products and… read more »

Do you know how eating high fiber foods will affect your health? Learn all about fiber and how it affects… read more »

The Paleo diet is a way of eating inspired by the diet of our ancestors living in prehistoric times. What… read more »

The ketogenic diet is based on the effects of ketosis, making it a great way to lose weight. See what… read more »

Do you know what the fibromyalgia diet should be? Find out what to eat and what to avoid. Create the… read more »