Laryngitis is a larynx inflammation (voice box). It happens when the larynx becomes irritated, infected, or overused. If vocal cords work correctly, they open and close flawlessly, and the air passing them vibrates and produces sounds.
Inflamed vocal cords, on the other hand, get swollen, which causes their surface to be uneven and makes air get distorted when passing through them, which, as a result, causes hoarseness.
Acute laryngitis usually goes away on its own within 1-2 weeks. It is considered chronic (long-lasting) laryngitis if it persists for over three weeks.
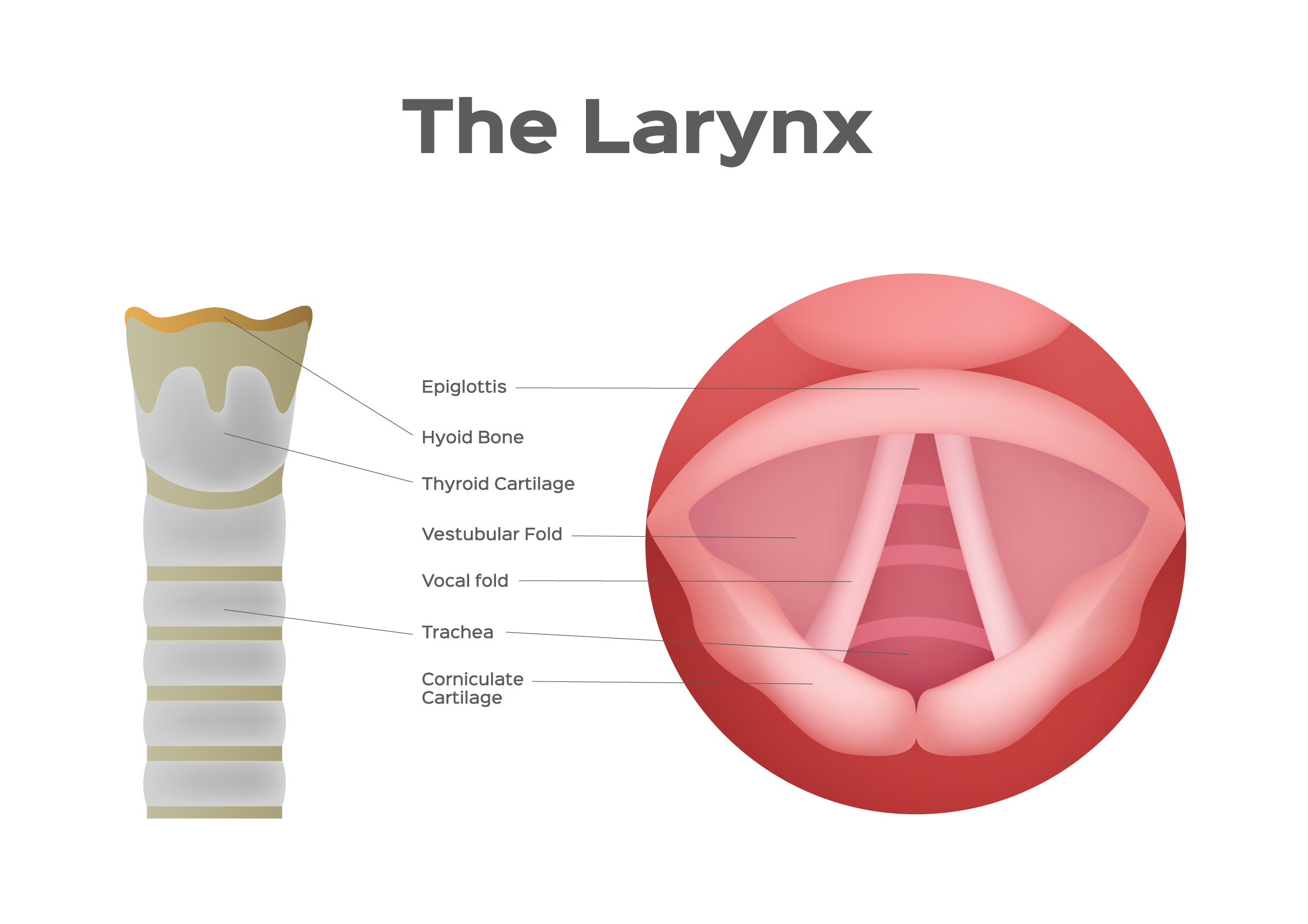
The larynx is a part of the upper respiratory tract between the pharynx and the trachea (windpipe). It is a tube about 4-5 centimeters long that lets the air pass through it to the trachea so it can reach the lungs. Since the larynx contains voice cords, its other function is making a voice, which is why it is sometimes called a voice box.
The larynx is divided into three sections![]() :
:
The larynx is built out of nine cartilages connected by ligaments and muscles. Thyroid cartilage, one of the larynx cartilages, is commonly known as Adam’s apple![]() . The entries to the larynx and esophagus are near each other. The elastic cartilage called epiglottis closes the entry to the larynx to prevent the food from entering the respiratory tract when swallowing.
. The entries to the larynx and esophagus are near each other. The elastic cartilage called epiglottis closes the entry to the larynx to prevent the food from entering the respiratory tract when swallowing.
The middle part of the larynx contains voice cords. During voice production, the vocal cords vibrate transversely to each other, opening and closing, which interrupts the airflow. It is the vibration of air waves that produces sound.
The pitch of the sound depends on the vocal cords' tension, length, and thickness. The larynx of children and women produces higher sounds than the larynx of men because it has shorter vocal cords.
The loudness of the voice depends on the strength of the air current and the amplitude of the vibrations of the vocal cords. In voiceless whispering, the vocal function of the larynx is inactive.
Several factors may cause laryngitis. Causes slightly differ depending on whether it’s an acute or chronic condition.
Acute laryngitis is most often caused by:
Chronic laryngitis causes include:
Laryngitis might spread to others from a germ like a virus, bacteria, or fungus. But, if it happens because of allergies, smoking, strong chemicals, stomach acid, or shouting too much, then it’s not something that you can catch from someone else.
Around one in five individuals![]() might experience chronic laryngitis at some point. While this condition can affect anyone, adults are more often affected than kids. It affects men and women in similar proportions. It rarely happens to children under three, and when it does, the doctors usually look more thoroughly at the child's condition as it may suggest a more severe problem.
might experience chronic laryngitis at some point. While this condition can affect anyone, adults are more often affected than kids. It affects men and women in similar proportions. It rarely happens to children under three, and when it does, the doctors usually look more thoroughly at the child's condition as it may suggest a more severe problem.
The symptoms that may appear during laryngitis include:
Small children may also show symptoms such as:
Symptoms of acute laryngitis most often appear suddenly and increase in intensity quickly. In the case of chronic laryngitis, the symptoms develop gradually and may initially be overlooked by the patient.
Uncomplicated laryngitis lasts about ten days and typically goes away on its own.

Larynx inflammation sometimes also happens to children. However, it presents differently than in adults. The child's larynx is smaller than a grownup's and is higher. That’s why the edema and symptoms of breathing difficulties appear faster in children.
Croup is a unique form of acute laryngitis in children that usually affects children between 1 and 5 years old. It is typically caused by viruses and usually starts with flu-like symptoms (runny nose, fever). After a few days, a barking cough, breathing difficulties, hoarseness, and stridor (a high, rough sound resulting from impaired airflow through narrowed airways) develop. Symptoms typically get worse at night![]() and get better when breathing cold air
and get better when breathing cold air![]() .
.
In most cases, croup isn’t life-threatening. However, you should seek emergency medical attention in case of extreme symptoms, especially severe shortness of breath.
Some people have a higher risk of getting laryngitis than others. Risk factors include:
Your healthcare provider will probably recognize laryngitis based on characteristic symptoms, such as hoarseness, dry cough, and voice problems. Acute laryngitis typically doesn’t require tests as it is easy for doctors to recognize based only on presenting symptoms. If your symptoms persist for a more extended period or are especially alarming, your doctor may look into your medical history in search of possible factors that trigger inflammation. The doctor may examine your voice cords, and you may be referred to an ear, nose, and throat specialist for further diagnostics.
If necessary, your doctor may use the following techniques to determine if you have laryngitis and how bad it is:

If left untreated, laryngitis usually goes away within ten days. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe you medications to make the recovery process quicker or if your symptoms are severe.
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, various medications can be used:
For most people with laryngitis, the disease goes away on its own. Here are some self-care tips you can use during laryngitis to relieve symptoms and reduce voice strain:
Although the throat and larynx are very close, the inflammation of these organs is different. Pharyngitis is a term that refers to the inflammation of the pharynx, commonly known as a sore throat. Laryngitis is often confused with pharyngitis because the same pathogens can cause both diseases and initially cause similar symptoms. However, laryngitis is a much more dangerous disease that can quickly escalate to life-threatening shortness of breath. It is distinguished from pharyngitis primarily by a characteristic barking cough but also by problems with speaking and breathing.
Usually, laryngitis is caused by non-infectious factors or viruses and passes without complications. However, bacterial superinfection may be the reason if the infection doesn’t disappear after ten days.
One of the complications is further developing the infection and involvement of the lower respiratory tract, Inflammation of the trachea, bronchi, or lungs, and permanent dysfunction of the vocal cords. In some situations, untreated long-term laryngitis may cause the development of cancer.
Laryngitis can be contagious and may have a complicated course, especially in the youngest children. Therefore, the best solution is to avoid getting sick. This is not always possible, but appropriate prevention can reduce the risk.
Supporting your immune system and taking care of your voice is vital. Properly humidified air in rooms, frequent ventilation, reasonable use of air conditioning, and quitting smoking are worth keeping in mind. People working in conditions exposing them to vapors of irritating substances should pay special attention to proper respiratory protection to limit the inhalation of harmful substances.
To keep your voice box and vocal cords healthy, especially if your job requires you to talk or sing a lot, experts say it's crucial not to yell or whisper too much. Staying hydrated helps prevent voice box swelling, too. So, it's best to steer clear of smoking and anything that dries out your throat and voice box.
Typically, laryngitis goes away on its own by staying hydrated and resting the voice. However, if you notice the following symptoms, seek emergency medical help:
If symptoms persist for over two weeks, you should see a doctor, even if your symptoms are mild. In the case of long-term laryngitis, the cause needs to be identified. In more challenging or complicated cases of larynx inflammation, the ear, nose, and throat specialist is the one who treats it.
Table of Contents
Croup is a common respiratory disease It is often seen in children under the age of 5 years. Learn about… read more »

Voice change, which individuals regularly call voice mutation, is when the vocal characteristics like pitch or tone (how high or… read more »

Cough is a natural, necessary reflex that protects the body from factors such as germs and pollens. When it is… read more »
Cancer within the throat, which therapeutic experts call pharyngeal cancer, happens when the disease starts in parts just like the… read more »

Discover Sore Throat Remedies for quick and effective pain relief. Many herbs and foods have healing properties. Learn how to… read more »

Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs during breathing. What does it inform you about? read more »

An otolaryngologist, too alluded to as an ENT pro, is an critical player within the complex world of medication. This… read more »

Tourette syndrome is characterized by tics. What are its causes? What to do if we observe disturbing symptoms? read more »
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that affects the throat and tonsils. Around 11 million people are infected with this… read more »