Hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol, dyslipidemia) is a disorder with too high lipid (fat) levels in the blood. Lipids are necessary for the proper functioning of the human body, but when they accumulate excessively, it can lead to dangerous complications.
Lipids are produced in the liver and supplied with food. Your liver produces enough lipids for your body’s needs, so the fats you get from food are extra. Lipids include, among others, triglycerides and cholesterol.
Cholesterol plays a significant role in the proper functioning of the body: it is a component of cell membranes, is necessary for producing bile acids![]() , steroid hormones, and vitamin D3, and is involved in nervous system signals transmission.
, steroid hormones, and vitamin D3, and is involved in nervous system signals transmission.
The body uses triglycerides to produce energy for tissues, especially muscles. Fatty acids are part of cell membranes and are used to produce substances involved in, among others, regulating the function of platelets, vessels, the digestive tract, and the kidneys.
Circulating lipids are carried in lipoproteins, transporting them to various tissues for energy use, lipid deposition, steroid hormone, and bile acid production.
There are several types of lipoproteins:
Think of your bloodstream as a busy road, blood flowing like cars. LDL cholesterol, however, is like a big truck that breaks down and causes traffic jams. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol is a reliable tow truck that picks up broken-down trucks from the arteries and transports them to the liver. This process clears the road, allowing blood to flow smoothly.
Congenital hyperlipidemia is extremely rare – in most cases, hyperlipidemia is caused by improper nutrition, lousy lifestyle, overweight, genetic predisposition, alcohol abuse, and stress. Other diseases, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, increase cholesterol production. The first symptoms of hyperlipidemia are usually those related to its complications, such as cardiovascular diseases.
Although congenital hyperlipidemia is a rare condition, secondary hyperlipidemia is a common disorder. According to the CDC, about 10% of adults in the United States have high cholesterol levels. About 7% of children have high total cholesterol levels. Many people don’t know they have high cholesterol since it doesn’t give symptoms until the disease is advanced.
There are two causes of hyperlipidemia. The first is related to genetic factors. It is usually a hereditary form, passed down from generation to generation, and is characterized by a tendency to elevated lipid levels despite eating a balanced diet. The reason for its occurrence is genetic mutations.
Primary hyperlipidemias include:
However, secondary hyperlipidemias are more common and are not caused by hereditary factors.
The causes of secondary hyperlipidemia![]() include:
include:
What are the consequences of untreated hypercholesterolemia? Long-term elevated blood cholesterol levels may lead to serious health problems. First of all, high cholesterol is one of the primary factors in the development of atherosclerosis and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Increased cholesterol is also associated with the risk of gallstones, as it may be a component.
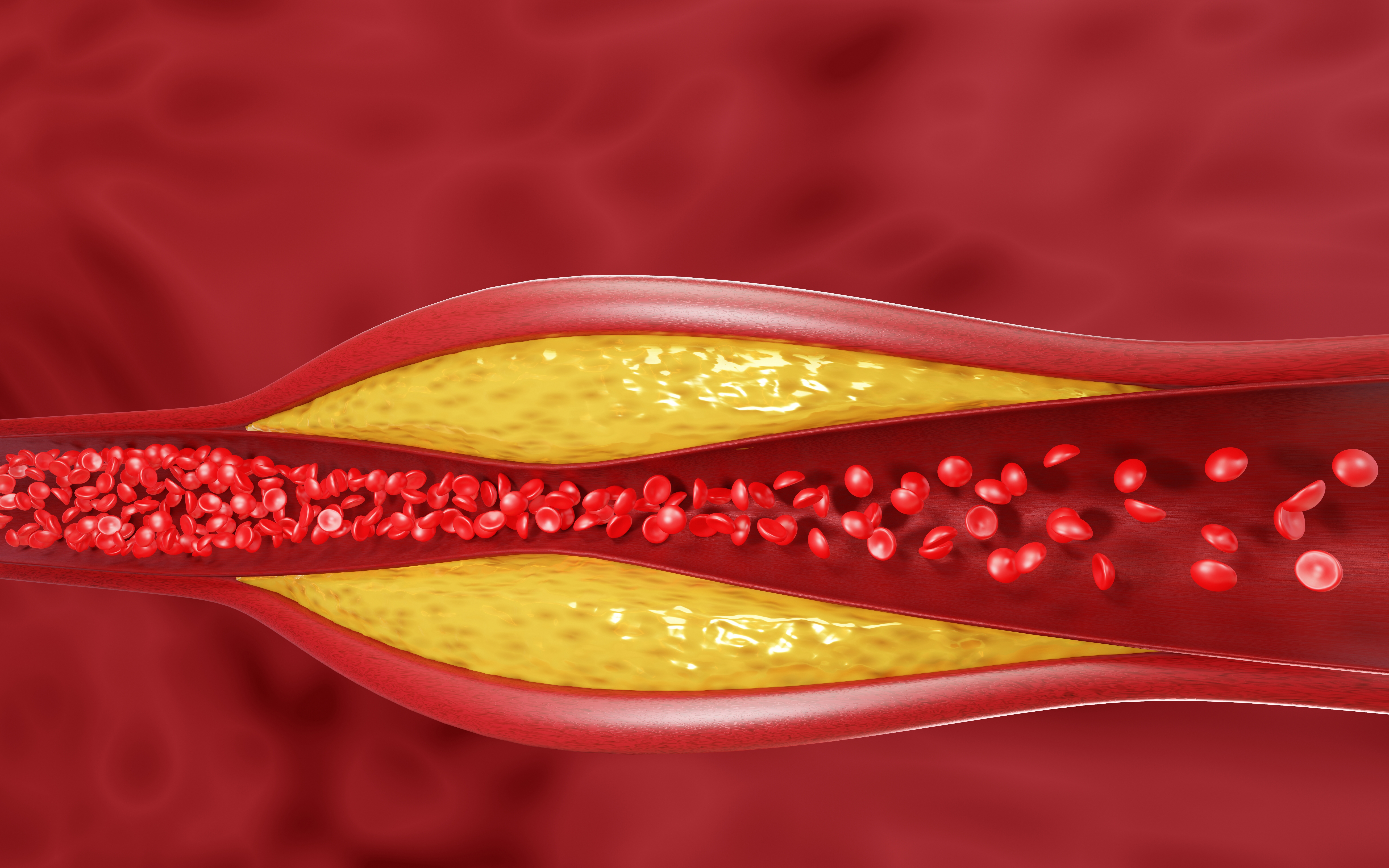
Atherosclerosis is a disease that leads to the narrowing of the artery lumen due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques composed mainly of cholesterol. It is associated with abnormal blood flow caused by narrowing the lumen of blood vessels and, consequently, not enough oxygen getting to the individual organs. In severe cases, it can lead to complications such as coronary heart disease and even stroke.
Hyperlipidemia is strongly related to atherosclerosis since it is LDL lipoproteins that, after penetrating under the blood vessel wall, cause cholesterol to be deposited there. On the other hand, HDL lipoproteins take cholesterol from the artery wall and carry it to the liver, so they have an anti-atherosclerotic effect. Therefore, the higher the level of bad cholesterol in the plasma, the greater the risk of atherosclerosis. Conversely, high levels of good cholesterol prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
High cholesterol is a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease, leading to complications like heart attack and stroke. It's closely linked to an increased risk of death from coronary heart disease. However, the good news is that you can lower your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of developing these conditions. Identifying high cholesterol early on is crucial, as well as taking the necessary steps to treat it and make lifestyle changes. This will help prevent the occurrence of these dangerous complications.
Very high triglyceride levels of up to 1,000 milligrams/dL are a risk factor for the development of acute pancreatitis![]() (inflammation of the pancreas). The reasons for this connection are not fully known.
(inflammation of the pancreas). The reasons for this connection are not fully known.
High LDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of developing gallstones. Gallstones are a disease affecting the bile ducts, in which bile components collect in the gallbladder and harden. These components are hard lumps of cholesterol, bilirubin, bile acids, and calcium salts. Cholesterol and pigment gallstones are distinguished depending on the substance from which they are formed. The cause of the formation of gallstones![]() is a disturbance in the metabolism of cholesterol contained in bile – if there is more cholesterol than can be dissolved, cholesterol crystals precipitate, gradually clumping into larger lumps and forming stones.
is a disturbance in the metabolism of cholesterol contained in bile – if there is more cholesterol than can be dissolved, cholesterol crystals precipitate, gradually clumping into larger lumps and forming stones.
People with hyperlipidemia usually find out about it late. This is because this disease does not produce any characteristic symptoms. Only in the case of hypercholesterolemia may the so-called xanthelasma![]() appear, which are yellow lumps of cholesterol under the skin around the eyelids.
appear, which are yellow lumps of cholesterol under the skin around the eyelids.
Hyperlipidemia is usually detected accidentally during routine blood tests or when severe cardiovascular diseases such as a heart attack or stroke have already developed.
Hyperlipidemias are disorders that accelerate the development of atherosclerosis and its complications; therefore, indirect symptoms of lipid metabolism disorders are symptoms of atherosclerosis complications:
Some people have higher chances of hyperlipidemia development. The risk factors include:
To determine whether you are at risk for hyperlipidemia, your doctor may need to:
A test called a lipid panel is performed to determine the level of lipids in the blood. The lipid panel measures different types of cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood. It includes total cholesterol, LDL “bad” cholesterol, HDL “good” cholesterol, and triglycerides. The test can also determine the concentration of the VLDL fraction.
| Cholesterol Type: | Optimal value: |
| Total Cholesterol | Less than 200 mg/dL |
| LDL Cholesterol | Less than 100 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | Greater than or equal to 60 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides | Less than 150 mg/dL |
The doctor can calculate the 10-year risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD![]() ) using a unique calculator based on the information obtained. The doctor will need information such as your gender, age, race, blood pressure values, cholesterol level, and whether you have diabetes, hypertension, or smoked cigarettes.
) using a unique calculator based on the information obtained. The doctor will need information such as your gender, age, race, blood pressure values, cholesterol level, and whether you have diabetes, hypertension, or smoked cigarettes.

The test should be performed in people who have a family history of lipid (fat) disorders and heart attacks, as well as in obese people and smokers. The test is also recommended in patients with hypertension, diabetes, kidney disease, and in people over 40 years of age![]() .
.
A lipid panel is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment with lipid-lowering medications and the condition of patients after a stroke or heart attack.
The test is sometimes (but not always) performed on an empty stomach. You may be asked to eat your last meal up to 12 hours before the test. You must not drink alcohol 24 hours before it is performed.
For some people, lifestyle changes are enough to lower their cholesterol levels, while for others, they aren't enough. However, only some people are willing to improve their lifestyle habits. Then, medication treatment is required.
Lifestyle habits that should be followed include:
The main hyperlipidemia medications are statins![]() – the drugs whose job is to lower levels of bad cholesterol circulating in your blood. However, your doctor may prescribe you another medicine if:
– the drugs whose job is to lower levels of bad cholesterol circulating in your blood. However, your doctor may prescribe you another medicine if:
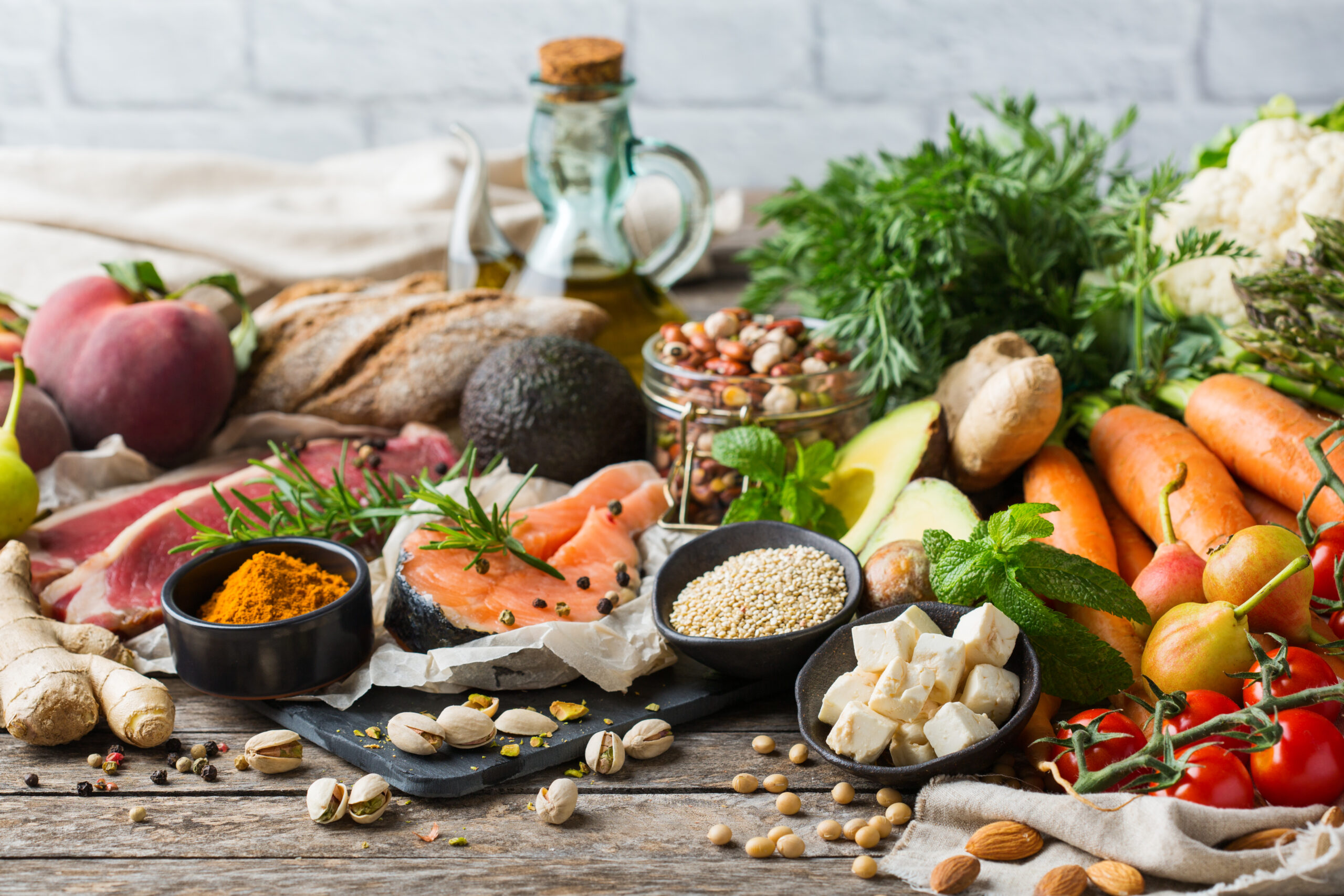

To prevent the increase in lipid levels, it is important to make some lifestyle modifications. These changes have a positive impact on cholesterol levels and help maintain normal blood pressure and sugar levels.
Exercise helps maintain or restore a favorable proportion between HDL and LDL levels. Training should be regular. Per week, performing at least 150 minutes![]() (2.5 hours) of exercise is recommended. Start with gentle forms of exercise – walking, marching, and over time, decide on more intense ones – running, swimming, cycling.
(2.5 hours) of exercise is recommended. Start with gentle forms of exercise – walking, marching, and over time, decide on more intense ones – running, swimming, cycling.
To lower the levels of unhealthy cholesterol in your bloodstream, try to cut back on fatty foods, particularly those high in saturated fats.
Try to eat more:
However, try to avoid products such as:
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption increase the chances of serious cardiovascular events such as heart attack or stroke. If you require help quitting smoking or reducing your alcohol intake, contact your GP for advice.
You should contact your GP for routine tests if you are in the risk group of developing hyperlipidemia (you have a family history of high cholesterol, are over 40 years old, obese, or smoking).
If you have hyperlipidemia and experience symptoms of a heart attack or stroke, call an ambulance immediately.