An urologist is a doctor who specializes in the conclusion, administration, and research of issues relating to the male reproductive framework and the female urinary tract. Various organ frameworks are treated by urology, counting the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, as well as the male reproductive framework, which incorporates the penis, prostate, and testicles.
Therapeutic school, a urology residency program, and habitually advanced pro courses in reconstructive urology, pediatric urology, or urologic oncology are all portions of the comprehensive preparation that urologists get.
A urologist could be a specialist, and a surgeon joined together. To carry out this double part, they have to have a special set of abilities that combine the exactness of a specialist with the symptomatic understanding of a vital master. They give treatment for a wide run of ailments, including kidney stones, urinary tract diseases, and complex cancers of the male framework and urinary tract. Urologists collaborate with other specialists, such as gynecologists, nephrologists, and oncologists, to provide comprehensive care. It is fundamental for individuals to keep up with patient's health and well-being, regardless of sex, especially as individuals age and become more vulnerable to urological issues.

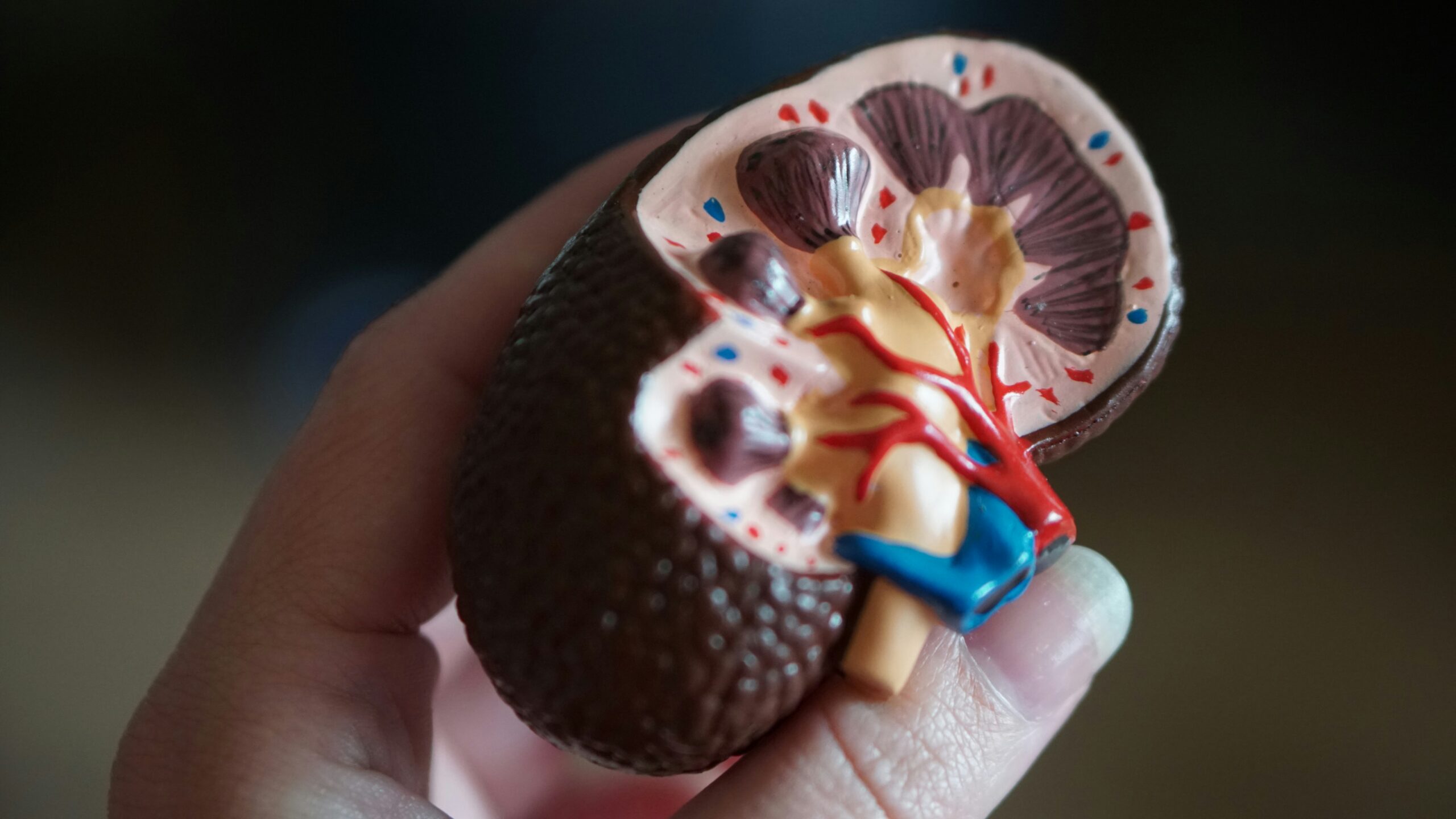
The conclusion and treatment of conditions influencing the male reproductive framework and urinary tract are the most common concerns of urology. This medication zone treats a wide range of ailments, counting generous and harmful illnesses and congenital abnormalities. One of the foremost critical frameworks within the body, the urinary tract, is responsible for killing squander and additional liquid while protecting electrolyte adjust. Any disturbance to its operation may have deplorable impacts on one's well-being.
The combination of therapeutic and surgical treatment makes urology uncommon. From negligibly obtrusive methods like laparoscopy and endoscopic surgery to more included strategies like robotic-assisted prostatectomy and kidney transplantation, urologists are prepared to embrace a wide extend of surgeries. In expansion to their surgical mastery, they have a vital understanding of treating urological clutters, such as endorsing antimicrobials for urinary tract diseases, over-the-counter drugs for bladder hyperactivity, or hormonal treatment for prostate cancer.
Individuals of all ages and sexual orientations may have to see a urologist a few times, depending on their concerns. Even though it is ordinarily connected with male well-being, specifically illnesses of the prostate and male reproductive framework, urology may be a claim to fame that treats major well-being issues in both ladies and children. Knowing when to call a urologist is basic for the early location and treatment of conceivable well-being issues.
Guys are more likely to require urological administrations, especially as they get more seasoned. Erectile brokenness, prostate cancer, and prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) are common in more seasoned men and may require specialized treatment. Men who have urination issues, blood in their pee, or any other sexual well-being issues ought to contact a urologist. Moreover, men with a family history of prostate cancer are frequently urged to see a urologist on a normal premise to evaluate the well-being of their prostate.
Moreover, ladies visit urologists routinely, strikingly for pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, and UTIs. UTIs are more common in ladies due to the anatomical arrangement of the female urinary framework, and repetitive diseases may demonstrate a fundamental condition requiring urological examination. Ladies who have trouble purging their bladder, blood in their urine, or persistent pelvic torment ought to see a urologist to decide the cause and look for treatment.
A kid may have to see a urologist if they have innate anomalies of the genitalia or urinary framework, such as hypospadias, vesicoureteral reflux, or undescended testicles. Specialists in both conclusion and treatment and pediatric urologists guarantee that kids get the care they require to create ordinarily and maintain long-term well-being.

In urology, an exact determination is fundamental for viable treatment. Urologists utilize various demonstrative strategies to assess the reproductive framework and urinary tract. These approaches extend from straightforward pee testing to complex imaging gear and less intrusive strategies. The conclusion handle is decided by the patient's side effects, therapeutic history, and plausible condition.
One of the foremost essential, however imperative, symptomatic devices in urology is the urinalysis![]() . As a portion of this examination, urine samples are analyzed to look for inconsistencies showing various urological issues. The nearness of blood, microbes, protein, or glucose within the urine might indicate several well-being issues. Blood within the pee, called hematuria, can cause kidney stones, bladder cancer, or urinary tract diseases. Peepee-containing microbes may be a clear sign of ailment, but pee-containing protein may be a sign of kidney harm. A urinalysis is frequently the primary step in concluding numerous urological conditions. On the off chance that irregularities are found, extra advanced testing is more often than not carried out.
. As a portion of this examination, urine samples are analyzed to look for inconsistencies showing various urological issues. The nearness of blood, microbes, protein, or glucose within the urine might indicate several well-being issues. Blood within the pee, called hematuria, can cause kidney stones, bladder cancer, or urinary tract diseases. Peepee-containing microbes may be a clear sign of ailment, but pee-containing protein may be a sign of kidney harm. A urinalysis is frequently the primary step in concluding numerous urological conditions. On the off chance that irregularities are found, extra advanced testing is more often than not carried out.
Urological determination is mostly based on imaging modalities that give careful pictures of the urinary tract and reproductive organs. These strategies incorporate ultrasound, X-rays, computed tomography (CT) checks, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ultrasound is routinely used to assess the kidneys, bladder, and prostate, and it is exceptionally successful in finding kidney stones, tumors, and sores. It could be a noninvasive treatment that employs sound waves to create photos of the interior organs.
CT looks, and MRIs are commonly utilized for more in-depth evaluations since they deliver more nitty gritty pictures. A CT check, for example, can create cross-sectional images of the urinary tract that can be utilized to analyze conditions such as kidney stones, cancers, and intrinsic inabilities. An MRI can be used to analyze delicate tissue structures such as the bladder or prostate, and it is very valuable within the recognizable proof of extreme bladder cancer cases or prostate cancer.
A cystoscopy, a negligibly obtrusive treatment, permits a urologist to look at the bladder and urethra. This treatment includes embedding a lean, camera-equipped tube (cystoscope) into the bladder through the urethra. That permits the urologist to coordinate exams of the bladder and urethra linings, identify inconsistencies, and attempt minor medications such as expelling little bladder stones or collecting tissue tests for biopsy. Cystoscopy broadly recognizes urinary strictures, interstitial cystitis, and bladder cancer. Even though the operation is, for the most part, well-gotten, patients are regularly given a nearby anesthetic to lighten any inconvenience.
Urodynamic testing could be an arrangement of tests that decide how well the bladder and urethra store and discharge pee. These tests are exceptionally advantageous in diagnosing overactive bladder, urinary maintenance, and incontinence. Urodynamic ponders degree the bladder's inner weight, pee stream rate, and muscular contractions. Urologists can utilize this information to set up the basic cause of a patient's pee challenges and alter their treatment approach.
Amid a biopsy, a little test of tissue from an organ or other real portion is taken, and it is inspected beneath a magnifying instrument. In urology, biopsies are as often as possible done to identify malignancies of the prostate, bladder, and kidney. For illustration, amid a prostate biopsy, minor tissue tests are taken from the prostate organ employing a needle guided by ultrasound innovation. A pathologist at that point looks over these tests to decide whether cancer cells are shown. In order to affirm a cancer determination and discover the organization and seriousness of the infection, which influences treatment proposals, biopsies are fundamental.
Urologists treat a wide range of health issues, including basic sicknesses like urinary tract infections and more serious conditions like bladder and reproductive cancer. They offer a number of treatments that are suited to each patient's individual needs. The following will include a few of the foremost visit health concerns that urologists address, as well as the medicines that are utilized.
Difficult stores of minerals and salts that shape the interior of the kidney are called kidney stones. They may result in serious torment, nausea, and issues urinating. Depending on the measure, area, and cosmetics of kidney stones, urologists utilize a run of treatment strategies. More prominent liquid admissions and torment medicine can offer assistance to little stones that pass on their possession, but bigger stones frequently require therapeutic consideration.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy![]() (ESWL) may be a noninvasive method that utilizes sound waves to break down stones into little pieces that can be disposed of through pee. Ureteroscopy could be a device that urologists can utilize to distinguish and expel huge stones or stones that are situated so that endoscopic sutures don't work. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), which includes making a minor entry point within the back to reach and evacuate the stone, is required in a few cases.
(ESWL) may be a noninvasive method that utilizes sound waves to break down stones into little pieces that can be disposed of through pee. Ureteroscopy could be a device that urologists can utilize to distinguish and expel huge stones or stones that are situated so that endoscopic sutures don't work. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), which includes making a minor entry point within the back to reach and evacuate the stone, is required in a few cases.
Urinary tract diseases are a driving cause of urological visits. Urinary tract contaminations (UTIs) are caused by microbes that enter the urinary tract and cause side effects such as burning while urinating visit, urination, and ridiculous or dinky pee. The larger part of UTIs can be treated with antimicrobials by a common professional, but extreme or tireless diseases may require the interview of a urologist.
An ultrasound or CT check are two imaging modalities that urologists may use to rummage around for anatomical variations from the norm within the urinary tract, which will be the source of repetitive diseases. They also exhort people to change their count of calories or drink more water to assist in warding off diseases in the future. Treating the basic condition, such as kidney stones or a broadened prostate, may be essential to avoid further UTIs on the off chance that it is found to be the cause of repetitive diseases.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia![]() , or BPH, maybe a predominant condition influencing more seasoned men that causes the prostate organ to grow and press against the urethra. This sickness causes urinary tract indications such as decreased pee stream, trouble voiding, and frequent urination, particularly at night. Even though BPH isn't threatening, it can radically diminish a man's quality of life.
, or BPH, maybe a predominant condition influencing more seasoned men that causes the prostate organ to grow and press against the urethra. This sickness causes urinary tract indications such as decreased pee stream, trouble voiding, and frequent urination, particularly at night. Even though BPH isn't threatening, it can radically diminish a man's quality of life.
The seriousness of side effects decides treatment for BPH. Mellow cases can be treated with a way of life alterations, such as constraining liquid admissions time recent sleep time, or with drugs that unwind the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, in this manner progressing pee stream. In more serious circumstances, urologists may propose surgical methods. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) could be a common surgical treatment that evacuates additional prostate tissue and calms blockage. Other negligibly intrusive prostate-lessening treatments incorporate laser treatment and transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT).
Urologists are very concerned about prostate cancer since it is one of the foremost common tumors in guys. Urologists are fundamental in the conclusion, treatment, and ceaseless observation of this issue since early discovery is basic to a great result. The PSA blood test![]() , which gauges the level of prostate-specific antigens in the blood, is the foremost broadly utilized screening method. Prostate cancer may be shown by raised PSA levels, but more testing, such as a biopsy, is required to affirm the conclusion.
, which gauges the level of prostate-specific antigens in the blood, is the foremost broadly utilized screening method. Prostate cancer may be shown by raised PSA levels, but more testing, such as a biopsy, is required to affirm the conclusion.
Prostate cancer treatment choices contrast depending on the malady arrangement, understanding of age, and general well-being. In a few circumstances, dynamic observation may be demonstrated, including frequently assessing the tumor but not treating it immediately.