The trachea, colloquially known as the windpipe, is one of the operational components of the respiratory framework, whose part is to create, beyond any doubt, the rest of the framework is working well. The airway is the trachea, where the bronchi interface to the larynx – the voice box – and interfaces to the lungs.
Among all parts of the transport framework, the trachea is one of the pivotal parts that the body needs for oxygen conveyance to outlive. The truth is that the trachea is utilized as an air section amid breathing in, and the breathing out of the airflow that goes straight to the trachea is the reason for its being the foremost vital portion of the respiratory framework.
The trachea's flexibility is the figure that empowers it to be sloped or bowed to some degree and still stay clear of the air channels. The trachea's unique highlight of employing a solid cartilage ring to create it is the most reason for this. For grown-ups, its diameter is 2-3 centimeters, and its length is 10-12 centimeters. Its length is additionally approximately thirty centimeters. The clarification for this can be that being within the neck and chest region, there's a high probability that air can pass through and not be obstructed by external forces.
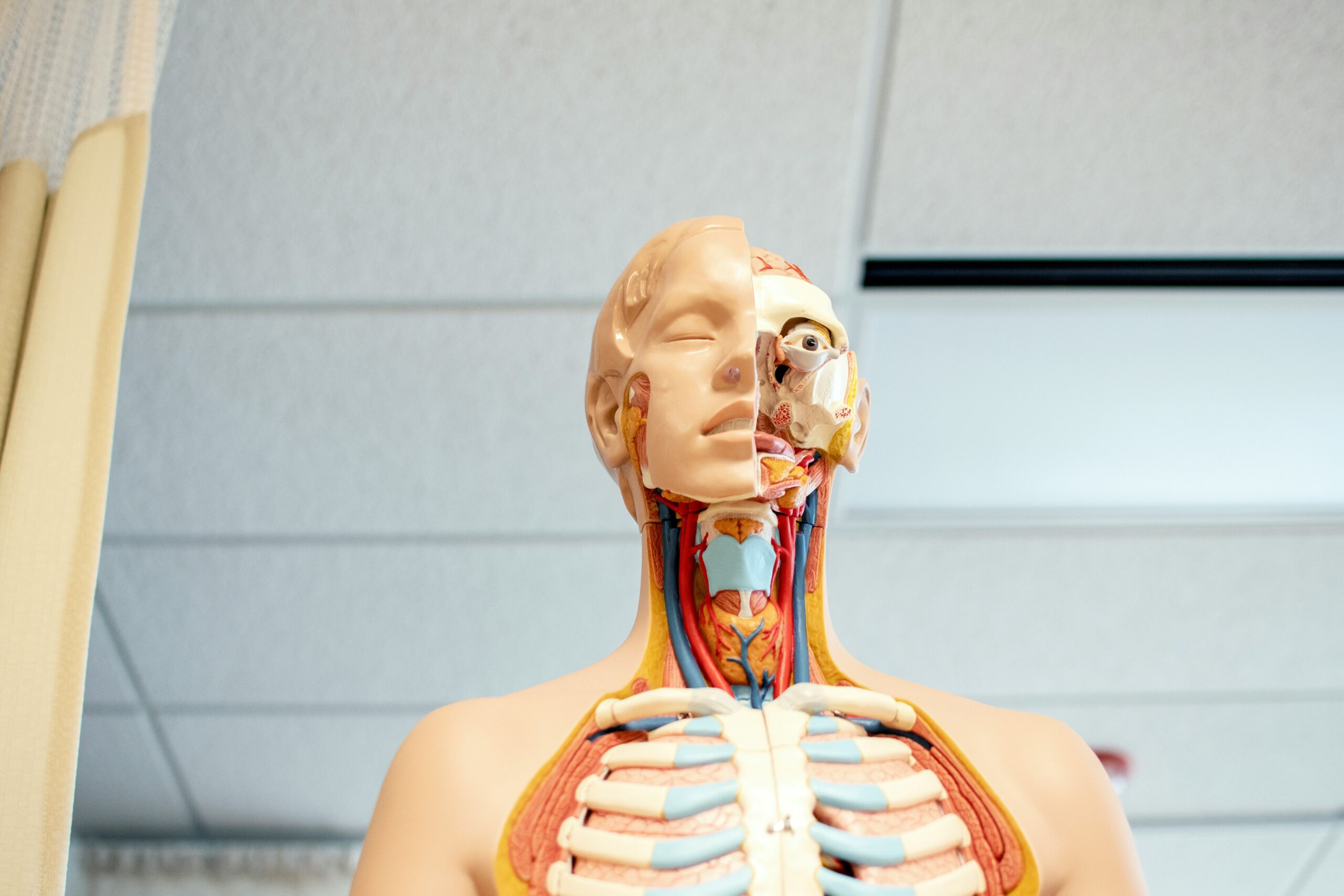
A tube made of delicate tissue and cartilage is known as the trachea. It starts right before the esophagus and voyages the complete way down from the larynx to the chest, where it forks into the left and right primary bronchi![]() . At that point, the bronchi go down into the lungs, where they advance partition to make little airways. The exceedingly delicate region in which the trachea parts into the two fundamental bronchi is, as a rule, called the carina. This zone can be exasperated, and hacking may happen.
. At that point, the bronchi go down into the lungs, where they advance partition to make little airways. The exceedingly delicate region in which the trachea parts into the two fundamental bronchi is, as a rule, called the carina. This zone can be exasperated, and hacking may happen.
The structure of the trachea includes a few strata. The highest layer is connective tissue, which is the most important component of the trachea. As it were, it is mindful of holding the trachea in place and securing it from harm. The other one contains around 15 to 20 C-shaped rings made of cartilage that guarantee the trachea's unconventional, unbending nature and adaptability. Nourishment goes through the esophagus, which is precisely found behind the trachea, and these rings are missing at the back, so the trachea can compress just a division. The extraordinary plan of this gadget permits bolstering and breathing to happen simultaneously without any impedances.
The epithelial layer of the trachea is lined with cilia that are secured by the tracheal layer. These little, hair-like particles work together in a bunch to assemble the dust, microbes, and other particulates from the breath of our being. As a result, the air is exceptionally immaculate. Underneath this mucous layer are the smooth muscle filaments that contract and dilate the trachea, in this way tweaking ventilation.
The errand of the trachea is to communicate oxygen from the mouth and nostrils to the lungs. The air passes through the nasal or oral cavities, through the larynx, and then the trachea, where it trades carbon dioxide for oxygen during breath. The trachea is crucial for breathing since it consequently carries out this work during breath.
The trachea is another exceptionally vital organ with other essential functions besides providing oxygen. The most important one is to guarantee the respiratory framework is secure. Tidy and pathogens are halted at the mucosal lining and cilia of the trachea, where they can't reach the delicate tissues of the lungs. The component secures the body from respiratory, inflammatory, and irresistible infections.
Moreover, the trachea produces sound. The voice is delivered primarily by air within the trachea, but the vocal strings are too vibrated by air within the larynx. Tracheal blockages or aggravation can change the timbre of a person's voice.
The trachea also produces sound. Voice generation is straightforwardly affected by the larynx, in spite of the fact that the vocal strings are vibrated by air within the trachea during speech. Tracheal blockages or irritation can impact the timbre of one's voice.
One of the other vital errands of the trachea is managing airway weight. Amid the method of breathing, the trachea experiences little development and withdrawal to adjust the weight differential. The weight varieties are critical for the lungs' expansion and flattening. Amid physically strenuous endeavors, for example, a workout, the trachea can be widened, and in this way, more air can be bolstered to the lungs, and the next sum of oxygen will enter the body.

The area of the trachea is one of the reasons why it is harmed; it acts as a clear pathway for air to pass through. Various wounds, peculiarities, and illnesses may lead to diminished productivity of the trachea. Regarding tracheitis, the trachea remains the major point of reference. Usually, the irritation of the trachea is caused by microscopic organisms or viral infection. The trachea is among the foremost commonly specified sicknesses found in medical writing. Burning throat, respiratory inconveniences, and a hack are the classic side effects of tracheitis. The same are the normal side effects of the affliction. Other than that, a complicated ailment may result in airway hindrance.
Tracheal stenosis, a condition in which the trachea is contracted, is one of the major concerns for numerous. The leading causes of scarring, tumors, or inherent peculiarities are the ones that are the causes of stenosis. Stenosis could be a condition where the airway to the lungs gets smaller, causing wheezing, dyspnea, and respiratory contaminations. Stenosis is a condition that can be gone with a few other side effects. Injury, surgical mediation, and delayed endotracheal tube utilization are the most likely causes of tracheal stenosis.
Tracheomalacia could be a situation where the cartilage rings of the trachea get weak. This can be the reason why the trachea collapses once you breathe. The condition is additionally exacerbated by rehashed assaults of respiratory contaminations, wheezing, and breathing challenges, which in some cases could put an individual in a basic condition. Tracheomalacia can be separated into two groups: congenital, which exists at birth, and obtained, which can be caused by persistent contaminations or mechanical wounds.
Even though it isn't a frequent case, the event of tracheal tumors isn't an abnormal one, and they can come in two sorts:
Malignant and benign. They may well be the reason for the dynamic tracheal narrowing, which can cause the patient to have expanding respiratory troubles. Concurring to the measure and area of the tumor, surgical mediation may be the alternative.
Due to a mishap or harm, the trachea can burst, and a gap may be gotten to be a portion of it. Therapeutic movers must rapidly and accurately open aviation routes to keep appalling things from happening.
A full medical history and physical exam are used along with the symptoms to diagnose airway problems. If a doctor or nurse suspects that a patient has a condition with shortness of breath, a wet cough, or other breathing problems, then they may become suspicious. After that, more tests are needed.
Chest X-rays are initial lung evaluations. A beam is first sent across the chest and then via airways to the area to take pictures of the lungs. This way, the doctor can identify narrowings, tumors, and other lesions. An X-ray of the chest may give a big picture of the airway but may not show enough detail.
CT scans are the most reliable source of further data. They represent the airway and adjacent tissue cross-sectionally, helping the doctor determine if tracheal stenosis, a growth, or inflammation is present. CT studies can detect lung narrowings and indicate the location and severity of the problem.
A bronchoscope![]() is a thin, flexible tube with a camera inserted into the airways and bronchi through the nose or mouth to look inside. A biopsy of the trachea can be shifted and viewed. If you have tracheitis, lumps, or stenosis, the doctor might check you for those conditions.
is a thin, flexible tube with a camera inserted into the airways and bronchi through the nose or mouth to look inside. A biopsy of the trachea can be shifted and viewed. If you have tracheitis, lumps, or stenosis, the doctor might check you for those conditions.
Dynamic airway fluoroscopy is one of the technologies that may be used to treat people suspected of having an airway collapse. When surgical treatment is done, X-ray imaging can be used to check for abnormal movements of the trachea during breathing. The detection of tracheomalacia is the reason behind this: when the trachea moves strangely or even collapses during breathing.
If a tumor is suspected, a biopsy can be performed to determine whether the growth is cancerous. In this method, a small piece of tissue is taken from the trachea to be examined using bronchoscopy or surgical intervention. The sample is then examined with a microscope to determine whether it is a cancer cell.
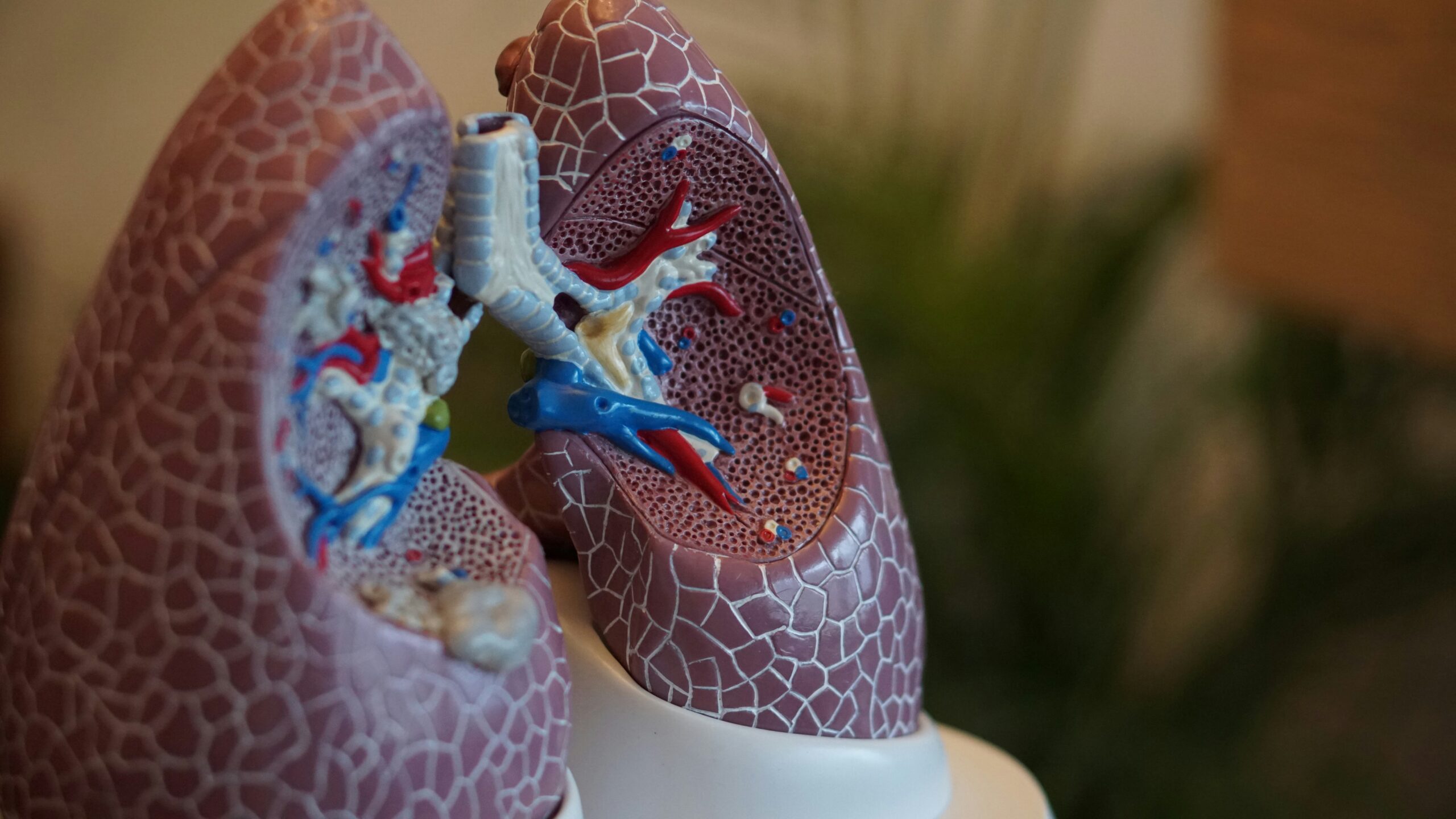
Treating tracheal challenges is decided by the patient's present well-being status, the degree of the sickness, and the fundamental causes. Non-invasive treatments and drugs are more often than not the treatment of choice; however, in a few cases, surgical intercession is required.
Antibiotics are the foremost common medicines used to treat tracheal contaminations caused by bacteria, such as tracheitis. The primary line of treatment for bacterial diseases is strong care, which may be done by understanding at home by taking rest, liquids, and anti-inflammatory medicines. These treatments can also offer assistance with other symptoms, including high temperatures and soreness. Airway suctioning could be a strategy that will be utilized to evacuate an abundance of bodily fluid from an obstructed airway.
Tracheal stenosis![]() treatment may, in some cases, require more intrusive methods. Tracheal dilation may be a procedure in which a doctor employs a balloon or a specialized tool to extend a narrow portion of the trachea. In a few cases, the widening procedure can work, but on the off chance that the narrowing happens again, the strategy may need to be rehashed.
treatment may, in some cases, require more intrusive methods. Tracheal dilation may be a procedure in which a doctor employs a balloon or a specialized tool to extend a narrow portion of the trachea. In a few cases, the widening procedure can work, but on the off chance that the narrowing happens again, the strategy may need to be rehashed.
The elective administration of stenosis through the stent situating within the stenosis can be utilized. For trachea stenting, a metal or silicone fabric is permitted to be embedded into the trachea's stenosis to preserve the trachea's patency and the ordinary stream of air at the side, keeping up ordinary wind current regulation. The stent is planned in such a way that it acts like a part of the trachea that is open. This permits the other portion to stay unaltered. Patients who may benefit from a stent situation are those who qualify for surgery and have repetitive stenosis.
In most cases, tracheal extraction is the as it were resort for serious harm or malady.
This strategy includes cutting off the damaged area of the trachea and joining the two remaining parts to reestablish ordinary work. Tracheal resection is commonly performed for neoplasms, impressive stenosis, and injury.
Patients with tracheomalacia may be treated with positive airway pressure (PAP) through the trachea to keep the airway tract open during breath. In extraordinary cases, a tracheal prop or a tracheotomy may be utilized to prevent the airway from collapsing.
The surgical removal of tracheal tumors is possible if they are well-circumscribed and the tumors are operable or can be managed with other therapy modalities. In the case of the malignant type tumor, radiation or chemotherapy will be given either alone or together with surgery.
A tracheostomy![]() procedure may be required in life-threatening situations of airway obstruction or restricting airflow. A tiny opening is created at the front of the neck, and a tube is positioned through the trachea for the patient to breathe. Depending on the cause, a tracheostomy can be either temporary or permanent.
procedure may be required in life-threatening situations of airway obstruction or restricting airflow. A tiny opening is created at the front of the neck, and a tube is positioned through the trachea for the patient to breathe. Depending on the cause, a tracheostomy can be either temporary or permanent.
Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatories, which are prescribed to people with COPD and asthma, dilate the airways, mainly the trachea.