The field of medicine known as neurology studies the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's vital parameters, known as homeostasis, and is responsible for cognitive functions and memory.
On the other hand, the spinal cord aids in transmitting nerve impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous system, enabling conscious movement, coordination, balance control, muscle tension, and sensation of touch, pressure, and pain. Diseases affecting the central nervous system can result from e.g. impaired blood flow, infections, injuries, and congenital or acquired neurodegenerative diseases.
The peripheral nervous system comprises nerves and ganglia, which transmit information between the central nervous system and individual organs. Diseases of the peripheral nervous system are typically acquired, often due to conditions like diabetes, nutrient deficiencies, injuries, and alcohol abuse. These conditions can lead to sensory disorders, paresis, paralysis, and muscle atrophy.
The cornerstone of diagnosing and treating these disorders involves interviewing the patient and conducting a neurological examination.

The diseases most frequently treated by a neurologist![]() include:
include:
Before running specific tests, the neurologist conducts a detailed medical interview with the patient. This interview aims to learn about the patient's past neurological diseases, which may help determine which tests are needed. Before making a diagnosis, the neurologist performs or orders neurological tests![]() , including functional, physical, vascular, and imaging tests.
, including functional, physical, vascular, and imaging tests.
EEG (electroencephalogram![]() ) is necessary to assess the electrical activity of the brain, which is irreplaceable for making a diagnosis in cases in which the doctor suspects the occurrence of:
) is necessary to assess the electrical activity of the brain, which is irreplaceable for making a diagnosis in cases in which the doctor suspects the occurrence of:
An EMG test![]() is used when a doctor assesses the electrical activity of muscles and peripheral nerves. This examination is used to diagnose:
is used when a doctor assesses the electrical activity of muscles and peripheral nerves. This examination is used to diagnose:
Examination of the limbs and chest is performed to assess physiological reflexes, which include:
Doppler ultrasound![]() of intracerebral arteries – blood flow in the intracerebral veins and arteries is determined by observing the wavelength of the ultrasound wave. This method is used to diagnose diseases such as:
of intracerebral arteries – blood flow in the intracerebral veins and arteries is determined by observing the wavelength of the ultrasound wave. This method is used to diagnose diseases such as:
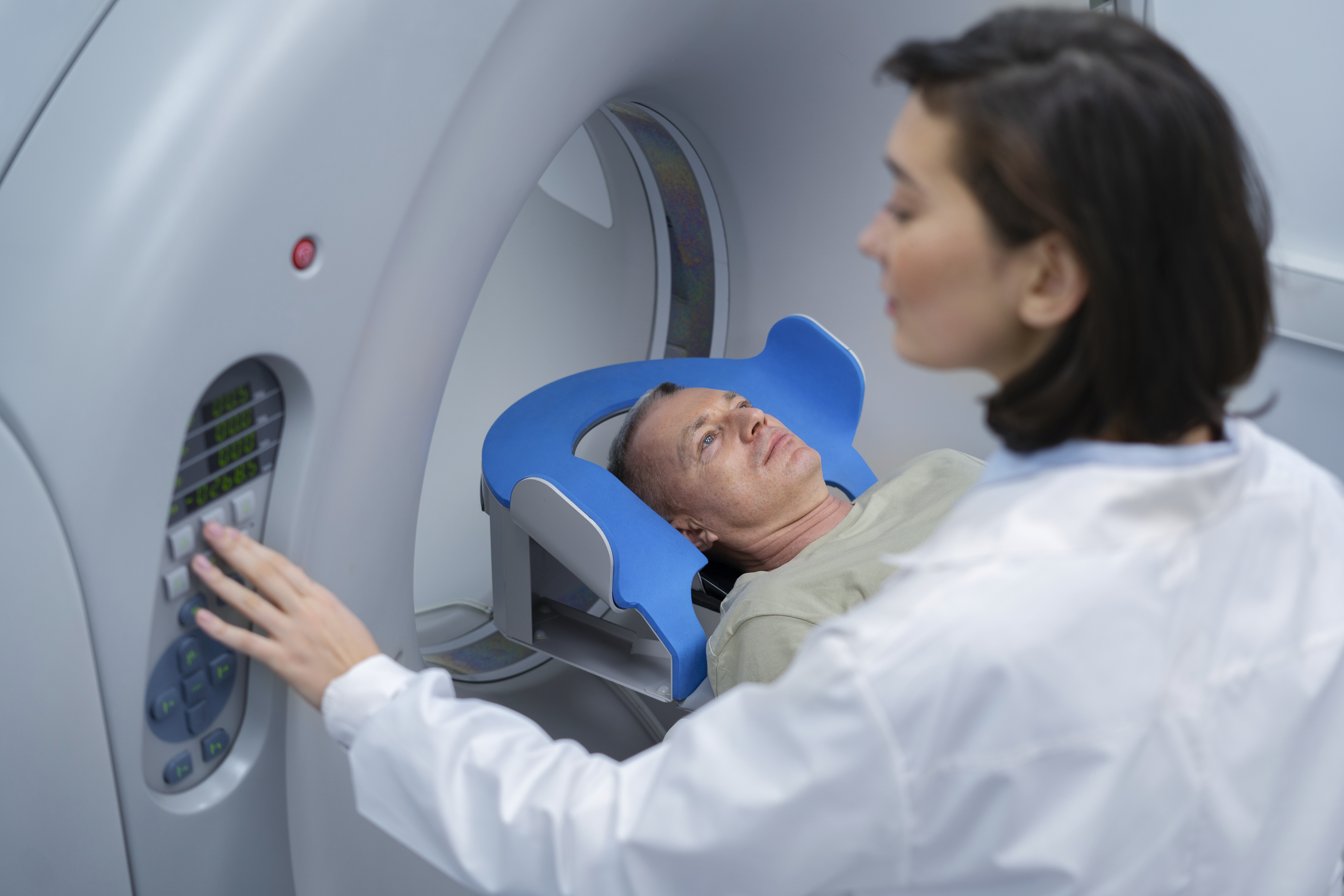
Computed tomography![]() is based on X-rays, enabling the detection of abnormalities in, among others, the brain or spine. Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to diagnose diseases such as:
is based on X-rays, enabling the detection of abnormalities in, among others, the brain or spine. Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to diagnose diseases such as:
Thanks to X-rays, the doctor can detect changes, among others within:
A visit to a neurologist is similar to other visits to specialists. However, it requires appropriate preparation. The patient needs to keep a diary noting the symptoms and associated ailments. The more detailed and specific the description, the greater the chance for an accurate diagnosis during the visit and appropriately selected pharmacology. It is worth including the following information in the diary regarding:
Consider starting a diary before your neurologist appointment. The more details you include, the better your chances of an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. Also, think about potential questions for the specialist. Don't forget to bring all your current medical records, such as blood tests, ESR, and cholesterol levels.
When you first meet with the neurologist, you are in for a thorough medical interview. The doctor may ask about your medications, symptoms, past illnesses, and family history of neurological diseases. Your lifestyle, job, and diet may also be discussed. This information helps the doctor form a complete understanding and aids in making an accurate diagnosis.
Following the interview, the neurologist will move on to a basic nervous system examination. It usually involves testing physiological reflexes like the biceps, knee, ankle, and brachioradial reflexes. The specialist will also assess speech, sensation, body posture, and walking patterns. Often, the interview and examination are enough for a diagnosis. If there's any uncertainty, the neurologist may recommend additional neurological tests.
If you notice repeating neurological symptoms, seeing a neurologist as soon as possible is important. The first time the symptoms occur might go unnoticed, but if they return regularly, it's a clear sign to get medical help. Neurological symptoms that the patient should not underestimate include:
There are emergencies and unexpected symptoms that we cannot ignore in any way. Immediate intervention by a neurologist may save the patient's life and health. Disturbing symptoms that should be immediately consulted with a neurologist include:
Sometimes, a neonatologist, pediatrician, or family doctor may recommend a newborn or infant to see a pediatric neurologist![]() for a preventive visit. It might be necessary if the baby was part of a high-risk pregnancy, born from a cesarean section, exposed to infections during pregnancy, or born prematurely with low birth weight. Since infants develop rapidly, it's significant to closely monitor their developmental milestones – skills acquired in a particular order and time. All disturbing symptoms or possible delays should be reported to the pediatrician or family doctor, especially:
for a preventive visit. It might be necessary if the baby was part of a high-risk pregnancy, born from a cesarean section, exposed to infections during pregnancy, or born prematurely with low birth weight. Since infants develop rapidly, it's significant to closely monitor their developmental milestones – skills acquired in a particular order and time. All disturbing symptoms or possible delays should be reported to the pediatrician or family doctor, especially:
Neurological symptoms in older children and teenagers may resemble those in adults. Particular attention should be paid to:
A neurological consultation may also be indicated when diagnosing ADHD or autism spectrum disorders.

Neurological rehabilitation![]() is a process, a series of activities optimizing a person's participation and functioning in society. It also involves restoring the highest possible quality of life. Rehabilitation in neurological diseases should not be treated as a special type of intervention, and attention must be focused on the patient as a person when selecting actions. Formulated short—and long-term goals should be based on social functioning, functional efficiency, and the psychological sphere.
is a process, a series of activities optimizing a person's participation and functioning in society. It also involves restoring the highest possible quality of life. Rehabilitation in neurological diseases should not be treated as a special type of intervention, and attention must be focused on the patient as a person when selecting actions. Formulated short—and long-term goals should be based on social functioning, functional efficiency, and the psychological sphere.
Rehabilitation and physiotherapy in neurology should not cover all patients, not only those with good prospects.
Early neurological rehabilitation is almost a guarantee of improved functional efficiency. It is the main component of treatment for many different diseases. The basic indications for the use of neurological rehabilitation and exercises include:
Neurological rehabilitation methods include a wide repertoire of concepts that provide opportunities to regain fitness. It is essential to know the indications for their use and to carry out rehabilitation procedures by applicable rules and only by qualified people.
Neurological rehabilitation is divided into early and chronic stages, with the selection depending on the specific disease presented. To ensure effectiveness, it requires a multidisciplinary team, including physiotherapists, psychologists, neurologists, and rehabilitation doctors. Early intervention has been shown to help complete recovery or reduce negative effects. Specialized facilities offering comprehensive assistance in rehabilitation activities are available for conditions like Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke recovery, craniocerebral injury, cerebral palsy, and neurosurgical patients.
Neurorehabilitation can occur in a rehabilitator's office, where the exercises are discussed thoroughly with the patient. The rehabilitator may then prescribe exercises to be performed independently at home. Some patients may also opt for rehabilitation centers that provide comprehensive support in the neurorehabilitation process. The following are the most commonly used methods in neurorehabilitation: