Liposuction is a procedure that is performed on patients to remove fatty tissue. Different names for the procedure include lipoplasty and lipectomy. The method of body contouring is invasive and requires recovery after the procedure.
Getting rid of fat deposits from various body parts is a popular surgical procedure for achieving results. The procedure is helpful, especially in cases where fat accumulates excessively in one place and could be more manageable.
Getting rid of fat by surgery is carried out under anesthesia. Before the procedure, patients specify which areas they wish to have fat removed from. The procedure is most commonly performed on the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks, but it is also possible to remove fat from different, unusual areas such as the arms or face. There are various methods of doing liposuction. During the procedure, fat deposits are broken up and then removed. The surgical procedure gets rid of large amounts of fatty tissue. It results in a reduction in body weight and the circumference of the part of the body being treated.

However, the total result is achieved after a few months, as patients need time to return to a regulated state after an invasive procedure. It is also important to follow post-surgery instructions to avoid problems. Lipoplasty can be risky, and patients may experience some complications. Awareness of the indications and contraindications of liposuction is also essential. Find out who can have lipoplasty and for whom the procedure may be risky.
Liposuction is an irreversible procedure to eliminate unnecessary or unwanted accumulations of fatty tissue called lipocytes. Fat tissue in the human body has a superficial and deep layer. The superficial layers of tissue contain a fibrous layer![]() , which is less amenable to the liposuction procedure. The deep layer, on the other hand, includes the areolar fat
, which is less amenable to the liposuction procedure. The deep layer, on the other hand, includes the areolar fat![]() , and this part is usually the goal of the procedure, as it is highly amenable to liposuction. The superficial layer can also be a procedure goal but is more prone to complications due to its low susceptibility.
, and this part is usually the goal of the procedure, as it is highly amenable to liposuction. The superficial layer can also be a procedure goal but is more prone to complications due to its low susceptibility.
The procedure began in the 1980s, and significant technological and procedural advances have occurred. The lipoplasty methods used include:
It is the classic type of lipoplasty procedure. The procedure is suction-assisted, using vacuum suction, which makes it possible to remove subcutaneous fat from various body areas. The suction is performed using special suction cannulas![]() . The devices are inserted under the skin through small incisions. There are multiple types and sizes of cannulas used for suction, depending on the area of the body to be treated.
. The devices are inserted under the skin through small incisions. There are multiple types and sizes of cannulas used for suction, depending on the area of the body to be treated.
Advances have made it possible to use narrower cannulas that allow superficial lipoplasty. A vibration technique is also possible, which uses a cannula that vibrates, making it easier and quicker to break up fatty deposits. After the procedure, specialists inform patients of the amount of fat extracted.
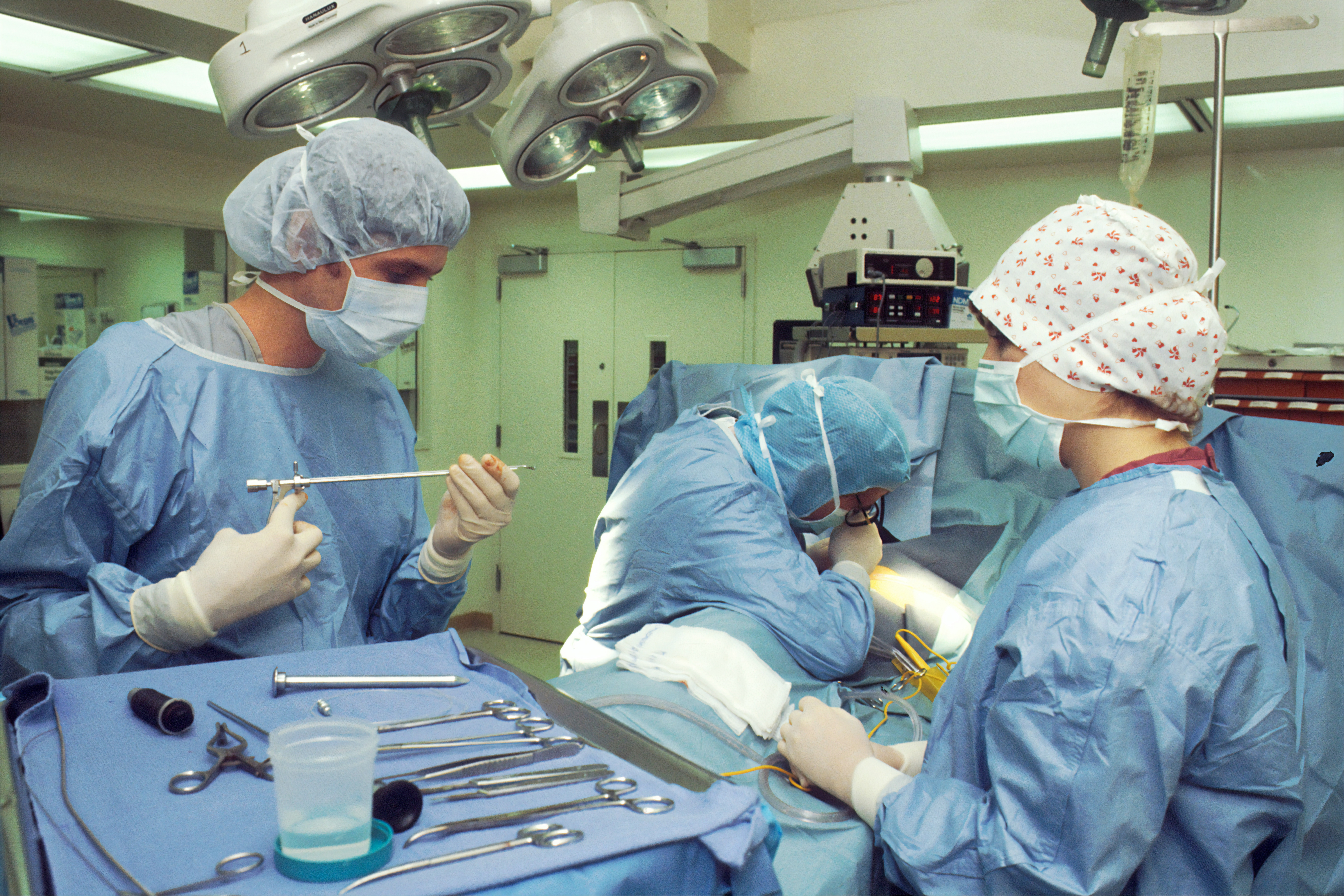
Syringe liposuction is the extraction of fat using a cannula and a special syringe with negative pressure, allowing precise control of the suction force. The procedure is recommended for selected body areas where it is difficult to eliminate excess fat despite diet and exercise. With syringe liposuction, the fat removed can be accurately measured and controlled. This type of lipoplasty is less invasive than classic procedures. Syringe liposuction removes relatively tiny amounts of fat, unlike a surgical method such as classic liposuction, which uses pumps to suction the fat.
The laser is a relatively new advancement in treating fatty tissue abnormalities. During an internal laser lipoplasty procedure, a cannula with a laser fiber is inserted. The fat tissue is broken up by the high energy emitted by the laser. The tissue is dissolved. The laser causes damage to the adipocyte membrane and the release of extracellular fluid. The laser also affects collagen coagulation, resulting in less trauma for patients. The dissolved fat is suctioned out and removed from the body.
The laser can also be applied externally transdermally. During the treatment, the skin is tightened, which is particularly beneficial for patients with reduced skin elasticity or excess skin. Various types of lasers with different powers are used in the procedures. The complications and effects of laser-assisted lipoplasty are similar to the classic method.
Suction lipoplasty enhanced with ultrasound can have many benefits. The procedure involves inserting a cannula that emits ultrasound waves through small incisions in the skin. Ultrasound can destroy the walls of fat cells, which causes the fat to liquefy, making it easier to suction it out. Using ultrasound makes it possible to separate the fat tissue from the surrounding tissues precisely.
Thanks to the use of ultrasound, the procedure can be trauma-free and painless and does not involve damage to nerves, muscles, or blood vessels. Studies have shown that ultrasound liposuction can reduce fat in these areas without causing significant damage or side effects.
Another method of lipoplasty is the aqueous technique, which involves using a jet of water to perform liposuction. It is a state-of-the-art procedure that produces quick results and is minimally invasive, so it does not require a long-term recovery time. In this method, fat is removed through a special needle.
The fat is quickly removed by injecting a cannula with a jet of a unique water solution into the tissues and drawing off the fluid and fat cells. The water beam fluffs up the fat cells, changing the structure of the tissue, which facilitates the procedure. In addition, the fat extracted by the aqueous method can be successfully used for autografting.
Patients who opt for lipoplasty should be carefully informed by specialists about the realistic results and risks. Many people mistakenly think that lipoplasty is a modern method of weight loss. Liposuction, on the other hand, is a method of body contouring and modeling that involves a certain level of invasiveness, depending on the technique used. It should also be borne in mind that fat removal surgery does not guarantee skin improvement results. The patient will proceed with an aesthetic lipoplasty procedure where the following indications are met:
Liposuction of fat from a particular region is possible where fat tissue is realistically present. There are cases of psychological disturbances where patients see a distorted body image and may perceive certain areas as fat, while anatomically, there is no excessive fat tissue there. In such cases, performing the procedure is not an option as it may worsen the health of the patients who should receive psychological care. Patients must, therefore, be excessively obese in the body region in question, showing a deviation from the normal body contour.

The ideal situation for liposuction is moderate to no excess body fat. Obese people often present for this type of surgery, but excessive obesity can pose a risk of complications after the procedure. Patients' body mass index (BMI) should include 30%![]() of normal. Patients with a high BMI, on the other hand, should undergo a series of pre-operative tests and laboratory work. It is also essential for patients to maintain a stable weight. It is recommended that the procedure be performed for a minimum of six months
of normal. Patients with a high BMI, on the other hand, should undergo a series of pre-operative tests and laboratory work. It is also essential for patients to maintain a stable weight. It is recommended that the procedure be performed for a minimum of six months![]() before undergoing it.
before undergoing it.
The best condition for a patient's skin during the procedure is minimal flaccidity. Patients with high skin flaccidity may experience postoperative complications related to excess skin tissue. The skin at the liposuction site may not shrink. In such situations, flabby, wrinkled skin with no tension above the corrected contour may not meet patients' expectations of the desired aesthetic outcome.
Patients should be informed of any risks before undergoing lipoplasty so that their choice is as informed as possible. It is, therefore, essential to carry out a detailed interview before lipoplasty, including about lifestyle and health habits. Patients not meeting the required criteria cannot proceed with the health-risky procedure. Contraindications to liposuction include:

The patient's history must include alcohol consumption and smoking. The patient needs to stop smoking at least four weeks before the procedure. The smoking ban extends to all patients and is necessary to reduce the risk of lipoplasty complications and increase wound healing after the procedure. The substances contained in cigarettes and alcohol affect the possibility of adverse effects. These harmful substances should also not be used long after the procedure.
Another contraindication to lipoplasty is a disease that can pose a very high, catastrophic risk. Deep vein thrombosis has a high burden of complications. Patients with a condition or risk group for deep vein thrombosis should not proceed with the procedure. Thus, such a condition is associated with the fatal complication of pulmonary embolism![]() . The risk group analysis for these diseases is calculated using the Caprini scale. Symptoms typical of an ongoing pathological condition in a vein include pain in the vein, swelling, and redness running along the affected vein.
. The risk group analysis for these diseases is calculated using the Caprini scale. Symptoms typical of an ongoing pathological condition in a vein include pain in the vein, swelling, and redness running along the affected vein.
A large percentage of patients who are interested in cosmetic surgery have psychological disorders concerning body image. Body dysmorphia occurs in patients who have a distorted and incongruent perception of their body or specific parts of it. Based on questionnaires, it is possible to investigate whether a patient may have body dysmorphia initially. Patients with a suspicion of this disorder should not proceed to irreversible surgery such as lipoplasty. In addition, patients who are insufficiently familiar with the procedure or have unrealistic expectations should also not be doing lipoplasty. Therefore, an assessment by a psychiatric specialist is also essential before proceeding with the procedure.
Invasive lipoplasty procedures carry the risk of various complications. It can also be temporary postoperative symptoms, but patients should be given information about any possible problems and complications. Common complications of liposuction include:
Natural postoperative complications include bruising and swelling. Lipoplasty is a significant procedure followed by a comeback process. During recovery, the treated areas have bruising and swelling, making it difficult to see the full results. Swelling can cause contour deformity![]() , so the final shape of the body is not visible until the swelling subsides. These complications persist from one to several weeks after the procedure.
, so the final shape of the body is not visible until the swelling subsides. These complications persist from one to several weeks after the procedure.
Seroma is another postoperative complication. It occurs when tissue is disrupted during lipoplasty and blood and lymphatic vessels are damaged. The body can activate an inflammatory response and fluid production in such cases. When the body produces more fluid than it can absorb, seroma occurs. The area where the fluid has accumulated becomes rigid and tender. If you have worrying symptoms, report the problem to your doctor immediately. If detected early, the problem is not a health risk, but downplaying the problem can lead to necrosis.
In some cases, patients experience temporary weight gain after lipoplasty. It is also worth mentioning that liposuction surgery does not provide lifelong results. Even if a large area of fat is removed, the remaining fat cells may increase in size. They can grow due to unhealthy eating and lack of physical activity, so a healthy lifestyle should be maintained after the procedure to maintain the results.

Paresthesias can occur after lipoplasty as a post-procedure complication. The invasive procedure can disrupt normal blood circulation, resulting in numbness in various parts of the body. Paresthesias are unpleasant sensations that can include tingling, numbness, and changes in body temperature.
A rarer but more dangerous complication includes fat embolism. The term fat embolism refers to the occlusion of blood vessels by fat particles. It causes a mechanical blockage of the blood flow. Fat particles can pass through the venous route to the lungs and later to different organs. Consequently, the embolism can manifest as dyspnoea and tachycardia. Fat embolism is a catastrophic complication that can lead to pulmonary embolism, thus like deep vein thrombosis.
The anesthetic agent lidocaine can be used during liposuction surgery. If the recommended doses of the substance are not exceeded, lidocaine is generally safe and rarely causes problems. However, a reaction to toxicity is possible in patients. The substance's toxicity can cause various symptoms, including cardiovascular disorders. Doctors initiate special management to avoid further complications once a patient's abnormal reaction to an anesthetic is noted.