Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). This virus is hepatotropic, meaning it has an affinity for the liver and belongs to RNA viruses.
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is the cause of hepatitis C, which can result in severe damage to this organ. It is mainly spread by contact with infected blood. Many people infected with HCV are unaware of the infection because it is usually asymptomatic for many years.
The virus is present in six different types, each divided into subtypes. Individual types and their subtypes differ in how they respond to treatment. The most common subtypes in the US and Europe are 1a and 1b![]() .
.
HCV infection causes inflammation in the liver cells (hepatocytes), which results in inflammatory changes and destruction of the liver cells.
If the disease lasts more than six months, it is called chronic hepatitis C. About 30 percent![]() of those infected eliminate HCV from the body, and in the rest, the disease turns into chronic hepatitis C, which is associated with progressive liver fibrosis.
of those infected eliminate HCV from the body, and in the rest, the disease turns into chronic hepatitis C, which is associated with progressive liver fibrosis.
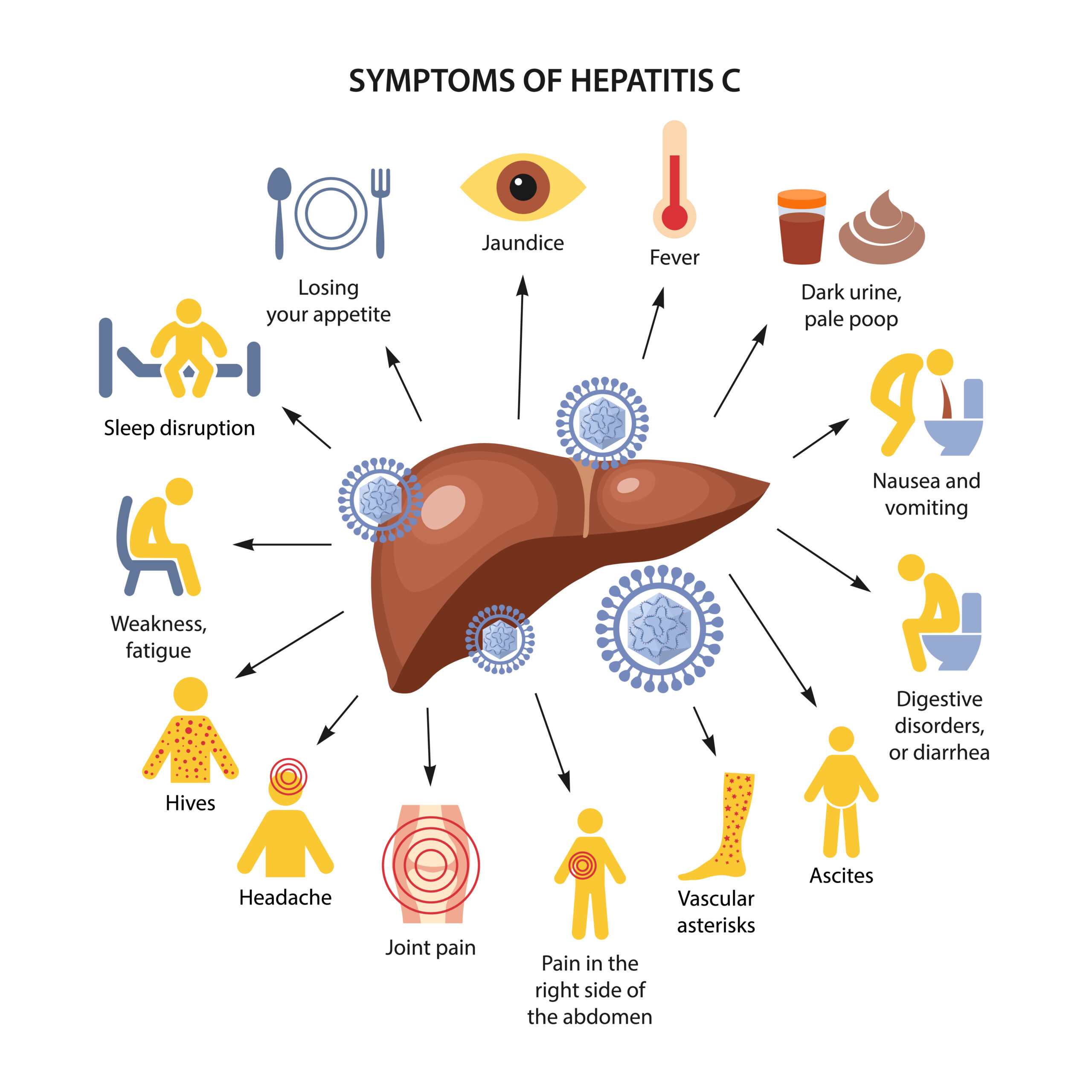
Most HVC infections are asymptomatic. However, some symptoms![]() may occur. These symptoms include:
may occur. These symptoms include:
Usually, the symptoms are mild.
Humans are the source of HCV infection. There are three routes to getting HCV:
Infections occur through contact with blood and its by-products, non-sterile medical instruments, transplanted organs, hemodialysis, and non-medical devices (for example, razor blades or razors, cocaine inhalation tubes, toothbrushes, and tattoo devices). In the majority of infected people, it is not possible to determine the risk factor.
Infections in people in stable relationships are rare, while frequent changes in sexual partners and not using condoms increase the risk of disease.
The doctor will take a thorough medical history, primarily regarding possible predispositions to hepatitis C infection, and examine you. Because chronic hepatitis C is usually asymptomatic, laboratory tests are necessary to make the diagnosis.
The test most often performed in diagnosing hepatitis C is a blood test for the presence of antibodies against HCV![]() . Antibodies are proteins the human immune system produces after contact with a given germ to fight it. They are specific to a given pathogen.
. Antibodies are proteins the human immune system produces after contact with a given germ to fight it. They are specific to a given pathogen.
These antibodies appear in the blood on average seven weeks after infection, so a negative result does not always mean the absence of the virus in the body and may occur if the test was done before the body had time to produce antibodies.
If you got a negative test result and you have symptoms or the risk of infection is high, the doctor will probably recommend retesting or a PCR test.
A positive test result does not necessarily mean that you are infected because you may have had an infection, and your body has already eliminated the virus from your body. A PCR test is required to confirm the presence of the virus in the body.
In some patients, such as those with weakened immune systems or on dialysis, antibodies may not be detectable in the blood despite the existing infection with the hepatitis C virus.
Before antibodies, about 1-3 weeks after infection, the virus's genetic material![]() – HCV RNA – can be detected in the blood. However, it only occasionally appears in the patient's blood, so a single negative result does not rule out infection.
– HCV RNA – can be detected in the blood. However, it only occasionally appears in the patient's blood, so a single negative result does not rule out infection.
In addition, your doctor may refer you for other laboratory blood tests – liver enzymes (ALT and ASP), bilirubin, and GGT. The results of these tests show the condition of the liver and its functioning.
Hepatitis C destroys liver cells, which is why during the diagnosis of this disease, it is so important to check the condition of the liver to choose the proper treatment.
In the past, liver biopsy (puncturing with a special needle and taking a small amount of tissue) with microscopic evaluation of the collected material was used to assess the degree of liver damage and fibrosis. Nowadays, it is used only in doubtful cases, and an ultrasound method called elastography is used to evaluate the degree of liver damage.
Experts recommend the following people get tested for hepatitis C![]() :
:
Treatment includes leading a healthy lifestyle and pharmacological treatment.
The lifestyle directions for people with chronic hepatitis C include:
The goal of medicine treatment is to eliminate the hepatitis C![]() virus from the body, which significantly reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer.
virus from the body, which significantly reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Due to the safety and effectiveness of the treatment, it is recommended for all infected patients, regardless of the stage of fibrosis. The exception is people whose disease is so advanced that a liver transplant is necessary. In them, however, antiviral treatment is carried out after the transplant.
In recent years, the treatment of chronic hepatitis C has developed a lot, is effective, safe, and accessible. In hepatitis C treatment, the so-called direct-acting antivirals (DAA) are used. They are highly effective in eliminating the hepatitis C virus.
The doctor determines the specific treatment regimen for a given patient. When choosing the regimen and duration of treatment, the doctor considers possible interactions of treatment with other drugs used by the patient, the results of any previous treatment, and the degree of impairment of liver and kidney function.
There is no causal treatment for acute hepatitis C. More severe or complicated cases may require hospitalization, and treatment goals are to maintain adequate nutrition and hydration.
Drugs reducing feelings of itching are also used if jaundice develops.
It should be remembered, however, that most hepatitis C infections are asymptomatic, and patients only learn about the infection when chronic hepatitis C develops.
Hepatitis C can be cured entirely. Treatment with new antiviral drugs is very effective. The virus is eliminated from the body in about 95% of patients![]() .
.
Certain groups of people are at particular risk for hepatitis C infection![]() :
:
Complications of chronic hepatitis C include:
Chronic hepatitis C is a disease that progresses slowly, but within 20–25 years, it leads to cirrhosis in about 20% of people with hepatitis C![]() .
.
This complication occurs in the absence of effective treatment. The risk depends on the severity of inflammatory changes and fibrosis in the liver at the time of diagnosis. Factors accelerating the development of cirrhosis include:
HCV infection causes numerous symptoms affecting other organs and systems. These include complications:
Liver failure![]() is a condition in which the liver is almost entirely or entirely unable to function effectively. This is a hazardous situation due to the numerous functions that the liver has in your body, including synthesis, metabolism, detoxification, storage, filtration, and many more.
is a condition in which the liver is almost entirely or entirely unable to function effectively. This is a hazardous situation due to the numerous functions that the liver has in your body, including synthesis, metabolism, detoxification, storage, filtration, and many more.
This condition is characterized by the onset of hepatic encephalopathy (disorders of the nervous system that result from the action of toxins accumulation in the body) and blood clotting disorders.
Symptoms of liver failure include jaundice, edema, ascites (a buildup of water in the abdomen), nosebleeds, dark urine, and black stools.
A liver transplant is the only option for full recovery if liver failure develops, as the liver damage is irreversible at this stage.
Hepatocellular carcinoma![]() is a type of liver cancer. It develops in about 5% of patients over 20 years. The risk increases significantly in patients with cirrhosis.
is a type of liver cancer. It develops in about 5% of patients over 20 years. The risk increases significantly in patients with cirrhosis.
The symptoms that can indicate the development of liver cancer include unintentional weight loss, stomach pain, jaundice (yellowish discoloration of the skin and eye whites), nausea, vomiting, fever, persistent itching, and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
The risk of virus transmission from a mother with hepatitis C to her baby is estimated at around 5%.
In the US, every pregnant woman is tested for HCV. If a woman is planning a pregnancy, it is worth performing such a test before pregnancy because treatment for hepatitis C is not recommended during pregnancy (so it is worth reducing the level of the virus in the body before pregnancy if possible).
Special treatment is required if the hepatitis C virus is detected during or before pregnancy. First, to protect yourself against other liver diseases, it is good to get vaccinated against hepatitis B and hepatitis A. You should also avoid drugs that are toxic to the liver, such as paracetamol (remember that during pregnancy, it is best to avoid all medications and consult your doctor before taking any drugs).
Babies of women who had hepatitis C during pregnancy should be tested after birth.
The PCR test detecting the presence of the virus can be carried out from the age of 2 months, while the antigen test detecting antibodies against the virus should be performed as late as 1.5 years of age. This is because earlier, the result of such a test may be falsified by antibodies from the mother that persist in the baby’s blood.
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C.
Treating the acute phase of hepatitis C reduces the risk of progression to chronic inflammation.
The general principles of preventing blood-borne diseases should be followed: