Hay Fever occurs due to an abnormal reaction of the immune system to substances called allergens. For this reason, people who have been diagnosed with various types of allergies are most at risk of developing the disease.
Sometimes hay fever is accompanied by other symptoms such as skin flushing and even asthma attacks, depending on the allergen the allergy sufferer has been exposed to. Most often, a runny nose appears immediately after contact with the allergen. However, in some cases, the symptoms may appear later.
Seasonal factors![]() , i.e., those occurring only in specific seasons (usually spring and summer), include:
, i.e., those occurring only in specific seasons (usually spring and summer), include:

Year-round factors![]() that can cause hay fever
that can cause hay fever![]() include:
include:
Factors that increase the risk of hay fever![]() include:
include:
Hay fever symptoms occur due to direct contact with the allergen, i.e., they do not occur spontaneously. Patients complain of “water from the nose,” which is difficult to stop. Additionally, you may experience:
Allergic rhinitis usually does not pose a threat to the patient's life. However, you should pay attention to breathing problems or throat swelling. Then you should see a doctor immediately.
Patients often wonder how to distinguish allergic rhinitis from a common cold![]() . The difference is in how long a given symptom lasts. A standard runny nose goes away after about seven days, while hay fever may last from a few hours to several weeks, depending on the length of exposure to the allergen. Moreover, in the case of hay fever, patients report water running from the nose, while with a regular runny nose, we often encounter a thick liquid – its structure may change during the disease.
. The difference is in how long a given symptom lasts. A standard runny nose goes away after about seven days, while hay fever may last from a few hours to several weeks, depending on the length of exposure to the allergen. Moreover, in the case of hay fever, patients report water running from the nose, while with a regular runny nose, we often encounter a thick liquid – its structure may change during the disease.
If you notice allergy symptoms, go to a specialist. The basis of diagnosis![]() is an interview with the patient when the time of symptom occurrence is specified, which allows the determination of the specific allergen. The doctor will also measure the concentration of allergen-specific IgE in the blood
is an interview with the patient when the time of symptom occurrence is specified, which allows the determination of the specific allergen. The doctor will also measure the concentration of allergen-specific IgE in the blood![]() . The immune system produces antibodies during an allergic reaction, so their presence indicates previous contact with the allergen.
. The immune system produces antibodies during an allergic reaction, so their presence indicates previous contact with the allergen.
If the causes of the disease are still not clear or there is a suspicion of the coexistence of several different types of allergies, it may be necessary to perform further tests.
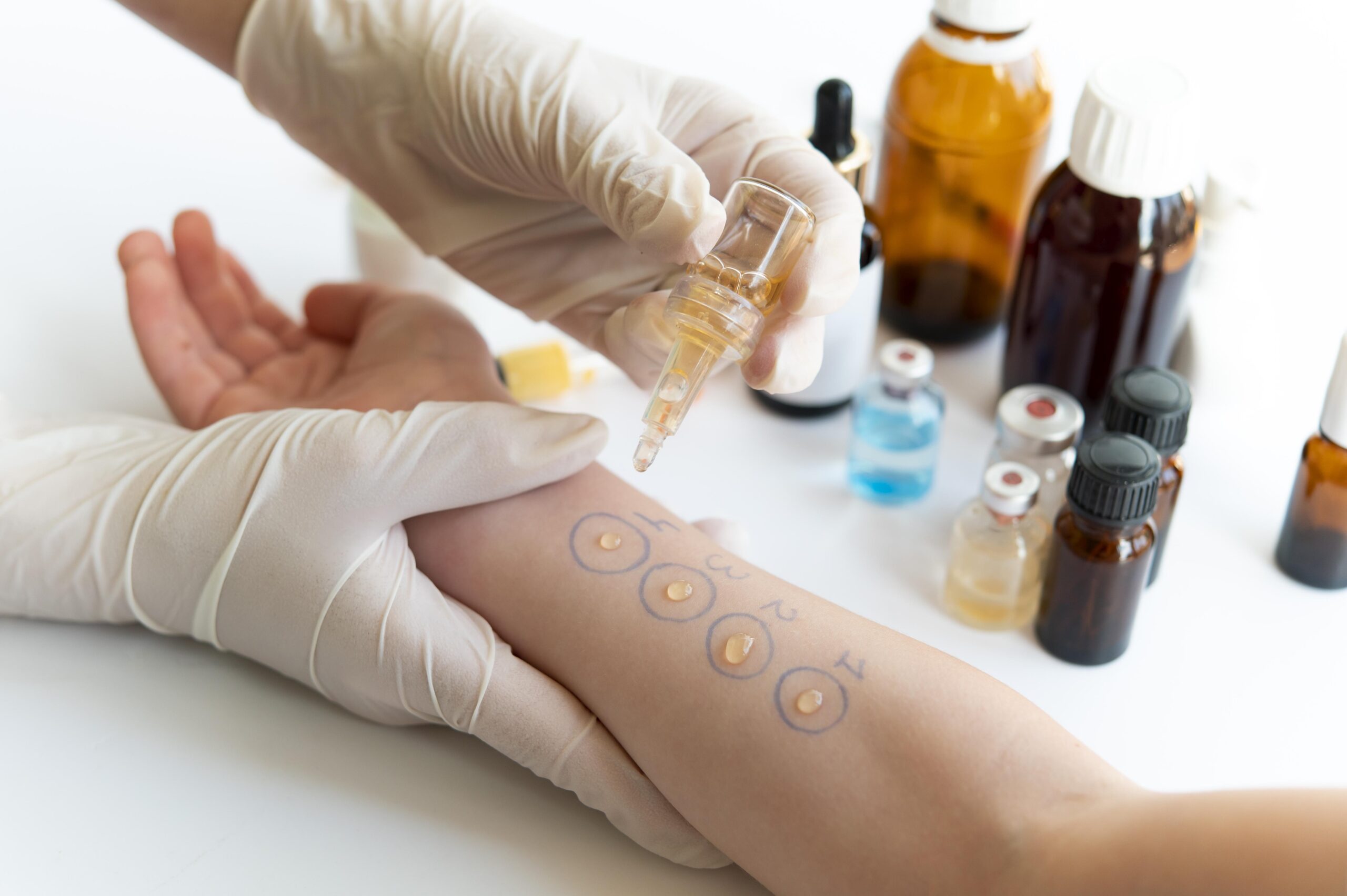
Specialists perform skin tests![]() using diluted preparations containing sensitizing allergens. They apply substances to small punctures made on the patient's body or injected under the skin. In people with allergies, after contact with a given allergen, an erythematous-wheal reaction will appear – the skin may be red and covered with erythema. In some cases, despite the presence of allergies, skin tests do not show the existence of the disease – such situations result from a weakened allergic skin reaction. The specialist will then use other diagnostic methods.
using diluted preparations containing sensitizing allergens. They apply substances to small punctures made on the patient's body or injected under the skin. In people with allergies, after contact with a given allergen, an erythematous-wheal reaction will appear – the skin may be red and covered with erythema. In some cases, despite the presence of allergies, skin tests do not show the existence of the disease – such situations result from a weakened allergic skin reaction. The specialist will then use other diagnostic methods.
Your doctor may perform blood tests, including the RAST test![]() , which measures the level of immunoglobulin (IgE antibody) directed against a specific allergen.
, which measures the level of immunoglobulin (IgE antibody) directed against a specific allergen.
Rhinoscopy![]() involves examining the nasal cavity using a particular device, the so-called rhinoscope. People suffering from hay fever experience bilateral swelling of the nasal mucosa covered with a watery or sticky secretion, and the nasal mucosa itself may be congested or pale.
involves examining the nasal cavity using a particular device, the so-called rhinoscope. People suffering from hay fever experience bilateral swelling of the nasal mucosa covered with a watery or sticky secretion, and the nasal mucosa itself may be congested or pale.
Sometimes, the specialist may recommend a CT scan![]() of the nose and sinuses. Such a test allows you to assess whether other diseases co-occur.
of the nose and sinuses. Such a test allows you to assess whether other diseases co-occur.
We can divide methods used to treat hay fever into pharmacological and non-pharmacological.
Drug treatment![]() often uses corticosteroids in the form of an intranasal spray. The products relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction, but a burning sensation in the nose may occur after using them.
often uses corticosteroids in the form of an intranasal spray. The products relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction, but a burning sensation in the nose may occur after using them.
Specialists also prescribe antihistamines. Histamine is one of the substances secreted during the immune system's response to an allergen. Its action focuses on causing allergy symptoms. For this reason, antihistamines, which reduce the secretion of substances and thus alleviate allergy symptoms, are recommended. These preparations have many different forms: tablets, drops, and syrups. We can use them intranasally or orally. When using newer generation preparations, there are usually no serious side effects due to the more complex mechanism effects of the substance. However, when using older-generation agents, drowsiness and fatigue sometimes occur.
Like steroids, specialists recommend using vasoconstrictors topically. We usually buy them in the form of nasal or eye drops. Thanks to the action of these preparations, the vessels dilate and narrow as a result of an allergic reaction. It helps alleviate allergy symptoms such as itching and redness of the conjunctiva and the feeling of a stuffy nose. They are usually used in combination with antihistamines.
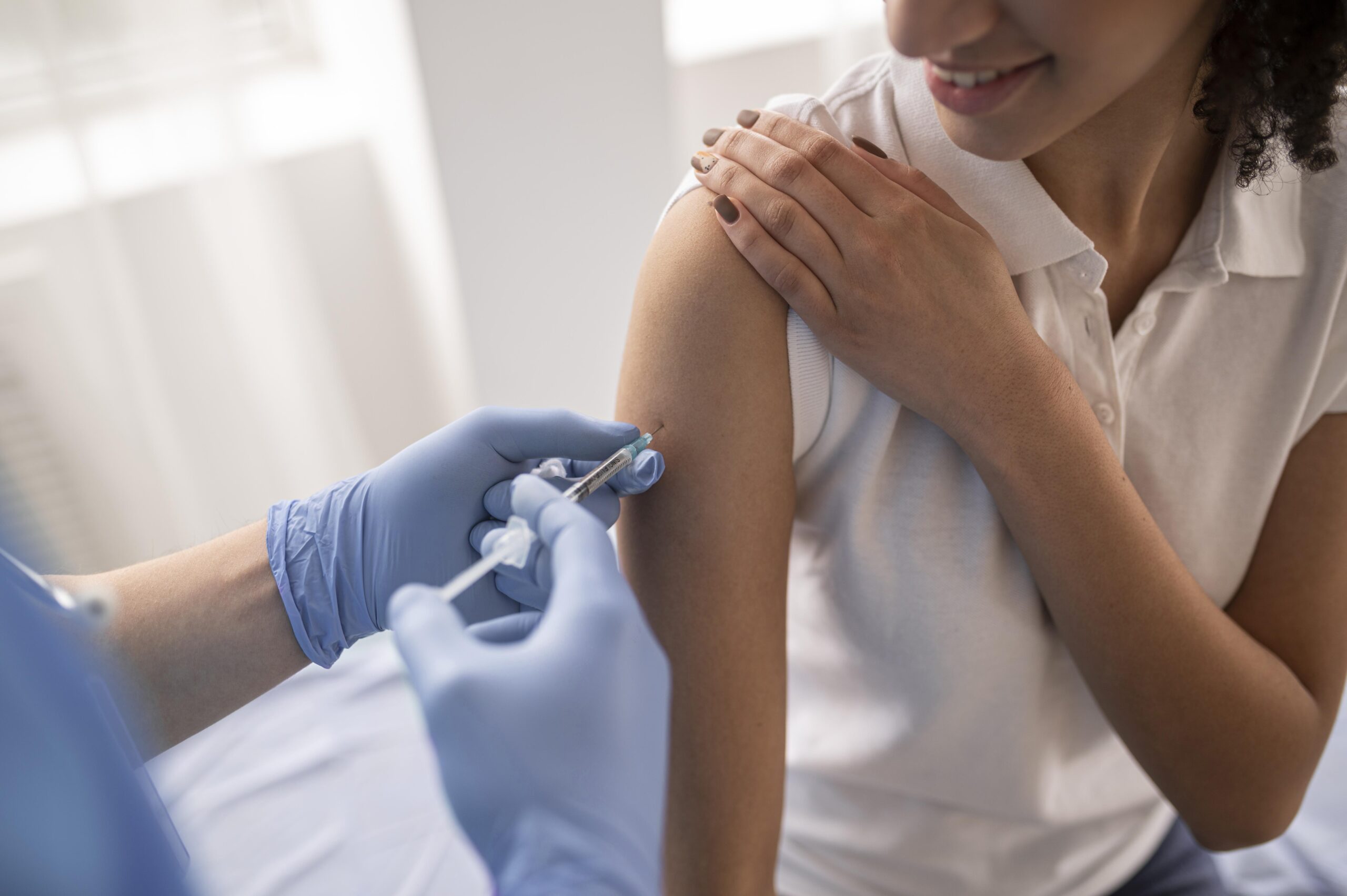
Desensitizing substances are also used in treatment. Specific immunotherapy involves administering subcutaneous injections of the so-called desensitizing vaccines – i.e., preparations containing appropriately low concentrations of allergens that cause symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Repeated exposure to sensitizing agents can cause an allergy to worsen. However, a treatment model involving weekly allergens administration under carefully controlled conditions can reduce the immune system's response to these agents. As a result, the allergy can become milder. Once the allergy is under control, a monthly maintenance dose may be required to maintain the treatment's effectiveness.
It is best to start the desensitization process as soon as possible, i.e., when there are indications for allergen-specific immunotherapy![]() . Treatment can be started at any time of the year. However, if the patient is allergic to tree and grass pollen, the best period is autumn-winter and early spring.
. Treatment can be started at any time of the year. However, if the patient is allergic to tree and grass pollen, the best period is autumn-winter and early spring.
Preparation for allergy immunotherapy should begin by determining the type of allergy. This can be done through skin tests or blood serum. Moreover, it is also significant that the patient is of the appropriate age and, according to specialists' recommendations, the age limit for starting this process is over five years. Allergy immunotherapy in children is similar to that in adults. However, for many reasons (for example, a common fear of needles in toddlers), children are usually given oral desensitizing substances.
The specialists do not recommend desensitization for everyone. The doctor makes the decision based on the specific case. Allergy immunotherapy is divided into two phases. In the first period, saturating desensitization is used, i.e., in which the body receives gradually increased doses of the allergen, in the next one – maintenance doses, which are already constant. Allergy immunotherapy involves administering the allergen every 1-2 weeks. However, during the maintenance period, every 4-6 weeks.
If the patient is desensitized continuously throughout the year, allergy immunotherapy lasts about three years. When they are desensitized seasonally, this period is extended to 5 years. However, it is worth remembering that the doctor always decides the duration of allergy immunotherapy. If they decide to extend the desensitization period, the patient should adapt to it. The patient should not interrupt the treatment period alone because arbitrary cessation of desensitization may result in not achieving the desired effects.
Before you undergo such therapy, talk to an allergist who will tell you the most necessary contraindications to allergy immunotherapy. This list includes ailments that prevent treatment:
Moreover, allergy immunotherapy is not initiated during pregnancy, but maintenance doses can be continued. Additionally, there are temporary contraindications, including a cold or taking antibiotics. Once short-term factors subside, this type of therapy can be used. Age may also be a contraindication, as desensitization is not used in children under five years of age or in adults over 50.
Allergy immunotherapy is an absolute contraindication to donating blood. Additionally, for 24 hours after treatment, it is recommended to avoid:
You should also not get a tattoo during the entire desensitization process. Specialists also recommend being careful when breastfeeding and consulting a doctor about this.
There are methods that, if implemented, will help alleviate the hay fever symptoms. It is important to emphasize that allergy symptoms should never be ignored. Lack of treatment or incorrect treatment of hay fever can exacerbate symptoms, develop severe side effects, and weaken immunity. For this reason, home treatment should never replace specialist treatment.
The fundamental method of home treatment![]() is to avoid allergens. For example, allergy sufferers should get a pollen calendar. It is worth reviewing current information on pollen concentrations and planning actions based on it. If there is a lot of irritating pollen in the air, it is worth avoiding outdoor sports or even simple walks – especially when it is dry and windy.
is to avoid allergens. For example, allergy sufferers should get a pollen calendar. It is worth reviewing current information on pollen concentrations and planning actions based on it. If there is a lot of irritating pollen in the air, it is worth avoiding outdoor sports or even simple walks – especially when it is dry and windy.
The pollen calendar will also help us answer how long hay fever lasts in our case. Provided, of course, that we know the cause of our allergy.
During periods of intense pollen, windows should be closed to limit the pollen spread. Moreover, it is worth considering installing dust filters or purchasing air purifiers. It is better to dry the laundry in a closed room, not outside, so that pollen will not settle on the fabrics.
When outdoors, wearing sunglasses, headgear, and clothes with longer sleeves or trouser legs is good to limit skin contact with pollen. When you get home, it's best to throw your clothes into the washing machine and take a shower. Grass in home gardens should be mowed regularly to reduce the formation of inflorescences.
It is worth making general changes at home if we are allergic to house dust mites. Let's limit the equipment that collects it. We can also find cleaning products in stores for allergy sufferers that neutralize dust mites. They usually come in the form of aerosols, which makes them easier to use safely. You can spray them on beds, mattresses, bedding, carpets, upholstery, and toys. These preparations reduce the symptoms of allergies caused by house dust mites, including cough, allergic rhinitis, and allergic conjunctivitis.
Improvement in well-being and health may not be immediately noticeable after eliminating contact with the allergen. It can take weeks to months for the patient to feel better. It's important to remember that removing the allergen from the patient's environment can be challenging and, in some cases, even impossible. However, every effort should be made to achieve this goal.
An effective home remedy for a stuffy night is to rinse your nose and sinuses with saline![]() . It is worth using ready-made sinus rinsing kits, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. The set includes a flexible bottle with an applicator and a sachet for preparing a saline solution. Thanks to irrigation, you can cleanse the nasal cavity of impurities and allergens. Moreover, the method allows you to moisturize the mucous membranes.
. It is worth using ready-made sinus rinsing kits, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. The set includes a flexible bottle with an applicator and a sachet for preparing a saline solution. Thanks to irrigation, you can cleanse the nasal cavity of impurities and allergens. Moreover, the method allows you to moisturize the mucous membranes.
Another home remedy for allergic rhinitis is inhalation![]() . This method is helpful for hay fever, cough, and sinusitis. Inhalations using water vapor and essential oils moisturize the irritated mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. They help thin the thick secretions that flow down the back of the throat. It is worth using oils that have disinfecting and anti-inflammatory properties. Products should be natural and come from a proven source. Before inhaling, let's test whether the oil does not cause allergies or worsen the symptoms, and remember always to use the product by the manufacturer's recommendations.
. This method is helpful for hay fever, cough, and sinusitis. Inhalations using water vapor and essential oils moisturize the irritated mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. They help thin the thick secretions that flow down the back of the throat. It is worth using oils that have disinfecting and anti-inflammatory properties. Products should be natural and come from a proven source. Before inhaling, let's test whether the oil does not cause allergies or worsen the symptoms, and remember always to use the product by the manufacturer's recommendations.
Another home remedy for a runny nose is to use air humidifiers![]() . Inhaling warm steam from a humidifier significantly helps thin and remove mucus and soothe irritated sinuses. However, please remember that if you use a humidifier, it must be cleaned regularly according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Otherwise, microorganisms such as mold and bacteria may develop, unfortunately exacerbating sinus problems.
. Inhaling warm steam from a humidifier significantly helps thin and remove mucus and soothe irritated sinuses. However, please remember that if you use a humidifier, it must be cleaned regularly according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Otherwise, microorganisms such as mold and bacteria may develop, unfortunately exacerbating sinus problems.
What we eat every day is also necessary in the fight against hay fever. The diet![]() should support our immune system. For this reason, it must be rich in wholesome products, i.e., fruits and vegetables. It is worth avoiding large amounts of sugar and highly processed foods.
should support our immune system. For this reason, it must be rich in wholesome products, i.e., fruits and vegetables. It is worth avoiding large amounts of sugar and highly processed foods.
The elimination diet involves excluding individual ingredients (always one at a time) while monitoring the severity of symptoms. Use it for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Introducing an elimination diet before identifying the source of a food allergy is based on gradually eliminating suspected products from the diet. Visible improvement indicates that a given product or group of products is a source of allergens.
If there is no improvement, it is necessary to continue eliminating other products this time and reintroducing previously excluded products into the diet. If your symptoms disappear after eliminating a specific food, you should confirm your observations by reintroducing it to your diet. Such treatment should exacerbate the symptoms and contribute to making the correct diagnosis.
Children, however, very often outgrow food allergies, so in their case, treatment with an elimination diet may be much shorter and usually last from 6 to 12 months because the introduction of therapy and the removal of harmful ingredients from the digestive tract overlap with the natural process of maturation of this system. Usually, after age 3, previously excluded foods can be gradually introduced.