Gonorrhea is a venereal disease most often transmitted sexually. Its cause is the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It usually lives in moist zones of the body, e.g., the mouth, rectum, or genitourinary tract. This condition can also be transmitted during oral and anal intercourse with an infected individual.
Very frequently, people with gonorrhea are not conscious of their infection. That is why they constantly undervalue the first signs of manifestation. And this, unfortunately, in extreme cases, leads to complete infertility. In addition, newborns are also at risk of gonorrhea. The infection is transferred during delivery, which in turn can cause disease of the eye tissues.
As you see, the condition is extremely severe. What else do you need to know? Gonorrhea can coexist with other STDs. That is why the prevention is so significant.
Gonorrhea is mainly caused by having anal, oral, or genital contact with a partner who is infected. Also, using the same everyday hygiene items, e.g., sponges or towels, can cause infections. Avoid sitting on public toilet seats. It is because this bacteria can survive on a toilet seat or towel for several hours.
Gonorrhea can affect not only genital areas but also the throat, anus, and conjunctival sac.
Anyone who has sex![]() with another person can get gonorrhea. Anyone exhibiting genital symptoms such as redness, discharge, strange sores, burning while urinating, or other symptoms should stop having sex right away and get medical attention.
with another person can get gonorrhea. Anyone exhibiting genital symptoms such as redness, discharge, strange sores, burning while urinating, or other symptoms should stop having sex right away and get medical attention.
Additionally, a medical expert should be consulted by anyone who has recently been told they have an STD by a partner for oral, anal, or vaginal sex.
Even if they do not have symptoms or are aware of a sexual partner who is infected, some persons should be examined for gonorrhea. If you engage in sexual activity talk to your doctor about risk factors and inquire about getting tested for gonorrhea or other STDs.
All recent anal, vaginal, or oral sex partners should be informed if gonorrhea has been identified and treated so they can seek medical attention and receive treatment 20. It lowers the danger of reinfection and the possibility that the sex partners would experience significant gonorrhea-related consequences. A gonorrhea patient must refrain from having intercourse with any potential partners.

Individuals who are infected with gonorrhea frequently go undiagnosed for a prolonged time. That may be because the manifestation can be confusing and unclear. The first indications of the condition may occur a few days after sexual intercourse with the person infected with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria.
In men![]() , signs develop much quicker than in women. It usually takes approximately 2 to 7 days. The primary place of disease is the urethra. In males, there is:
, signs develop much quicker than in women. It usually takes approximately 2 to 7 days. The primary place of disease is the urethra. In males, there is:
In some cases, the disease is asymptomatic. When it becomes chronic, the symptoms decrease.
In women![]() , the signs of gonorrhea typically appear 7-14 days after infection. The discharge associated with severe stages of the infection can be mistaken for symptoms of other ailments. That is why it can be overlooked. As a result, women go to the doctor only when gonorrhea reaches a chronic stage.
, the signs of gonorrhea typically appear 7-14 days after infection. The discharge associated with severe stages of the infection can be mistaken for symptoms of other ailments. That is why it can be overlooked. As a result, women go to the doctor only when gonorrhea reaches a chronic stage.
The primary area of the condition in women is considered to be the cervix, but the contagious disease can impact the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and also uterus. That is why, women may experience:
You should consult gonorrhea symptoms with a doctor. A venereologist is an expert in venereal diseases, but concerning modifications on the skin can also be consulted with a gynecologist or urologist. If we are not sure who to go to, we can also begin the diagnostic process by visiting the family doctor's office.
Do not leave gonorrhea untreated. In this case, it can lead to adnexitis in women. And in men, there is a risk of orchitis and epididymitis. Continue reading to find out more about the complications of this condition.
Gonorrhea is a disease that may impact not only the women's cervix or the men's urethra but even other different elements of the human body.
In most cases, gonococcal pharyngitis![]() does not cause any symptoms. But in some occasions, it is distinguished by swelling of the palatine arches and the back of the throat. There may also be redness. Additionally, purulent discharge can happen.
does not cause any symptoms. But in some occasions, it is distinguished by swelling of the palatine arches and the back of the throat. There may also be redness. Additionally, purulent discharge can happen.
Gonococcal proctitis![]() usually appears in individuals who have anal intercourse and, just like gonococcal pharyngitis, can not cause any symptoms. In the case of the symptomatic condition, people experience burning and itching feeling in the area of the anus, issues with defecating, and exudation of mucous discharge from the anus.
usually appears in individuals who have anal intercourse and, just like gonococcal pharyngitis, can not cause any symptoms. In the case of the symptomatic condition, people experience burning and itching feeling in the area of the anus, issues with defecating, and exudation of mucous discharge from the anus.
In disseminated gonococcal infection![]() Diococcus bacteria spread through the blood. It happens most often in women. The symptoms of this disease form are skin changes and joint pain.
Diococcus bacteria spread through the blood. It happens most often in women. The symptoms of this disease form are skin changes and joint pain.
Gonococcal conjunctivitis![]() is an infection that occurs mainly in infants. They get infected during childbirth. Its symptoms vary in severity. Untreated disease can lead to corneal damage and visual impairment.
is an infection that occurs mainly in infants. They get infected during childbirth. Its symptoms vary in severity. Untreated disease can lead to corneal damage and visual impairment.
In the gonorrhea diagnosis![]() , inform your doctor about a medical history. Then you need to perform tests for the presence of gonorrhea. For this purpose, a swab is taken. Depending on the location of the condition, it may be from the vagina, urethra, or cervix. The doctor can also take it from the throat and rectum. A swab taken from a patient is tested for bacterial genes' presence or used for checking bacterial culture. Then secretion sample with a suitable medium is transferred into the container. We need to wait for approximately two days. During this time the swab is incubated – the bacteria develop colonies observable to the naked eye.
, inform your doctor about a medical history. Then you need to perform tests for the presence of gonorrhea. For this purpose, a swab is taken. Depending on the location of the condition, it may be from the vagina, urethra, or cervix. The doctor can also take it from the throat and rectum. A swab taken from a patient is tested for bacterial genes' presence or used for checking bacterial culture. Then secretion sample with a suitable medium is transferred into the container. We need to wait for approximately two days. During this time the swab is incubated – the bacteria develop colonies observable to the naked eye.
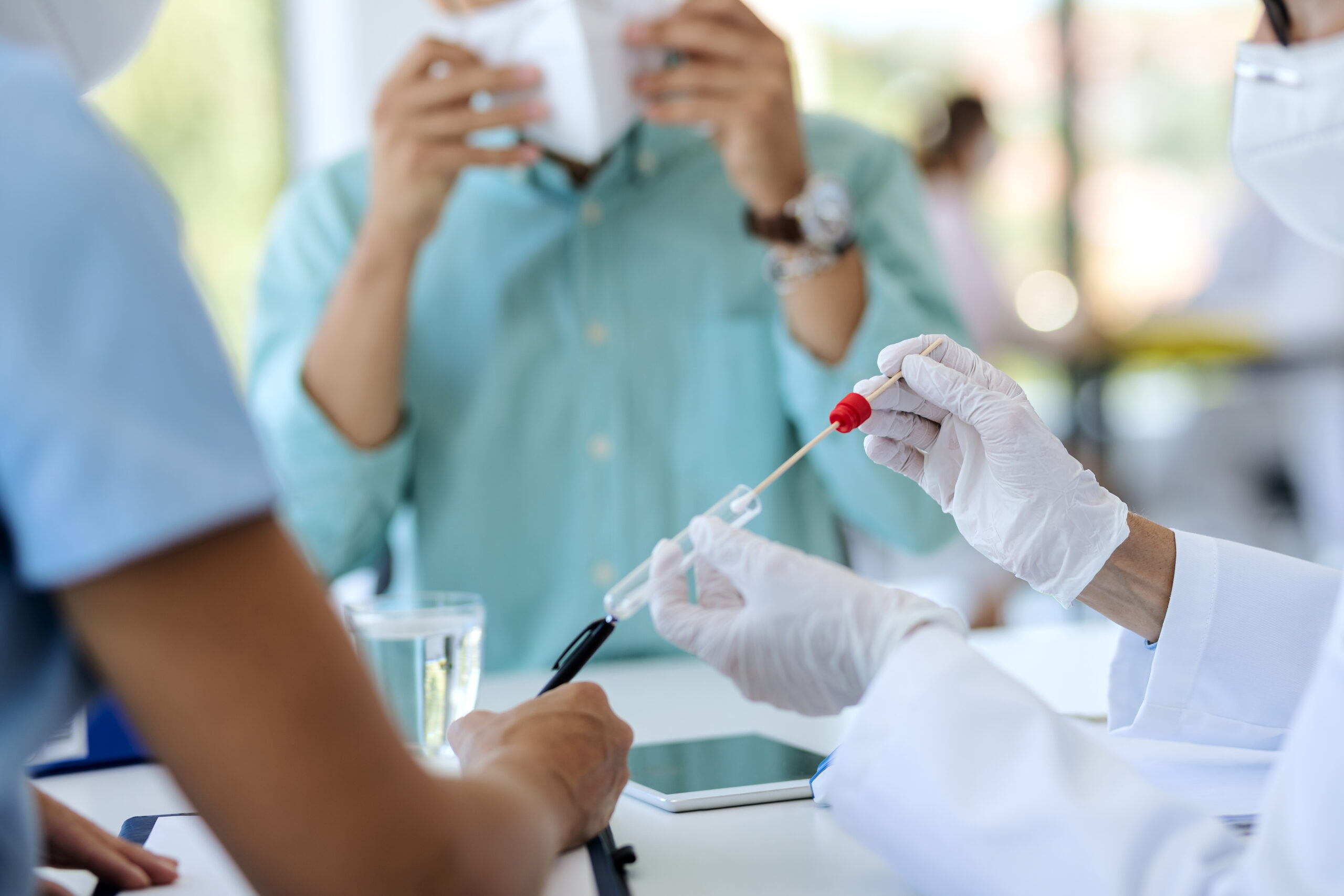
Diagnostic tests for gonorrhea![]() can include bacterial culture, microscopic examination (Gram's method or methyl blue), PCR, and LCR. A sugar fermentation test can help distinguish the bacteria causing throat gonorrhea from meningococcal gonorrhea.
can include bacterial culture, microscopic examination (Gram's method or methyl blue), PCR, and LCR. A sugar fermentation test can help distinguish the bacteria causing throat gonorrhea from meningococcal gonorrhea.
Any suspicious symptom resembling gonorrhea should be an indication for a visit to a gynecologist or urologist. If the test result is positive, the sick person should inform about the condition all former and current sexual partners. They also need to get tested for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, even if they do not observe any manifestation of gonorrhea.
If you experience symptoms of gonorrhea, you should visit a specialist who will make a diagnosis. Then they will guide you to pharmacological therapy. It is also essential to administer medication to the partner with whom the individual with gonorrhea has sexual intercourse.
We treat gonorrhea under medical management. The specialists recommend antibiotics![]() . Some doctors especially advise cephalosporins
. Some doctors especially advise cephalosporins![]() . However, some strains of gonococci have become invulnerable to this type of medicament.
. However, some strains of gonococci have become invulnerable to this type of medicament.
Keep in mind that attempting to treat gonorrhea by yourself can result in chronic infection and other medical problems.
Yes, it is achievable to fully treat this condition. At least three days after the end of therapy, the infected person should undergo a control bacterial tests.
Dismissing the manifestation of gonorrhea, not acknowledging the condition, not treating it, or not treating it correctly can result in complications![]() . We talk about, e.g.:
. We talk about, e.g.:
Sexual activity must be avoided to prevent sexually transmitted infections. However, this is neither practicable nor healthful, so we need to come up with a different strategy. It is advisable to get medical help if you get one of these diseases because they are frequently treatable.
Sexually transmitted illnesses can be a shameful issue. There is no need to feel ashamed, dermatologists, urologists, and gynecologists emphasize. Anybody can contract the illness, regardless of how promiscuous their sex life is.
Here are a few helpful pointers that are essential for gonorrhea prevention.
Try to maintain monogamy and refrain from having sexual intercourse with a lot of different partners.
Steer clear of casual sex.
Use condoms correctly and frequently to protect against STIs.
Remember to test for other STIs, e.g., HPV virus, syphilis, or chlamydia. That is because gonorrhea frequently coexists with mentioned conditions.
Remember to watch your own body for any alarming symptoms.
Avoid having sex with infected people or while they are being treated.
Do not sit on the toilet seat when using a public restroom.
Do not share private hygiene articles with others (e.g., household members). These even include towels or washing sponges.
Avoid lending both to and from someone's sex toys.
Condoms![]() , in the vast majority of cases, increase protection against infection with sexually transmitted diseases. However, it should be remembered that they do not give 100 percent of protection. Some viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites that are usually sexually transmitted can also be spread in other ways, e.g., through micro-abrasions during sexual contact. They can penetrate the skin or mucous membranes.
, in the vast majority of cases, increase protection against infection with sexually transmitted diseases. However, it should be remembered that they do not give 100 percent of protection. Some viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites that are usually sexually transmitted can also be spread in other ways, e.g., through micro-abrasions during sexual contact. They can penetrate the skin or mucous membranes.

Even though almost all of us will encounter bacteria and viruses during our lives, we are very ashamed to admit that we are infected. It is due to the lack of sex education in our homes from an early age. Parents or the closest environment instill in us the belief that sex is something to be ashamed of. Instead of enjoying their sexuality, children are taught to be ashamed of exposing their bodies and nakedness. Restrictive upbringing and demonstrating disapproval of matters related to sex and carnality become the beginning of a negative attitude towards gender issues and a kind of taboo.
If we are ashamed of our bodies, having sex, and the pleasure associated with it, it will be even more unthinkable to contract a sexually transmitted disease. How could we admit it? After all, it is like a stigma, a testimony of our wicked, lewd acts. By such logic, venereal disease is like a punishment for the sin of fornication.
Our parents don't teach us about sex education, and we don't have any knowledge about venereal diseases. Like our parents, we too are often ashamed to talk about it with friends, doctors, and our partners.
However, it is vital to let your partner know![]() about the potential danger of infection. We owe it to our partner, so we should analyze ourselves and seek treatment if necessary. Before deciding to have sex, you should discuss the pertinent tests and the risk of infection with your partner. Before sexual contact, emotions take over and cause us to lose our ability to reason. Instead of taking the chance of infecting him and his current justified rage, it is preferable to notify your spouse so they can make a decision. We would be reckless and irresponsible if we didn't let your partner know about this.
about the potential danger of infection. We owe it to our partner, so we should analyze ourselves and seek treatment if necessary. Before deciding to have sex, you should discuss the pertinent tests and the risk of infection with your partner. Before sexual contact, emotions take over and cause us to lose our ability to reason. Instead of taking the chance of infecting him and his current justified rage, it is preferable to notify your spouse so they can make a decision. We would be reckless and irresponsible if we didn't let your partner know about this.
To overcome your shame, it is worth realizing that cases of infection are not exceptions and do not indicate promiscuity or lack of personal hygiene. Doctors often encounter cases of such diseases.
Honesty with a partner is a condition of a successful relationship, so if we are afraid of losing him, if we reveal the truth, we take the risk of hiding it from our partner.
When talking to your partner, it is worth giving him the facts about the possible ways of contracting the disease virus. A sensitive partner, instead of arguments and accusations, will rather understand the situation and go to the doctor with us.