Fatty liver disease is a medical condition involving fat droplets accumulating in liver cells, i.e., hepatocytes. It is an abnormal medical condition that can lead to liver damage – fibrosis, and then cirrhosis.
The action of a toxic substance may cause fatty liver disease – often alcohol, and it is then called alcoholic fatty liver disease, or if there is no specific cause, then it is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Fatty liver disease is otherwise called steatosis. A normal liver contains very little fat. The doctors diagnose steatosis if the fat content in the liver exceeds 5% of its weight![]() .
.
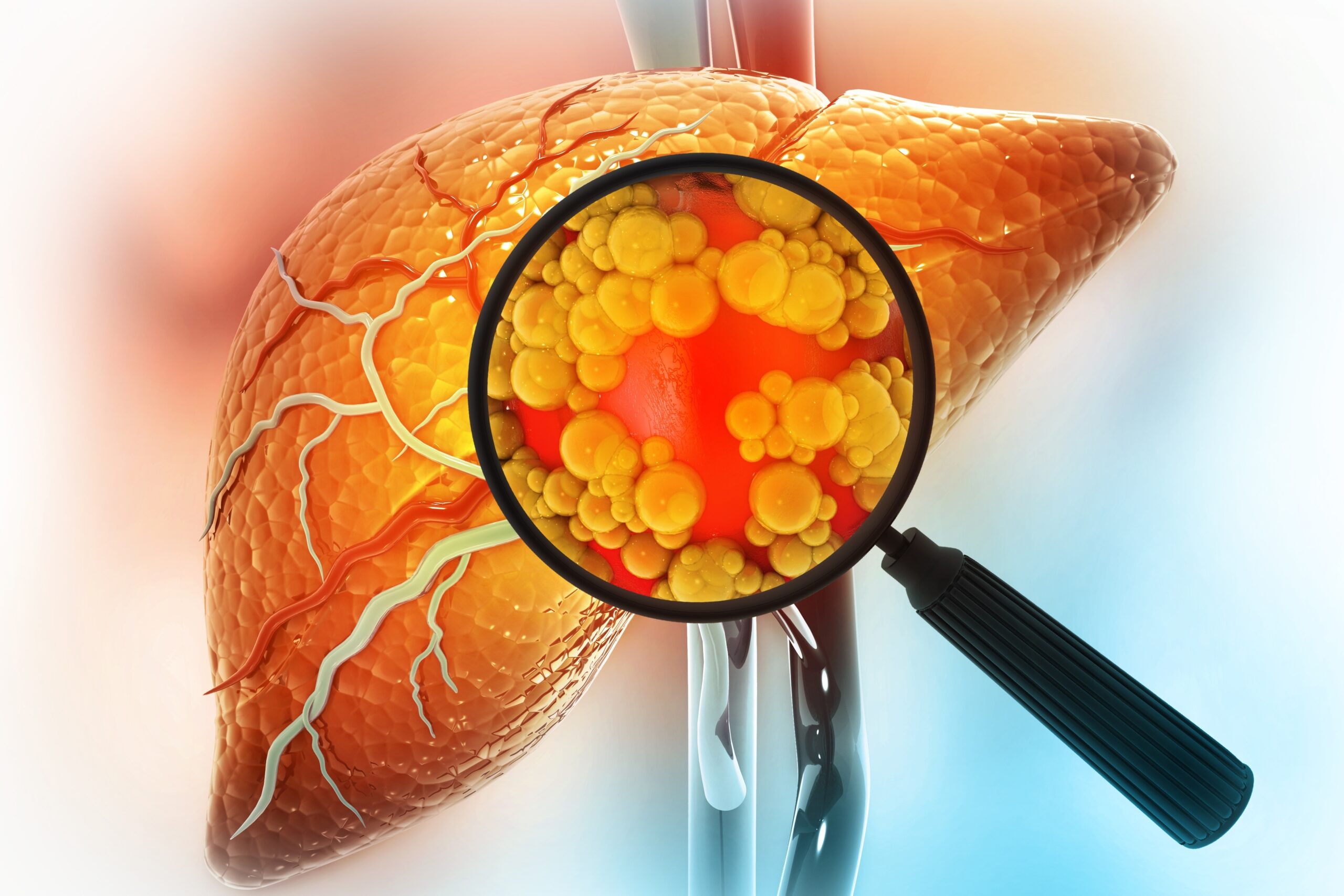
The liver is one of the heavier organs of our body – it weighs 1.5 kilograms and is located on the upper right side of the abdomen. The liver consists of the right, left, quadrate, and caudate lobes, which are composed of hepatocytes – liver cells. Blood flows to the liver from two different sources:
and flows out through the hepatic vein.
The portal vein supplies blood from various organs, including the intestines and pancreas, and that is why excess nutrients flowing from the digestive system, e.g., glucose, are stored in the liver.
The liver is a vital organ – it performs over 500 different bodily functions![]() . The most important of them include:
. The most important of them include:
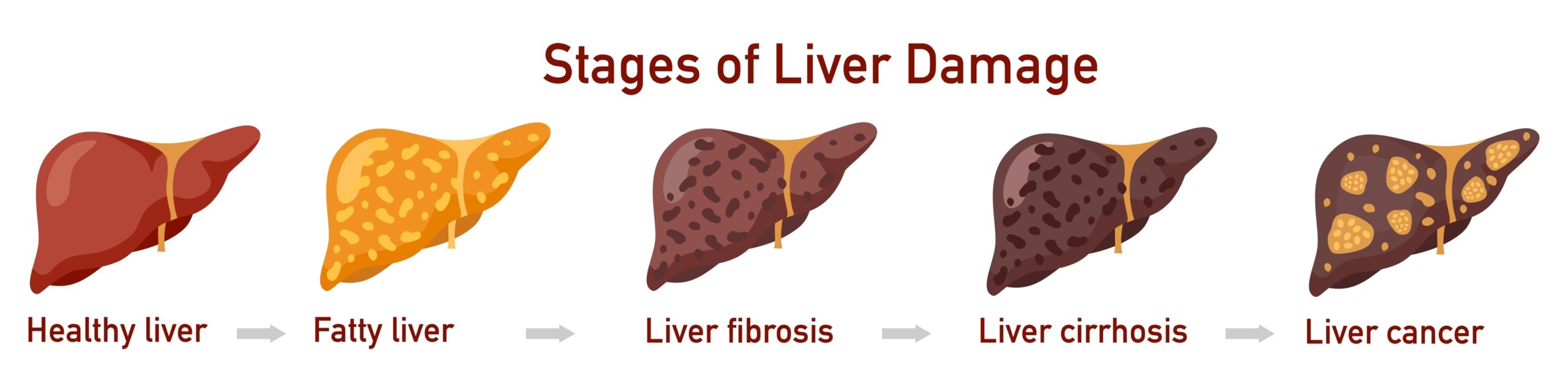
Liver disease has four main stages:
Fatty Liver is the first stage of liver disease![]() in which fat cells accumulate excessively. If it progresses, liver fibrosis occurs in abnormal amounts of scar tissue in the liver due to long-lasting inflammation. Fatty liver and liver fibrosis are reversible stages of liver damage.
in which fat cells accumulate excessively. If it progresses, liver fibrosis occurs in abnormal amounts of scar tissue in the liver due to long-lasting inflammation. Fatty liver and liver fibrosis are reversible stages of liver damage.
However, fibrosis can progress into cirrhosis of the liver, the disorder in which fibrosis reaches such intensity that the scar tissue destroys the typical structure of the liver. Cirrhosis of the liver is irreversible since the damage done to the organ is major. When cirrhosis of the liver occurs, it significantly increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
Once scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, it can’t function properly. That poses a great problem since the liver is highly significant for proper body functioning. If the scarring reaches a point where the organ can't work, it’s called liver failure. Then, the only remedy is a liver transplant, as replacing the damaged organ with a healthy one is the only hope for recovery.
There are a few types of fatty liver disease. Distinguishing between different kinds of disease is essential because they differ in the risk of progression to more severe forms of liver disease as well as in treatment.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a fatty liver disease not caused by alcohol abuse, chronic use of drugs that cause fatty liver disease, or congenital genetic diseases. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease stands as the most common chronic liver disease and holds the top position as the primary cause of abnormal liver function test results.
The leading role in the development of NAFLD![]() is played by insulin resistance and dysregulation of the hormone that regulates the body's energy balance. The causes include an unhealthy diet rich in carbohydrates, saturated fats, and sweetened drinks, which, together with low physical activity, leads to overweight and obesity. Genetic predisposition also plays a role.
is played by insulin resistance and dysregulation of the hormone that regulates the body's energy balance. The causes include an unhealthy diet rich in carbohydrates, saturated fats, and sweetened drinks, which, together with low physical activity, leads to overweight and obesity. Genetic predisposition also plays a role.
Usually, the disease does not cause any symptoms and is accidentally diagnosed during an ultrasound examination or after abnormally high levels of liver enzymes are detected in the blood.
In alcohol-related fatty liver disease, the cause of the disease is excessive alcohol consumption![]() . When you drink alcohol, the liver filters it, and every time, some of its cells get damaged. Usually, the liver can regenerate itself and replace damaged cells with new ones. But when you drink too much alcohol, liver damage may exceed its regeneration capacity, causing fatty liver disease.
. When you drink alcohol, the liver filters it, and every time, some of its cells get damaged. Usually, the liver can regenerate itself and replace damaged cells with new ones. But when you drink too much alcohol, liver damage may exceed its regeneration capacity, causing fatty liver disease.
Alcohol-related fatty liver disease usually doesn’t cause any symptoms until the disease is severely advanced. Then, symptoms include vomiting, weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, ascites (water buildup in the abdomen), and bloody vomit.
If you drink alcohol excessively, you should tell your physician about it to check your liver's condition.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is a fatty liver with chronic and progressive inflammation of the liver, which, if left untreated, leads to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The risk of progression to further liver disease stages is higher in NASH![]() than in NAFLD. In this type of disease, treatment options include a few medications that aim at protecting against further liver damage.
than in NAFLD. In this type of disease, treatment options include a few medications that aim at protecting against further liver damage.
Fatty liver disease may occur as a result of the toxic effects on the liver of various factors, such as:
Steatosis can also occur without the action of one specific toxic factor. Then, it is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The origins of this condition stem from an unbalanced diet high in saturated fats, coupled with insufficient physical activity, resulting in weight gain and obesity.
You have a higher chance![]() of getting fatty liver if you:
of getting fatty liver if you:
Fatty liver disease usually does not cause symptoms. Some people may experience the following:
Fatty liver disease is often diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound examination for another reason or after abnormal liver enzyme activity is detected in the blood.
Some people may experience symptoms of liver failure – this happens if complications of fatty liver disease have already developed, e.g., liver cirrhosis:
Fatty liver doesn’t usually cause any symptoms. For this reason, your physician may be the first to notice it during examination and tests for another reason. The first indication may be elevated levels of liver enzymes or changes in the ultrasound examination.
In making a diagnosis, your doctor may take the following steps:
Treatment depends on the cause of fatty liver disease. If steatosis is the result of the toxic effects of a specific substance, discontinuation of exposure usually causes remission of the disease. Alcoholic fatty liver disease usually resolves within a few weeks after cessation of alcohol consumption and slowly progresses![]() to hepatitis and cirrhosis if continued.
to hepatitis and cirrhosis if continued.
The treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mainly involves lifestyle modification and, in the case of NASH, drugs that protect the liver from liver disease progression.
Currently, there is no specific medication for fatty liver disease. However, for NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis), there are two medications approved by the experts: an antioxidant – vitamin E![]() , and a drug that decreases the levels of sugar in the blood and is also used in diabetes treatment.
, and a drug that decreases the levels of sugar in the blood and is also used in diabetes treatment.
However, not everyone can benefit from those drugs, and you should never start therapy on your own. If you have confirmed NASH, you can talk with your physician about possible drug therapy. Still, the doctor's decision to either start the treatment or not is based on the benefit-risk ratio, as every medication has associated side effects.
In addition, medications to treat conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes associated with the disease are essential.
The primary treatment method for fatty liver is lifestyle modification. Your physician may recommend some changes you should introduce to your life. These include:

Fatty liver can progress to cirrhosis. Then, the liver may stop functioning, and a liver transplant![]() can be necessary. In that case, your provider puts you on the waiting list, or you can receive part of the organ from a living donor. This is possible due to the liver's exceptional ability to regenerate itself. The transplanted section and the donor's remaining part of the liver can grow to regular sizes.
can be necessary. In that case, your provider puts you on the waiting list, or you can receive part of the organ from a living donor. This is possible due to the liver's exceptional ability to regenerate itself. The transplanted section and the donor's remaining part of the liver can grow to regular sizes.
Untreated fatty liver may progress into:
People with fatty liver disease are also at higher risk of developing heart disease.
Preventing alcoholic fatty liver disease is not drinking too much alcohol. Since nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development is associated with obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, or high blood cholesterol levels, it is worth implementing a healthy diet![]() and physical activity as preventive measures. You should follow a well-balanced diet and avoid eating products with high saturated fat content and fast food. Sustaining a healthy weight is crucial for minimizing the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. Changing your lifestyle can bring many beneficial effects, such as weight loss, which is very important in the case of overweight or obesity.
and physical activity as preventive measures. You should follow a well-balanced diet and avoid eating products with high saturated fat content and fast food. Sustaining a healthy weight is crucial for minimizing the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. Changing your lifestyle can bring many beneficial effects, such as weight loss, which is very important in the case of overweight or obesity.