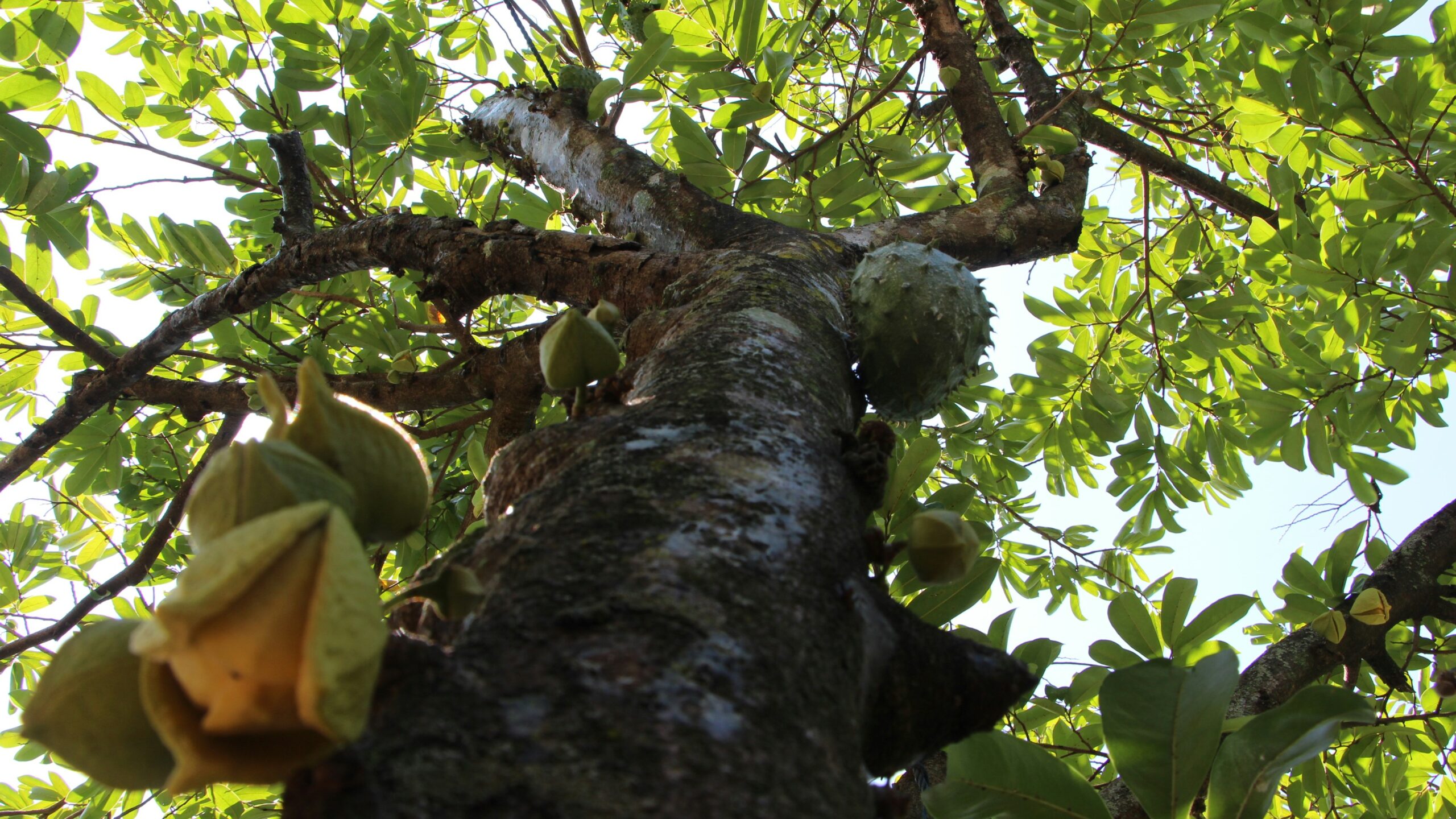
Originally from the Malay Peninsula, durian is a perennial tropical fruit. Now, it is widely grown in Southeast Asia. There has been great growth in the production, advertising, and consumption of this unique tropical fruit within the territory, and it has been exported in recent years. Durian is a highly potent fruit due to its unusual taste and smell. Only nine species of durian are edible. Many of the varieties have been recommended for commercial use.
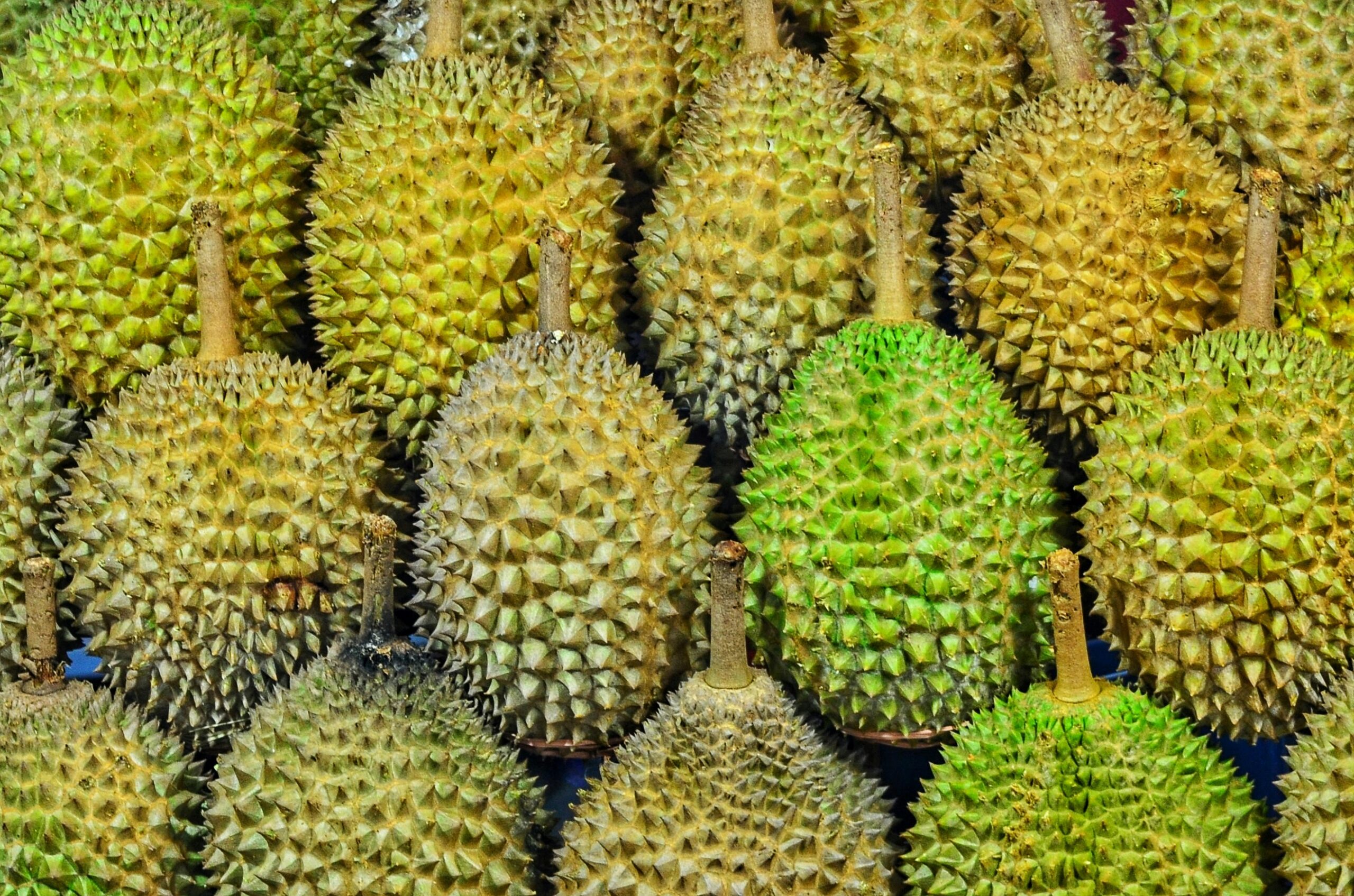
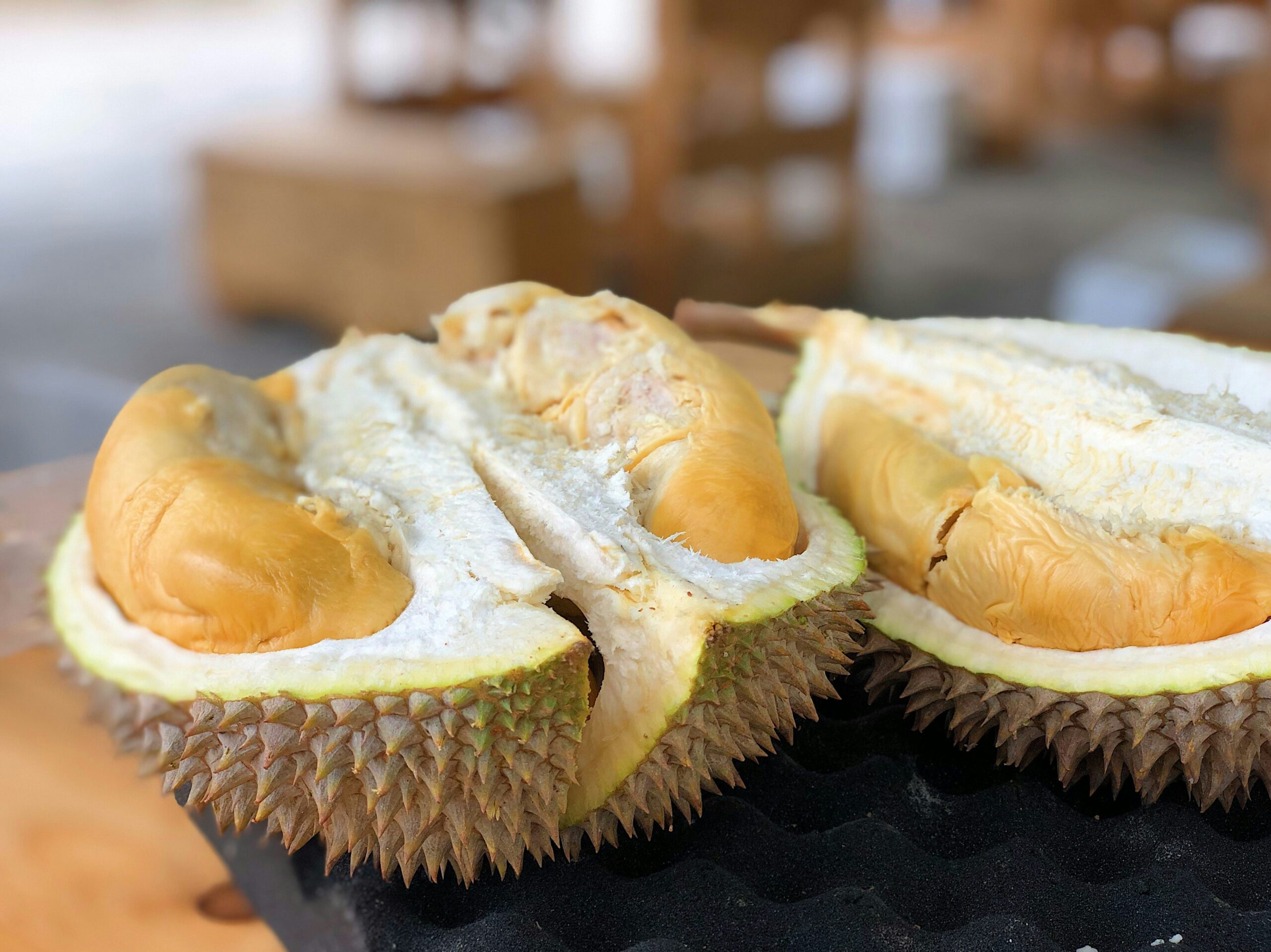
Durian grows on tall trees. It is a large and heavy fruit protected by spikes on its skin. Eating a durian involves slicing through its tough, thorny shell with a knife. Internally, the durian contains sections filled with rich, tender meat surrounding the sizeable seeds. The durian is round, egg-shaped, oval, or oblong pericarp color or brown. The edible seed can be in different colors, depending on the variety.

The fruit is consumed raw and perishable, lasting two to five days. Hence, it is one of the costliest fruits. It's expensive not only because it is seen as a rarity but also because growers have to use specialized growing techniques that are time- and resource-consuming. Like many other fruits, the taste and smell of fully ripened durian fruit depend largely on the presence of volatile compounds. Its scent is so spicy that it is off-putting to many.
On the other hand, durian has numerous lovers who enjoy eating it. Enjoying durian has many benefits because this fruit not only has a delicious taste but also contains a lot of nutrients. This text aims to describe the health benefits of durian species in Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia and their nutritional significance. Read on for more about the “king of fruits,” the fantastic durian.
Durian flesh, skin, and seeds are all parts of this fruit that have been shown to have some level of nutraceutical value. There are many inedible pieces produced from the cultivation of the fruit. However, on a positive note, durian edible waste can also be transformed into value-added goods. But you might now wonder how to eat durian. What can you do with it? Please find out more about why we use all the parts of the fruit.
But you can eat the flesh of the fruit raw. The fruit is also commonly served as sticky rice or can be added to bakery goods. Due to the limited supply, durian fruits have a low shelf life; this fruit must be consumed or processed within a limited period. The fruit should be stored for 2-5 days![]() at room temperature. Even so, overripe fruits do not get discarded as well. Tempoyak
at room temperature. Even so, overripe fruits do not get discarded as well. Tempoyak![]() , a fruit product processed with acid and salt, results from overripe durian fermentation. Fermented durian has a strong order, yellow color, soft texture, and sour taste. Another durian specialty, also typical in Malaysia, is lemon, which is made from boiling durian pulp with coarse sugar.
, a fruit product processed with acid and salt, results from overripe durian fermentation. Fermented durian has a strong order, yellow color, soft texture, and sour taste. Another durian specialty, also typical in Malaysia, is lemon, which is made from boiling durian pulp with coarse sugar.
Jam, candies, ice cream, durian wine, and milkshakes durian-based products are also widely processed in the food industry. Soup can also be made from unripe or partially ripe durian pulp. Durian juice is another popular traditional drink. Moreover, it is possible to dry the durian fruit, and making fruit bars is a practical way to market the fruit. Many people who enjoy durian prefer to eat it fresh. Now, to eat durian fresh, you have to take some steps. Some tropical fruits like durian need preparation before they can be eaten. Thus, before entering, it must be peeled.

Durian seeds are also an edible part of the durian. This means that durian blesses us with a diversification of food. For now, eating durian seeds can meet your body's energy. The fresh durian seeds have a mucilage, which can be used as a thickening agent. It has this thickening property because of its high starch content. This enables the seeds to be incorporated into flour that can be used as a thickening ingredient.
The seeds are frequently prepared in this manner, then roasted or cooked and consumed as a snack. Locally, the seeds are roasted, sliced, and sprinkled with sugar in Indonesia. In this kind, the seeds are consumed as sweets or broiled in zesty coconut oil and eaten as cooking alongside rice.
Locally, the durian is regarded as one of the most essential fruits due to the unique taste and smell of ripe fruit. Durian has a strong smell and distinctive taste. The pulp is sweet, yellow, white, golden, yellow, or red. But durian fruit is also bioactive rich. This is why durian is a very indispensable fruit. Studies show that the edible and non-edible parts of durian fruit have a high potential to be utilized in their food value. Moreover, processing waste from durian can also decrease pollution in the area where durian is grown and produce additional income for the farmers. Discover the benefits of eating durian for health.
Some studies suggest that durian has an anti-atherosclerotic effect. The consumption of this unusual fruit in the diet resulted in a decrease in postprandial total cholesterol levels. Ripe durian also protects the liver and aorta from exogenous cholesterol loading and protects the surface of the aortic inner membrane. Besides this, the elevated potassium concentration assists the cardiovascular system, as potassium contributes to maintaining normal blood pressure levels. Therefore, it can be suggested that consuming durian fruit is beneficial for heart health.
Since durian is high in sugar, overconsumption of it is not recommended. However, raw durian consumption might result in less GI (glycemic index![]() ) due to high fiber and fat content. The digestive process is inhibited, and fiber inhibits the body's conversion of carbohydrates to glucose. Conversely, fat is unrelated to the blood glucose response. Still, it may indirectly improve the glycemic response by retarding gastric emptying, thereby reducing the rate of appearance of glucose in the plasma.
) due to high fiber and fat content. The digestive process is inhibited, and fiber inhibits the body's conversion of carbohydrates to glucose. Conversely, fat is unrelated to the blood glucose response. Still, it may indirectly improve the glycemic response by retarding gastric emptying, thereby reducing the rate of appearance of glucose in the plasma.
Beyond that, freeze-dried fruit supplementation may improve blood sugar regulation. According to the study, supplementation didn't increase glucose as freshwater would. The impact of durian on blood glucose levels needs to be better established, and more results are required to confirm this association.

Like other fruit species, durian contains polyphenols, which are antioxidant-active compounds. Polyphenols also help humans mitigate their level of reactive oxygen species. Several studies demonstrate the protective role of polyphenolic compounds in vegetables, fruits, or herbs. These compounds prevent the development of cancer and other such diseases. Furthermore, durians containing antioxidants protect free radicals and delay aging. For instance, durian fruit may be a source of polyphenols that have protective effects against breast cancer. However, we need more research to confirm this effect.
One of them is the durian fruit, which is harvested and fermented with time at room temperature, turning sour and getting watery. Their sugar content and moisture create a nurturing environment for good bacteria. The main microorganisms in fermented durian-producing lactic acid bacteria benefit gut microflora. Different types of Lactobacillus![]() groups have been recognized. These species are called probiotics, which improve the body's overall health by boosting immunity. Conclusion: As such, fermented durian is proposed to have prebiotic potential and, thus, beneficial effects on the gastrointestinal microbiome.
groups have been recognized. These species are called probiotics, which improve the body's overall health by boosting immunity. Conclusion: As such, fermented durian is proposed to have prebiotic potential and, thus, beneficial effects on the gastrointestinal microbiome.
Along with creating good bacteria by itself, durian can also defend the body from bad bacteria. A gel produced by growing durian peel has antibacterial and immunomodulatory properties. The highest activities against pathogens like Escherichia coli![]() or Staphylococcus epidermidis
or Staphylococcus epidermidis![]() are found in compounds isolated from the durian peel. Likewise, the fruit's peel also exerts an antifungal effect, manifesting activity against Candida albicans
are found in compounds isolated from the durian peel. Likewise, the fruit's peel also exerts an antifungal effect, manifesting activity against Candida albicans![]() . The seeds, another portion of the durian, exhibit antimicrobial activity. These scientific reports merit further pursuit as durian consumption protects against infection.
. The seeds, another portion of the durian, exhibit antimicrobial activity. These scientific reports merit further pursuit as durian consumption protects against infection.

The durian's antibacterial properties are also beneficial for skin health. Durian fruit husk gel has been used in traditional medicine to treat wound-healing dressings. Durian peel extracts have active compounds that are effective against pathogens that attack the skin, leading to topical symptoms. These activities also suggest the durian's characteristic over antiseptic. This finding highlights the commercially valuable properties of polysaccharide gel prepared with durian waste in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Durian is a highly nutrient-dense fruit that you can find a new recipe. Now, come on down to see what is going on under the surface of the sweet flesh and seeds. Since the unrefined ripe fruit is high in sugar & carbohydrates, it is also very calorific. The primary sugar in durian is sucrose. Durian has an energy value of 84–185 kcal/100 g![]() of fresh fruit flesh. They fluctuate depending on the durian consumption. Unlike seeds of other varieties of fruits, the seeds in the fruit contain a highest of 185 kcal
of fresh fruit flesh. They fluctuate depending on the durian consumption. Unlike seeds of other varieties of fruits, the seeds in the fruit contain a highest of 185 kcal![]() . Among sweet fruits such as mango, papaya, and pineapple, durian has the highest energy content.
. Among sweet fruits such as mango, papaya, and pineapple, durian has the highest energy content.
Durian also has a little protein in it, but not a lot. As a rule, these fruits may not have large quantities of this, but the seeds already can give you a better scale. There is also some fat in durian, an amount that is roughly equivalent to one-third of that in ripe olives. Other essential elements are also found in durian fruit, along with the essential ingredients.
If you are enthusiastic about a healthy diet, you should already recognize that fiber is an incredibly crucial nutrient you want to offer. Include fruits like durian. Fruits are a good source of fiber, too. But it shouldn't be the sole provider of this component. You should feed the fiber to the body several times during the day, in advance or after eating. So, durian flesh has it on your menu as a healthy snack, but keep in mind that fresh durian packs a bundle of sugar.
Fats are one of the food nutrients that perform biological functions that are very important for life. In addition, they are a source of essential fatty acids. The durian varieties from Thailand were higher in monounsaturated fatty acids. This fruit is rich in different types of oleic acid![]() , among other things. It is an organic chemical compound belonging to the type of monounsaturated fatty acids of the omega-9 type. It is an element that has many significant properties; for example, it plays a role in the metabolic process.
, among other things. It is an organic chemical compound belonging to the type of monounsaturated fatty acids of the omega-9 type. It is an element that has many significant properties; for example, it plays a role in the metabolic process.
Of course, fruits are sources of minerals and vitamins. Durian does as well. Wondering what exactly this fruit can offer you? Durian is incredibly high in potassium![]() , giving it some health benefits. These figures are also similar to potassium-rich fruits like bananas. Durian can ensure that you meet your daily needs for this mineral. You will also find regular amounts of magnesium and phosphorus. Durian is also high in iron, copper, and zinc, giving us various compounds. If we have an overview of vitamins, durian will provide us with vitamins A, B, and E. What a powerhouse of healthy goodness!
, giving it some health benefits. These figures are also similar to potassium-rich fruits like bananas. Durian can ensure that you meet your daily needs for this mineral. You will also find regular amounts of magnesium and phosphorus. Durian is also high in iron, copper, and zinc, giving us various compounds. If we have an overview of vitamins, durian will provide us with vitamins A, B, and E. What a powerhouse of healthy goodness!
And this is not even the end of the impressive list of ingredients found in durian. This fruit possesses a wide range of bioactive chemical compounds, particularly polyphenols, in its flesh. This is, among other compounds, hesperidin![]() , a name that is hard to remember but a compound with needed properties. Hesperidin is the original substance, and the pharmaceutical industry uses its good properties; it is also a glycoside.
, a name that is hard to remember but a compound with needed properties. Hesperidin is the original substance, and the pharmaceutical industry uses its good properties; it is also a glycoside.
Hesperidin is a potent antioxidant that removes harmful free radicals, among many other things. Durian's production of bioactive compounds differs and is influenced by the variety, plant part, maturity, climate, cultivation conditions, and geographic production area. Still, whatever the variety, durians are a healthy fare because of the naturally high levels of antioxidants.
Now, malodourous components of durian are volatiles, so it is worth adding here. Durian has a strong smell, which may not be to everybody's liking. The strong scent is attributable to high values in components like esters, alcohols, and sulfur compounds. Sulfur![]() is the major volatile component of durian. The smell of this fruit is not pleasing for everyone because volatile sulfur compounds have an onion-like odor.
is the major volatile component of durian. The smell of this fruit is not pleasing for everyone because volatile sulfur compounds have an onion-like odor.
Because the content of sulfur compounds in Malaysian varieties was seven-fold higher than in Indonesian varieties, those sensitive to these aromas may prefer the unique varieties of lesser malodorous smell. Given the yogurt-cream smell and flavor of oily butter associated with some varieties, that should make the global market push more appealing for consumers to try the fruit. Additionally, esters are the second most abundant durian volatiles next to sulfur and are responsible for the sweet aroma of durian.

Finally, let's move on to the last important topic related to durian. Is it a healthy product? This fruit has a lot of controversy surrounding it. So, take some precautions while eating it. Combining durian fruit with drinks containing alcohol![]() is dangerous. The unsafe combination of sulfur compounds present in the pulp and alcohol can have adverse effects on human beings. Beware: this is highly hazardous. There have been instances of cardiac arrest and death, so why take the risk?
is dangerous. The unsafe combination of sulfur compounds present in the pulp and alcohol can have adverse effects on human beings. Beware: this is highly hazardous. There have been instances of cardiac arrest and death, so why take the risk?