Blood transfusion is a medical process in which the entire body or one of the patient's body parts is injected into an intravenous line. It happens when the blood gets into the patient's bloodstream. Usually, it occurs when a patient is unable to generate red blood cells that are healthy due to a disease or after being brought to a hospital with trauma.
The practice of blood transfusions is quite fashionable these days, although still, many people who are battling with new medications and learning their usage are the ones who give them. The first man-to-man transfusion proved successful because it came later than the early 1800s. Due to transfusions, the prevalence of new testing and safety measures has eliminated grievous dangers. It is not a major relaunch of the scheme, and it mostly accompanies people who move out of hospitals without injuries.
The blood may consist of either the entire or different parts of the blood, such as plasma, red blood cells, platelets, or clotting factor components that are part of the transfusion that the patient's body requires. In the case of the patient who receives a red blood cell transfusion, the shock condition for the stable oxygen patient is still the photo. On the other hand, when a person loses a lot of blood, a different situation can arise. Finally, the patient might need a transfusion with either plasma or platelets. Such an approach ensures that doctors and medical experts will only address the patient's specific issues.
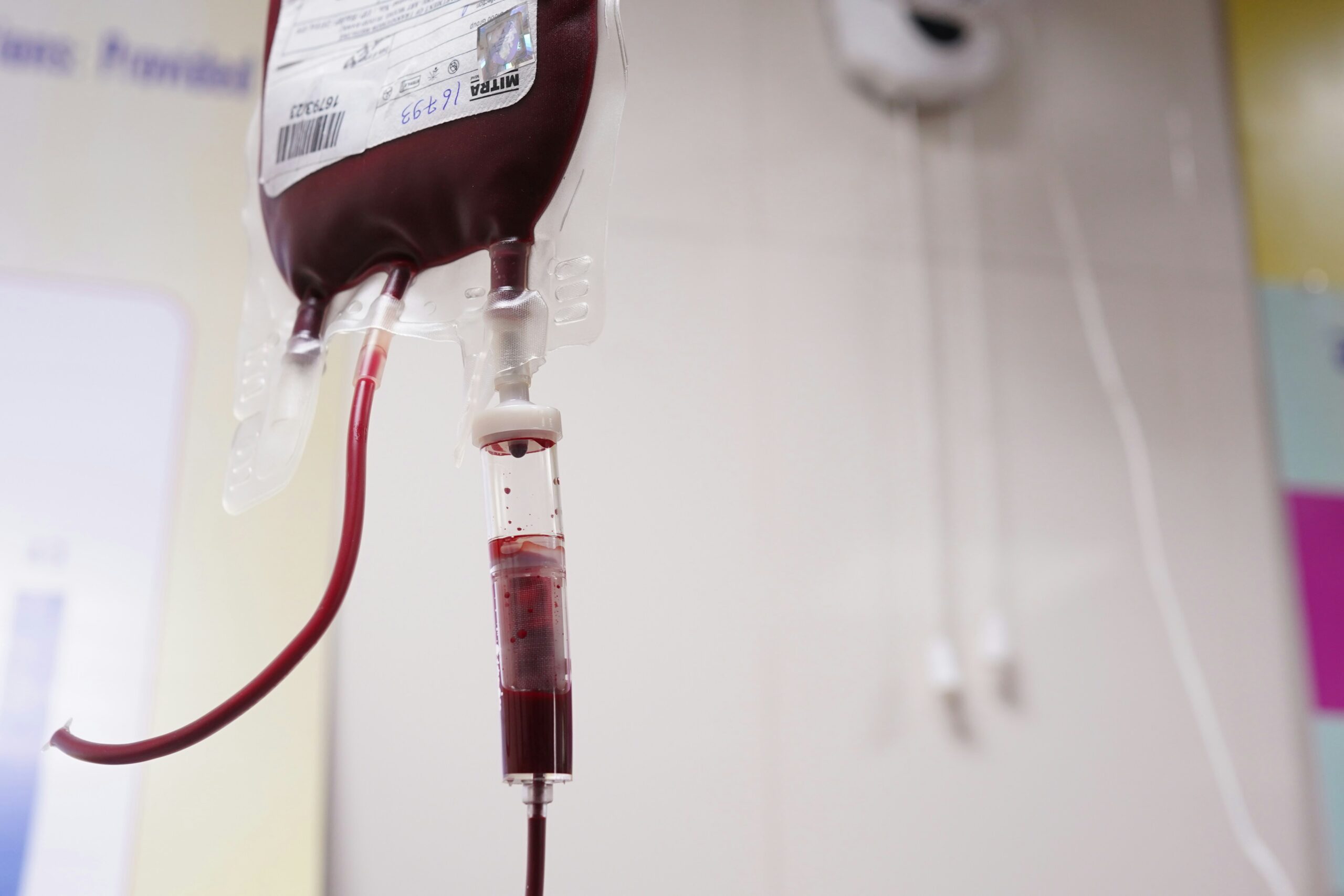
A blood transfusion is the main way of helping people whose blood is in trouble, e.g., the blood is too little or too weird when the normal level is missing. Furthermore, the following are some diseases that can be treated with blood transfusions. Some are above the situations where blood is the most significant thing, and a life savior is such.
Time and again, anemia causes the affected human to feel tired, but complications in the digestive system due to low blood flow with low oxygen can also occur. That makes it easier to get among the major tissues. The scenario of the whole body getting weaker or an organ getting injured could be there. Iron supplements such as taking iron tablets and excessive iron-intensive foods are some remedies for certain types of anemia. Although blood transfusion is caused by anemia, which could be a result of a long-standing kidney or autoimmune disease, the process is also needed because of the disease.
The congenital disorder thalassemia![]() affects the blood; therefore, the patient will have to cope with the whole of their life. Those patients suffering from severe thalassemia, in particular, thalassemia major, should deal with excessive RBC loss, which, in turn, culminates in anemia and other complications. The use of antibiotics for a short time in certain cases while medicines are only a small part of the issue. However, exchange transfusion patients sometimes feel even more active and have a better quality of life. They have a lower likelihood of suffering from organ failure and are less distressing.
affects the blood; therefore, the patient will have to cope with the whole of their life. Those patients suffering from severe thalassemia, in particular, thalassemia major, should deal with excessive RBC loss, which, in turn, culminates in anemia and other complications. The use of antibiotics for a short time in certain cases while medicines are only a small part of the issue. However, exchange transfusion patients sometimes feel even more active and have a better quality of life. They have a lower likelihood of suffering from organ failure and are less distressing.
The cancerous diseases of the blood (leukemia and lymphoma) are the ones that get in the way and make it harder for the body to make healthy blood cells. Thus, the low level of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets can make patients easy prey for infections, major blood loss, or bruise development. The patients undergoing chemotherapy or bone marrow transplants find the maximum advantage through this type of procedure. In extreme cases, patients' health conditions may improve so they can live a better quality of life and undergo rehabilitation with minimal complications due to the rapid drop in the parameters resulting from treatments.
Due to their insufficient blood clotting factors, the slightly skinned knee accident of a hemophilia patient can provoke a serious bleeding accident. Someone who needs a hemostatic operation for a trauma or surgery must have a plasma or platelet infusion infusion of clotting factors to stop blood loss and prevent complications. Patients who have nothing to do with the hospital are the ones at risk of dying because of it.
First and foremost, if there is a case of an emergency where a person needs to be rushed to a hospital due to a gunshot wound or being stabbed by another, the doctor can be a great help during their arrest. Much blood is lost in an accident that a sharp knife has caused. On one note, the person's blood pressure and oxygen levels lower to the permissible point. Medical services make it possible for transport to be fast, and the competent crew delivering the patient's red blood cells, plasma, and platelets will let the staff know if she is out of danger and remains safe. That minimizes the possibility of organ failure; thus, the patient will not become shocked. The doctors will also take the opportunity to get the needed seconds to do the reparatory actions that are required to be done after the patient has moved the damage that has been done during the transfusions.
Upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding is mainly due to long-term drug use or a diseased stomach lining. In this case, a large, rapid loss of blood can occur. Some people experience severe GI bleeding![]() that requires red blood cells to increase oxygen delivery and reduce arterial tension. Such long-term cases involve blood transfusions to maintain the patient's health until the issues are fully solved.
that requires red blood cells to increase oxygen delivery and reduce arterial tension. Such long-term cases involve blood transfusions to maintain the patient's health until the issues are fully solved.
On the one hand, if things are critical, then blood might be drained, which becomes a major issue, and, as such, critical issues like liver or heart transplantations are better handled from a holistic point of view. The organs are adequately supplied with oxygen, and the bleeding stops, transfusions greatly help patients during surgeries. Red blood cells concentrating to the point of delivery to the surgical stage will enhance patients healing, and their recovery will be faster.
The inheritance of sickle cell disease is from the parents to the children, and the disease is demonstrated by sickled red cells, which are strained into discoid or stellar shapes, making a blockade for blood that, in turn, makes circulation decrease. Connectively, blocking the blood vessels is the next step. Some of the organs are damaged, and stroke may be so painful to the extent that it is unbearable. Still, the transfers happen with the sickle cells, and the healthy ones coexist. In that way, the possibility of blockage events, the crisis of pain, and other problems will be greatly turned down.
Blood transfusion can be tolerated and met with cases that are nearly fatal only at the severe limit. This kind of treatment is also claimed to give people suffering from life-threatening injuries a longer time of living. The patient, who resembles a hero, has no injury to the most important organ, which is the heart, and his life continues will be a situation of no incoming stuffy blood within the veins causing the embolism. Blood infusions have been treated as one of the significant techniques that touch these people and make their lives easier by reducing the symptoms of fatigue, low breathing rate, and powerlessness.
Sickle cell anemia![]() , thalassemia, and other chronic disease patients have the chance of being alive if blood transfusions and therapies are performed regularly. This is most notably efficient in cancer patients, especially those who are receiving intrinsic therapies, for example, the folks who may prefer relying on transfusions to keep the blood cell counts stable. As a result, patients accepted the treatment without even being tired or at risk of infection; the treatment was very successful.
, thalassemia, and other chronic disease patients have the chance of being alive if blood transfusions and therapies are performed regularly. This is most notably efficient in cancer patients, especially those who are receiving intrinsic therapies, for example, the folks who may prefer relying on transfusions to keep the blood cell counts stable. As a result, patients accepted the treatment without even being tired or at risk of infection; the treatment was very successful.
Sometimes, the transfusions substitute the blood vessels that could have been damaged and may have reached the threshold that separates life from death in cases like surgeries. Vehicles have been a great resource for people whose blood is lost by wounds from car accidents to travel from one place to another.
Systematic and safeguard strategies have contributed the most to the likelihood of infection being reduced, allowing. Irrespective of blood transfusions, the risk still exists. Yet, these people who suffer from the mentioned allergies, such as urticaria and irritation, will not have to be sick with a disease. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury![]() (TRALI) is the most serious and rarest transfusion-related risk. This pathology results in pulmonary edema, and thus, the oxygen supply to the lungs is damaged – therefore, the breathing glands' function is impaired. The damage caused to the lung if the incident is related to a major issue. It can only be noticed during urgent first-aid care scenarios.
(TRALI) is the most serious and rarest transfusion-related risk. This pathology results in pulmonary edema, and thus, the oxygen supply to the lungs is damaged – therefore, the breathing glands' function is impaired. The damage caused to the lung if the incident is related to a major issue. It can only be noticed during urgent first-aid care scenarios.
Donor's red cells being attacked by a body's immune system is a rare and severe complication of blood transfusion. This reaction refers to red blood cell reactivity and may worsen the condition of the recipient's health by exhibiting fever and chills or manifesting in terms of kidney problems. Even though this is an improbable case, nobody can dispute that infection transmission is the key factor that brings about the infection. Nevertheless, the small benefit should not be taken lightly.
Sickle cell disease Patients who get transfusions frequently on and off for long periods of time may have very high iron levels in their body tissues. Excessive iron accumulates in the heart and liver and causes malfunction of other organs. The procedure entails the use of ferric acid, a chemical that competes with iron. This treatment, contraindicated in iron-deficient individuals, is designed to remove iron and fix the underlying problem.
Physicians who conduct the assignment by comprehending the medical history and blood type of the patient tend to prioritize the transmission procedure. Once the necessity has been determined, the subsequent step of the method is:
The health care team will first perform a blood test to find her blood type and compatibility with the donor. Consequently, the likelihood of a hemolytic reaction is lessened.
Blood is divided into different components, such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets, based on the patient's needs.
The injection eventually serves its purpose when the blood and its constituents reach the vein. A health professional regularly instructs the patient on how to spot several potential adverse after-effects of the medicine. The type of department or people involved may alter the time it takes to perform this procedure to one hour or four hours.
After the treatment with the drug, the patient is checked for potential side effects that the infused drug might have produced. The sample is taken from a patient to determine if it requires additional transfusions and if blood has been infused. Therefore, tests are executed.
Blood transfusion is believed to be the most appropriate choice because it often results in very positive results for patients. The program has no less been a breakthrough in that it diminished the effects of the life-threatening complications that can occur in trauma patients, and during the surgeries, their lives are saved. It also lowers the patient's symptoms, such as fatigue and breathlessness. To put it in patients' words who have chronic conditions, these blood donations are the main reason why they live happier lives now, that they are cancer-free and the welfare of their organs (stroke) is protected. Hence, these infusions are their silver bullets.
Iron overload is quite okay. Still, it is sometimes observed in people with diabetes, heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who have been subjected to transfusions frequently. When it comes to the dosage of drugs and the pace of treatment, they usually exhibit significant progress. The transfer was very important, particularly for cancer patients coping with chemotherapy side effects that they can slow down and even reverse the processes. They would rather continue the treatment dialysis to a full state of recovery. Cancer patients have anemia.