The blood circulates in your body inside the blood vessels. Blood pressure is the pressure that flowing blood exerts on the walls of the blood vessels. With each beat, the beating heart releases a portion of blood, which then flows through the arteries, supplying all the organs of our body, and returns to the heart through the venous system.
The pressure exerted by the blood is variable, constantly fluctuating between the maximum value – when a new portion of blood from the heart reaches the vessels and the minimum value – between the heartbeats. In practice, the maximum is called systolic pressure, and the minimum is called diastolic pressure.
The value of blood pressure depends on a few things. Factors that influence how high blood pressure is include:
Normal blood pressure is considered less than 120/80 mmHg.

High blood pressure (hypertension) is often called a “silent killer” because it rarely causes any symptoms. Untreated hypertension may lead to many cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke. Every year, 10 million![]() people die from diseases related to hypertension. Therefore, it is essential to measure blood pressure regularly to catch hypertension in time and implement treatment before severe complications occur.
people die from diseases related to hypertension. Therefore, it is essential to measure blood pressure regularly to catch hypertension in time and implement treatment before severe complications occur.
Measurement machines usually consist of measuring devices![]() with an arm cuff attached. The cuff is typically wrapped around the upper arm when performing a test. The cuff is then filled with air to the point where blood flow in the artery is blocked. That can cause some discomfort, but it only lasts a few seconds. Depending on the machine type, it may be:
with an arm cuff attached. The cuff is typically wrapped around the upper arm when performing a test. The cuff is then filled with air to the point where blood flow in the artery is blocked. That can cause some discomfort, but it only lasts a few seconds. Depending on the machine type, it may be:
The results from both types of devices should be ready straight away. The result is given in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure occurs when the heart pushes blood to the blood vessels, and diastolic pressure occurs between heartbeats. The first number of test results is always a systolic pressure, and the second is the diastolic pressure.
The optimal blood pressure levels vary between people and depend on age, health condition, time of day, emotional state, medications or stimulants used, and heart rate. The ideal blood pressure for adults is less than 120/80 mmHg. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), blood pressure charts for adults contain the following groups![]() :
:
| Category | Systolic mmHg | Diastolic mmHg |
| Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Less than 80 |
| Hypertension stage 1 | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Hypertension stage 2 | 140 and higher | 90 and higher |
| Hypertension stage 3 | 180 and higher | 120 and higher |
Low blood pressure occurs when the results are less than 90/60 mmHg![]() . Unlike high pressure, low pressure usually doesn’t pose a threat until it starts causing symptoms.
. Unlike high pressure, low pressure usually doesn’t pose a threat until it starts causing symptoms.
Hypertension is a condition in which high blood pressure, which means that the result is 140/90 mmHg or higher, is detected in an individual. The disease is diagnosed based on several blood pressure measurements, usually performed at intervals of several days or weeks. In most people, the exact cause of hypertension cannot be stated. Then, it is called primary (essential) hypertension. This type of hypertension occurs in 90% of affected people, and the cause is complex, including genes, environment, diet, stress, and lifestyle.
A small percentage of affected people have secondary hypertension, which is caused by an already existing disease that affects large arteries or organs, leading to hypertension. Secondary hypertension may be caused by:
Many factors contribute to primary hypertension![]() development. Those include:
development. Those include:
In most people, hypertension is symptomless until some organ damage is already done. Some symptoms that occur during hypertension are also common in other diseases (non-specific symptoms), which may make it difficult to connect the symptom with hypertension. That’s why checking your blood pressure regularly is crucial even if you feel well.
Hypertension may manifest in the following symptoms![]() :
:
In many people, the first symptoms of hypertension are related to its complications, such as heart attack or stroke. Call an ambulance if you experience chest pain, tight chest pain, pain that spreads to the shoulder, sudden shortness of breath, trouble speaking or seeing, sudden numbness, difficulty walking, or severe headache.
Treatment of secondary hypertension involves treating the disease that caused it. Treatment of primary hypertension aims at lowering blood pressure and preventing complications. Treatment methods differ depending on hypertension level, type, other diseases, and the patient’s age.
When an individual has mild hypertension and no comorbidities, the initial treatment involves lifestyle changes. Pharmacological therapy is implemented if a condition is too advanced or the lifestyle changes are insufficient.
Various antihypertensive![]() drugs are used in the treatment. They can have different effects on the body, including:
drugs are used in the treatment. They can have different effects on the body, including:
The doctor decides on which medications you should use based on your age, the stage of your hypertension, and other diseases you have.
Low blood pressure (hypotension![]() ) happens when the measurement result is 90/60 mmHg or less. Hypotension is usually not unhealthy unless additional symptoms that may worry your healthcare provider occur. Those symptoms include:
) happens when the measurement result is 90/60 mmHg or less. Hypotension is usually not unhealthy unless additional symptoms that may worry your healthcare provider occur. Those symptoms include:
If hypotension happens to you only occasionally, it usually shouldn’t cause worry. However, you should contact your doctor if you feel dizzy, nauseous, or faint.
Hypotension may happen for numerous reasons. The most common ones include:
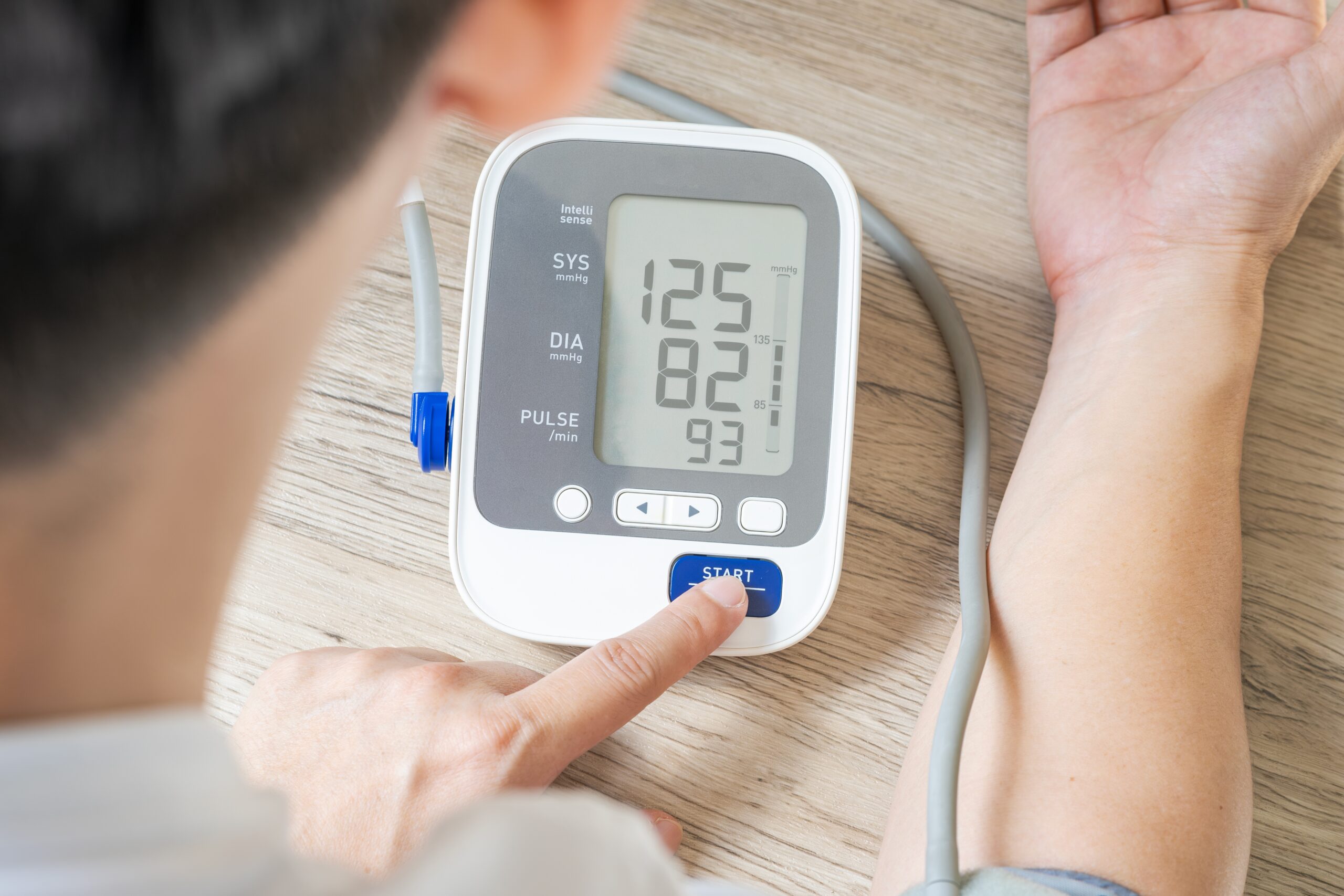
Strong evidence suggests that lifestyle habits help maintain normal blood pressure and prevent hypertension. Modifications that can be made include:
Monitoring your blood pressure regularly and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent the severe consequences of unnoticed hypertension, including stroke and heart attack.
A unique eating plan called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) was designed for people who should particularly care about keeping their blood pressure low. That balanced and flexible dietary plan helps create a heart-healthy eating style.
DASH![]() aims to achieve daily nutrition goals without requiring special foods. Some recommendations include:
aims to achieve daily nutrition goals without requiring special foods. Some recommendations include:
You should check your blood pressure regularly. Experts recommend that healthy adults over 40![]() should check themselves at their doctor’s office at least once every five years. If you are at risk of hypertension, you should get checked more often. Some African, South Asian, and Afro-Caribbean people may be at risk of developing hypertension at a younger age and are encouraged to get checked earlier.
should check themselves at their doctor’s office at least once every five years. If you are at risk of hypertension, you should get checked more often. Some African, South Asian, and Afro-Caribbean people may be at risk of developing hypertension at a younger age and are encouraged to get checked earlier.
You should make an appointment with your doctor if you notice any symptoms that may suggest hypertension, such as headaches, nosebleeds, buzzing in the ears, blurred vision, and shortness of breath. You should also make an appointment if you notice any hypotension symptoms, such as fainting, fatigue, dizziness, and heart palpitations.
Sometimes, your healthcare professional may recommend checking your blood pressure at home. Then, you can buy an electronic monitor at a pharmacy and measure your blood pressure daily to check how well you control it.