Inflammatory changes in the hair follicle may initiate the disease. Follicular keratinocytes release pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate endothelial cells.
This results in the accumulation of inflammatory cells around the follicle, mainly T lymphocytes and macrophages, intensifying the previously initiated inflammatory process. Damage to the hair follicle depends on the severity of the infiltration.
The consequence of inflammation is rapid hair loss. After the inflammation subsides, the hair follicles start functioning again. It is excellent news – the hair loss is reversible.
The etiological factors include genetic factors, atopy, psychological factors, hormonal factors (thyroid dysfunction), intracorporeal foci of infection (presence of bacterial superantigens), stress, and autoimmune phenomena.
Many internal and external factors, such as age, diet, hormonal disorders, diseases, stress, and pollution, influence the hair life cycle. It is also essential to where we come from, where we live, and what predispositions we inherit.
The hair life cycle runs individually for each follicle and consists of three phases:
When the hair life cycle is disturbed, the problem of hair loss and baldness occurs, depending on many factors, including hormonal, genetic, and external factors.
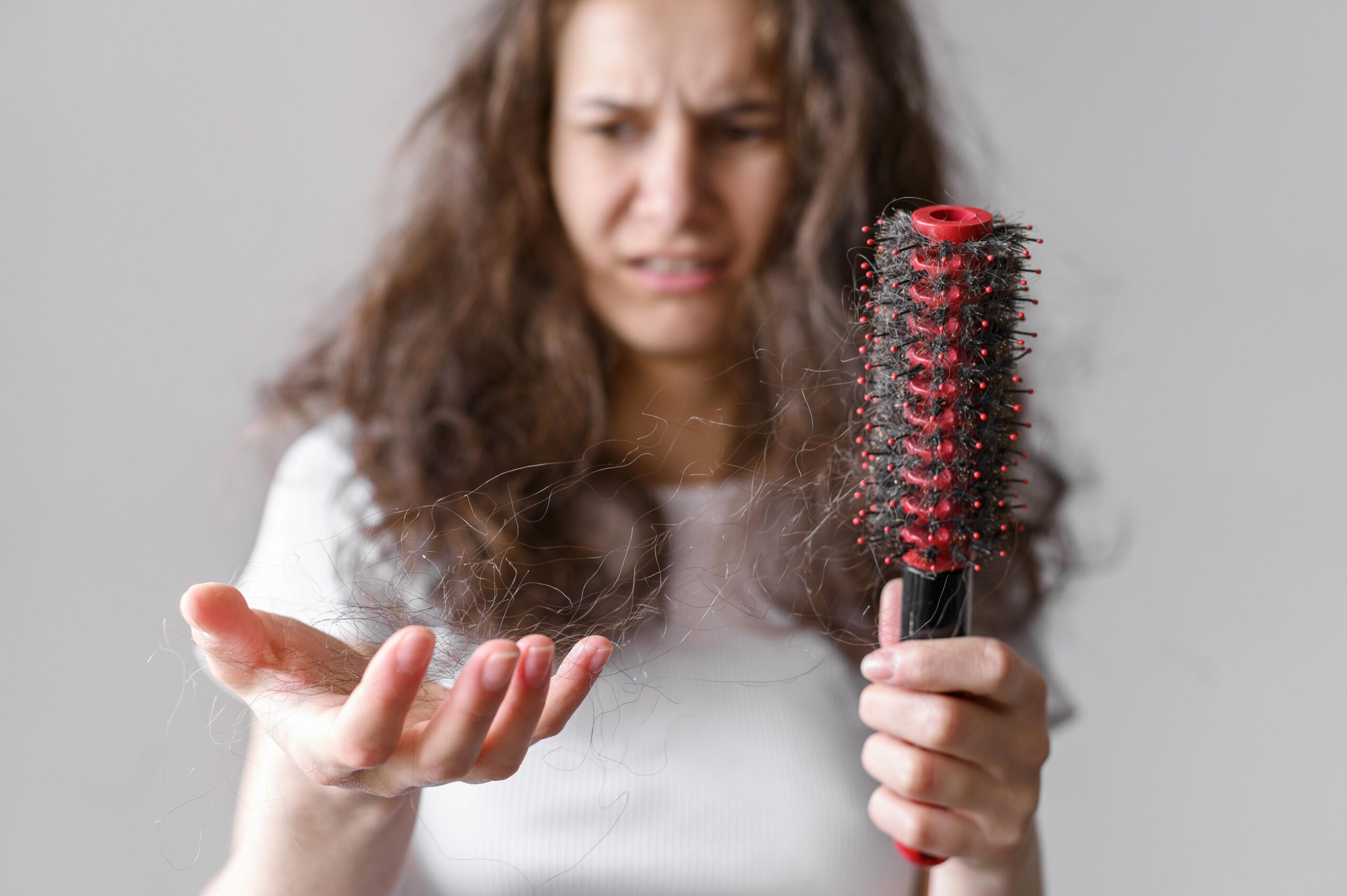
Excessive hair loss occurs when the balance between the number of hairs in the growing and resting phases is disturbed. Sometimes, such baldness lasts for a short time. After correct diagnosis and therapy, hair starts to grow again. Unfortunately, there is also a type of alopecia![]() that is caused by the death of hair follicles, and the consequences are permanent and irreversible.
that is caused by the death of hair follicles, and the consequences are permanent and irreversible.
It is the most common type of baldness, also called male pattern baldness, although it also affects women. Androgenetic alopecia![]() has a hormonal basis and is most often genetically determined. It may also occur as a result of hypertension, diabetes, or ischemic heart disease.
has a hormonal basis and is most often genetically determined. It may also occur as a result of hypertension, diabetes, or ischemic heart disease.
We talk about telogen effluvium![]() when too many hairs enter the resting phase at the same time. Hair stops growing and falls out excessively, which results in overall thinning. In this form of the disease, the hair follicles do not die, and there is no complete baldness. The problem is temporary.
when too many hairs enter the resting phase at the same time. Hair stops growing and falls out excessively, which results in overall thinning. In this form of the disease, the hair follicles do not die, and there is no complete baldness. The problem is temporary.
The condition is also known as dystrophic alopecia![]() . In this case, excessive hair loss is related to natural hair growth cycle irregularities.
. In this case, excessive hair loss is related to natural hair growth cycle irregularities.
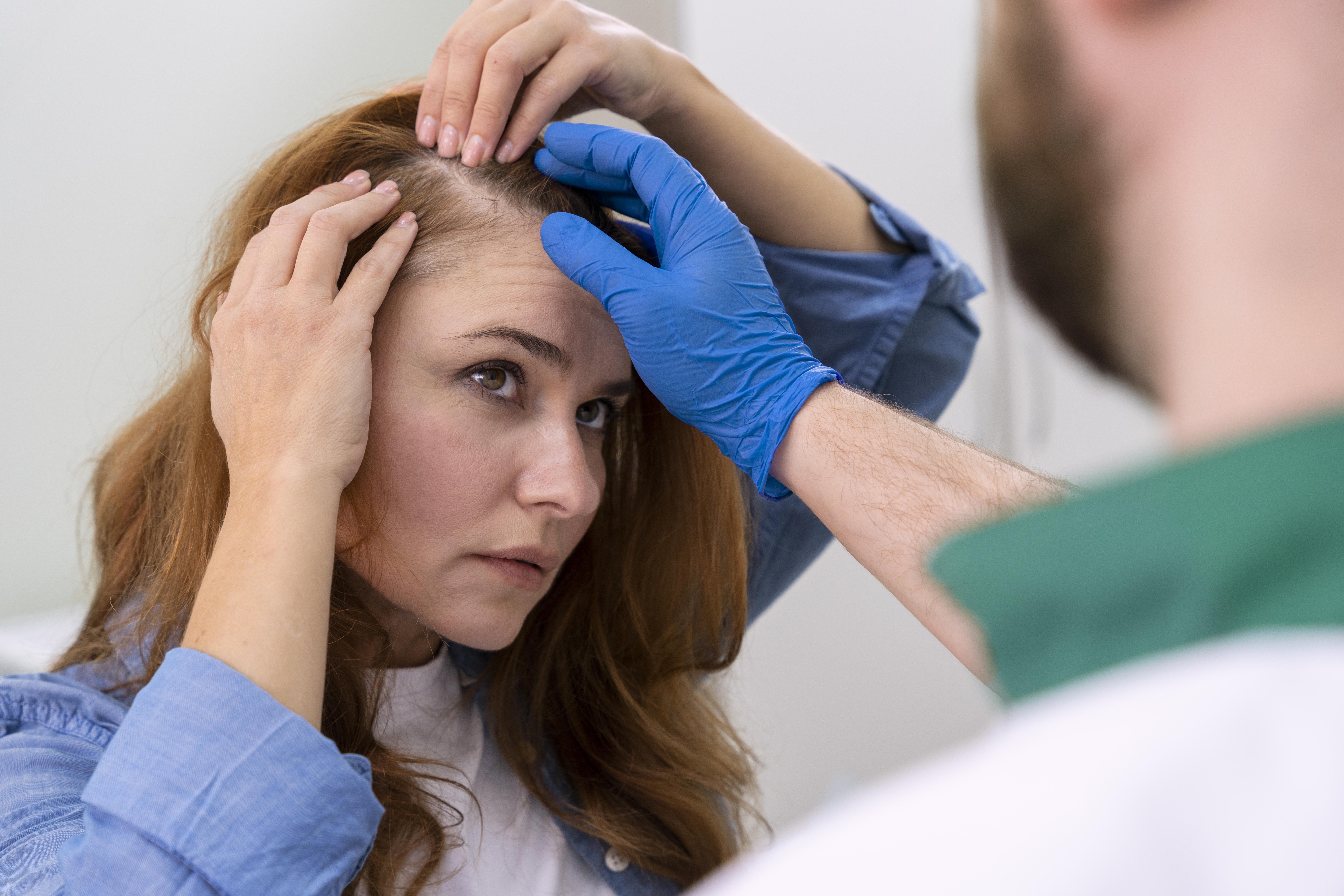
The name of this type of disease reflects its symptoms. Alopecia areata![]() is characterized by round spots without hair. They have a regular shape and the skin within them remains unchanged by the disease. Foci of baldness are usually located in the occipital and frontoparietal areas.
is characterized by round spots without hair. They have a regular shape and the skin within them remains unchanged by the disease. Foci of baldness are usually located in the occipital and frontoparietal areas.
Hair loss itself is not a strange or abnormal phenomenon. Some naturally age and fall out at the end of their lives, making room for new, healthy hair. However, if the amount of hair falling out suddenly increases, and you notice that your hairstyle is losing significant volume – you are dealing with the first symptoms of baldness that must be prevented.

Alopecia lesions most often have a regular shape, are hairless, and the skin remains unchanged by the disease. Most often, the changes are in the occipital and frontoparietal areas. Alopecia mainly affects the scalp, but it can also occur in other body parts.
Patients with alopecia may experience nail changes![]() of various types: nail pitting, Beau's lines, brittleness, creeping, thinning, thickening, or transverse furrowing of the plates.
of various types: nail pitting, Beau's lines, brittleness, creeping, thinning, thickening, or transverse furrowing of the plates.
If you experience symptoms indicating alopecia, you should consult a dermatologist.
This condition has various causes: genetic, hormonal, environmental, and even related to improper hair care and styling.
These two hormone types influence the hair condition:
External factors![]() of the exposome play an important role – these are all the factors we are exposed to throughout our lives. Many of them may hurt the hair and cause increased hair loss. Primarily:
of the exposome play an important role – these are all the factors we are exposed to throughout our lives. Many of them may hurt the hair and cause increased hair loss. Primarily:
Alopecia can be caused by various non-hair-related conditions, such as:
Improper treatment of hair daily can also weaken and damage it, leading to brittleness and, as a result, hair loss. Particularly harmful are:
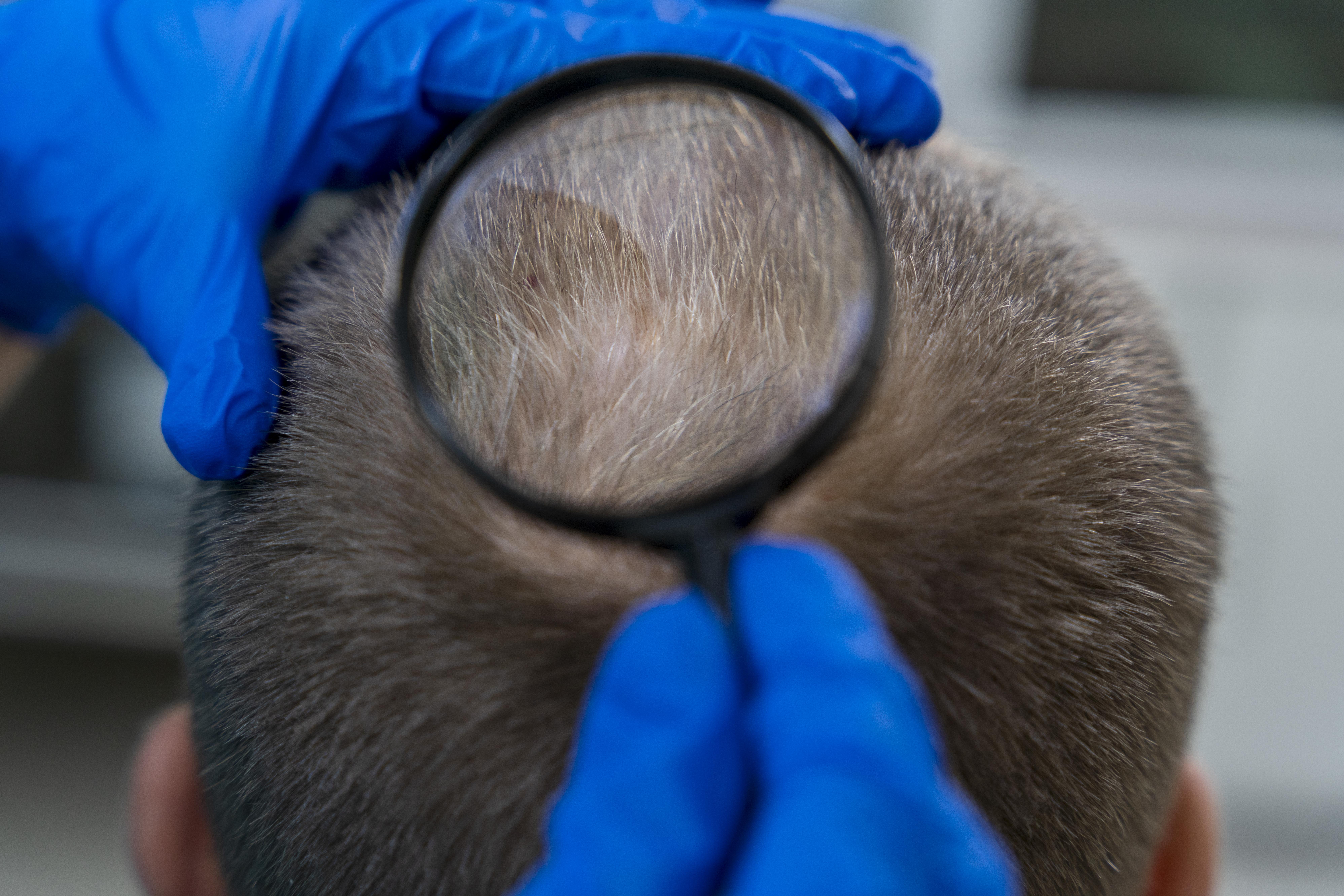
The doctor diagnoses alopecia![]() based on the clinical picture typical of this disease.
based on the clinical picture typical of this disease.
Hair loss depends on many factors. Therefore, its effective therapy requires a comprehensive and comprehensive approach. Although it is impossible to regain the lush hairstyle and thick hair typical of teenage years in adulthood, there are many effective methods of treating hair loss – both medical, psychological, and cosmetic.
Trichology ![]() – the science of scalp diseases and the treatment of baldness – is a relatively young field of medicine that is developing very quickly, offering more effective solutions and methods every year. Before starting treatment, however, you must first know the cause of the problem to select the appropriate type of therapy – not all treatments work on the same types of hair loss, and by using inappropriate methods, we can even harm ourselves. That is why it is important to visit a dermatologist or trichologist who will diagnose the causes of baldness and select the best therapy.
– the science of scalp diseases and the treatment of baldness – is a relatively young field of medicine that is developing very quickly, offering more effective solutions and methods every year. Before starting treatment, however, you must first know the cause of the problem to select the appropriate type of therapy – not all treatments work on the same types of hair loss, and by using inappropriate methods, we can even harm ourselves. That is why it is important to visit a dermatologist or trichologist who will diagnose the causes of baldness and select the best therapy.
There are many products of this type available on the market – mainly preparations with higher concentrations of ingredients that inhibit hair loss and stimulate hair regrowth. They can be in the form of ampoules, lotions, sprays, lotions, and other products applied topically to the scalp – such therapy should last at least 4-6 weeks. However, their effects may vary.
The most effective active substances with this effect are minoxidil![]() (in a concentration of 2 or 5%) and aminexil
(in a concentration of 2 or 5%) and aminexil![]() – which prevents the stiffening of the collagen sheath responsible for hair thinning in the case of androgenetic alopecia and also causes better attachment of the hair to the root and intense nourishment of the hair follicle, without side effects specific to minoxidil (such as excessive facial hair, allergies and contact irritation).
– which prevents the stiffening of the collagen sheath responsible for hair thinning in the case of androgenetic alopecia and also causes better attachment of the hair to the root and intense nourishment of the hair follicle, without side effects specific to minoxidil (such as excessive facial hair, allergies and contact irritation).
However, the thing about local treatments is that they work when they are used – so to maintain the effects, it is worth using them as a “reminder” (e.g., once every 6-12 months) and including a hair loss shampoo in your daily care. They are particularly helpful in cases of androgenetic alopecia and telogen effluvium in women (e.g., after pregnancy), as well as under the influence of stress.
Other types of lotions and shampoos strengthen the hair – by providing nutrients and trace elements, such as glucose, zinc, copper, amino acids, and vitamin A or B vitamins. However, they do not stop baldness and are best used as a support.
The most common cause of hair loss is androgenic alopecia. Several types of medications are approved to treat this problem. Minoxidil is mainly used topically at concentrations of 2 and 5%. In some cases – depending on the cause of alopecia – it may be justified to include oral medications in the therapy![]() , primarily such as:
, primarily such as:
Therapy should be recommended by a doctor and carried out under his supervision.
Very often, hair weakness and loss are caused by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals, mainly B vitamins, iron, zinc, copper, silicon, and vitamin D. Most often, it is a consequence of low-calorie and mono-ingredient slimming diets![]() .
.
You can also use supplementation from time to time – preparations with biotin, silicon, zinc, vitamins, and healthy fatty acids are particularly recommended. However, do not buy them blindly – it is worth checking whether they have been tested for absorption and effectiveness. It is important because many supplements available on the market will simply pass through your stomach without providing you with any nutrients.
Even the best supplements need to be used for at least three months to see their effects. It is best to combine them with a comprehensive treatment and the use of, for example, hair loss ampoules for even better results. They may also be helpful when using slimming diets, e.g., the popular low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet, which may lead to nutrient and vitamin deficiencies and, as a result, increased hair loss.
The psychological aspect is crucial in the problem of baldness. On the one hand, stress is one of the main factors causing hair loss (intense, traumatic experiences or chronic exposure to negative emotions), on the other – it causes low mood and sense of attractiveness, depression, and reluctance to socialize and socialize. It, in turn, causes stress and increases hair loss. Therefore, in many cases, the help of a psychologist![]() and learning how to deal with stress are significant and helpful in the treatment of baldness.
and learning how to deal with stress are significant and helpful in the treatment of baldness.
Many treatments are available in trichology, dermatology, and aesthetic medicine offices to stop hair loss and stimulate hair regrowth – in various types of baldness. Primarily: