Pesticides are chemical substances used to protect plants from dangerous factors. In many cases, crop selling can be highly complicated, so farmers use diverse methods to get as many yields as possible. Pesticides prevent crops from being influenced by different pieces and microbes that can be dangerous for plants and humans. Moreover, despite defined gains, many talk about the harmfulness of pesticides for humans.
There are two different types of pesticides. These can be pesticides, natural chemical compounds, and chemicals of artificial origin synthesized in the laboratory. Pesticides may be hazardous if a person is in a toxic environment for long periods. However, the harmful influence can also be delivered indirectly as well. If one keeps eating fruit and vegetable crops that have been treated with pesticides, they can get at risk of pesticide influence. The danger of the pesticide influent rises, increasing the doses of the substance and the toxicness of the chemical. Exposure to pesticides may even result in many different chronic diseases.
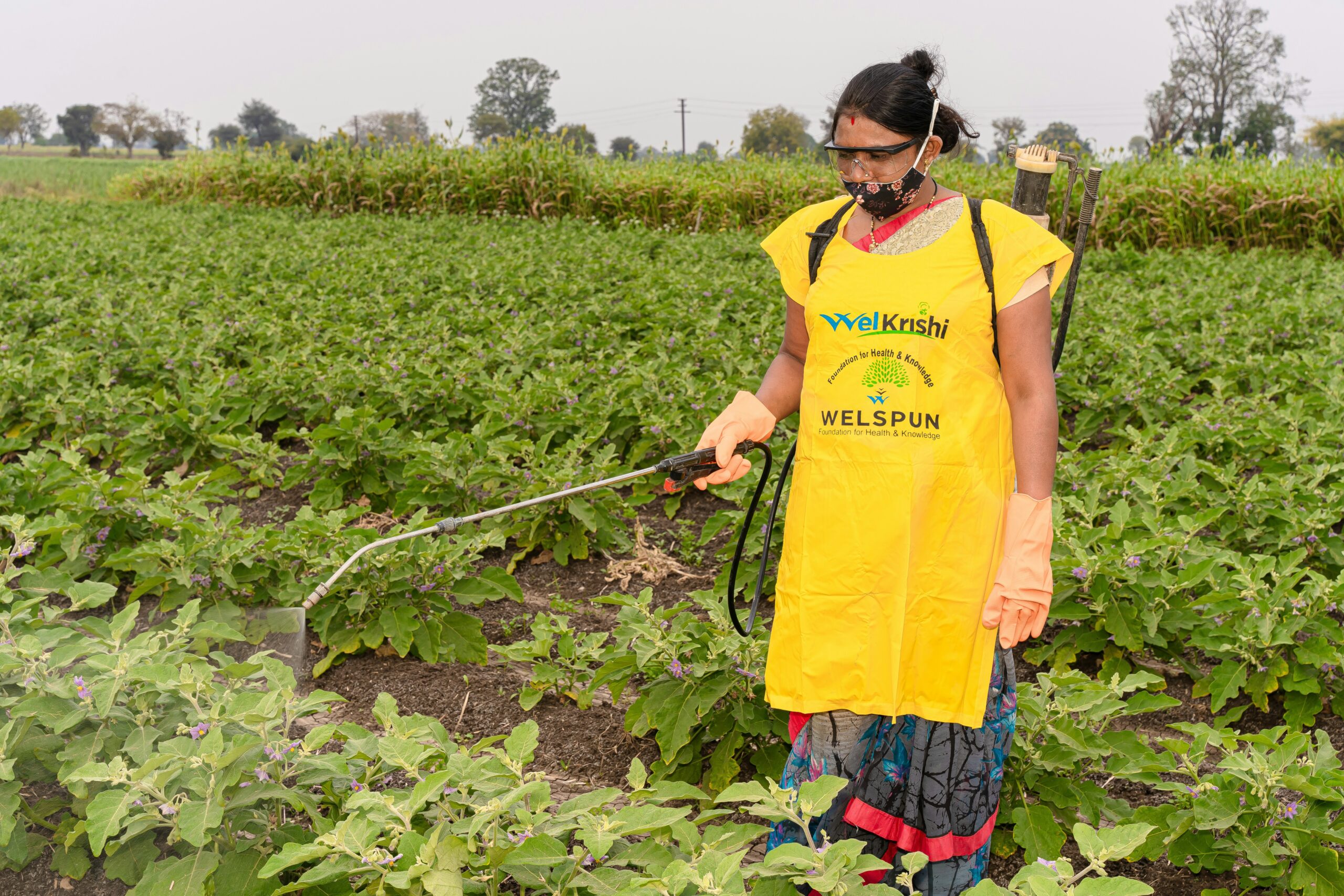

In addition, the use of pesticides can be dangerous for the environment in general. Some types of chemicals used in pesticides are called persistent organic pollutants. After being dropped into the environment, they cannot be corrupted and drastically affect the environment for many years. Therefore, using pesticides more than once has different dangerous effects and environmental changes, which can also influence humans. Pesticides are often developed to prevent, remove, or control dangerous pieces. However, many studies show that pesticides can be very dangerous for the environment and people.
Crops are threatened by weeds, insects, fungi, and rodents, so their yields may decrease. So, farmers are forced to take special measures. Pesticides may be used to avoid these problems, but releasing toxic substances into the environment may also be harmful in a different way. The sphere that makes the maximum use of pesticides is agriculture.
Moreover, pesticides are used in public health programs, where they control diseases and unwanted plants on ornamental landscapes. Chemicals are helpful in the agricultural and public health sectors and inhibit, decrease, or prevent the proliferation of spoilage agents in several items, such as electric and food packaging.
Pesticides are supposed to be poisonous, so they cause terrible and dangerous harm to humans and other living creatures. Nevertheless, various pesticides can differ in their toxicity. Pesticides can be grouped according to various criteria. Most pesticides contain active ingredients, either organic![]() or inorganic
or inorganic![]() .
.
The chemicals in organic pesticides are more complex and less soluble in water than inorganic pesticides. Organic pesticides, in turn, are classified into two groups, which include natural and synthetic substances. Natural pesticides are produced from sources that contain similar or the same chemicals in their structures. Synthetic pesticides are produced to imitate the structure of the natural product. Pesticides have different modes of action or the way the pesticide controls the target pest. Let us give you examples of pesticides grouped about the goal of use.
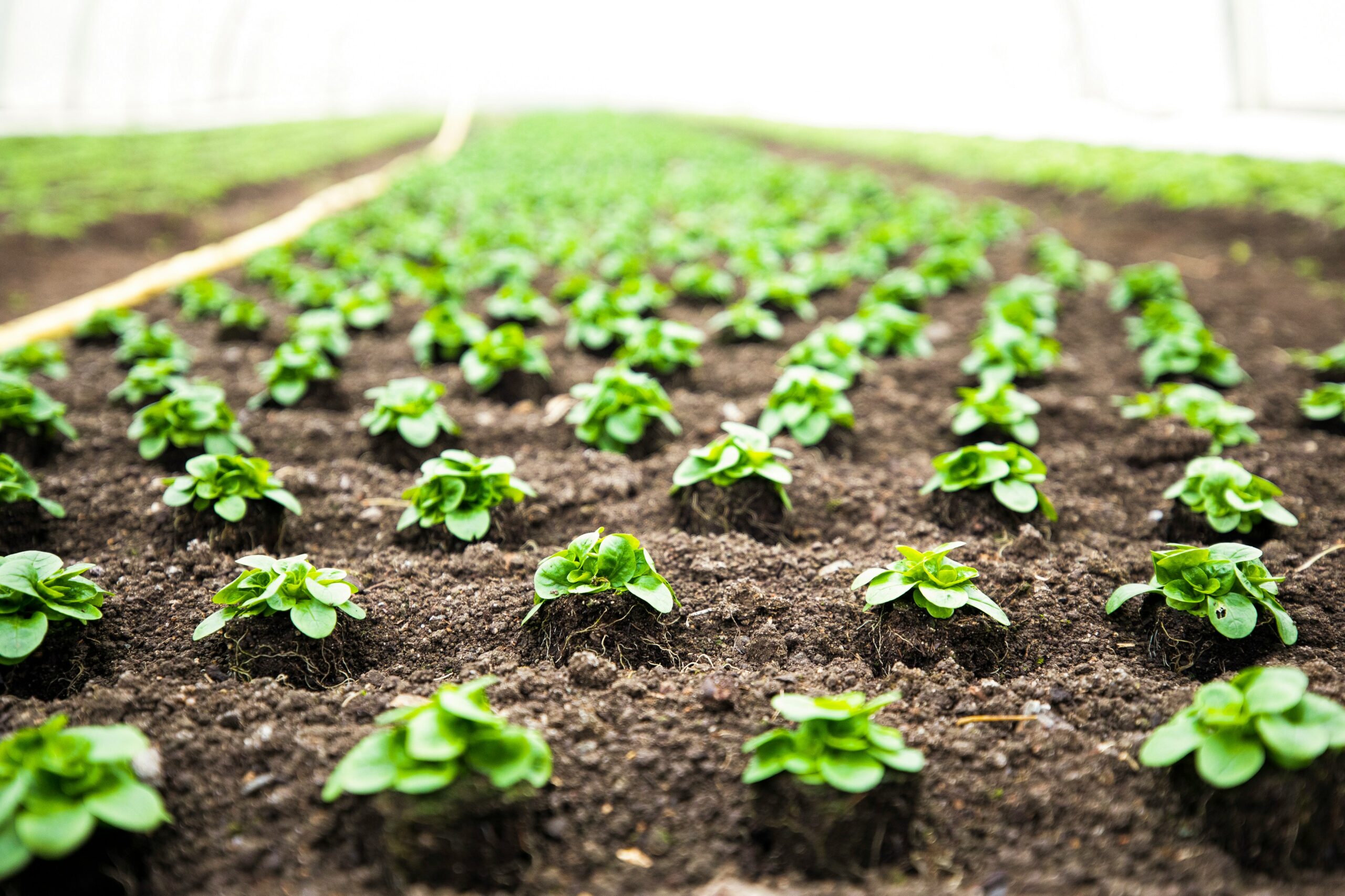

Fungicides are various chemical substances that help control fungi that target plants. They are applied to manage rather than eradicate existing diseases and protect any new, distinct disease process. This implies that fungicides have to destroy and stop fungi's growth. Certain fungicides could be organic, inorganic, or biochemical agents. Such agents could temporarily slow down the fungi's concentration according to the toxic component's concentration or suppress it permanently.
Insects are another type of nuisance creature for the farmers. They contaminate the food and affect the growth or total stop of the crops; these are just a few things they cause. Using insecticides is also a widely used method of protecting plants from the effects of creatures. Generally, insecticides can kill the insects as they can get into the body of the pests through direct contact. Pesticides can be absorbed through the skin, mouth, or respiratory canal by the pests. In addition, other pesticides work on the nervous system or the endocrine system of the pests. Therefore, the pests are killed while the crop remains.
Another threat for farmers is weeds – distinctly different weedy plants causing a decrease in the rate of growth of crops. Thus, weed control at the initial growth stage is essential for cultivating various cereals. Moreover, weeds are hosts to numerous noxious insects and pathogenic fungi; therefore, it is occasionally requisite to control them. Herbicides instantly kill plants upon touching or destroy weeds as leaves take them, stems, or roots. Therefore, the choice of herbicides has to be made wisely, correlating with the type of crops, group of undesirable plants, etc.
Scientific evidence fully supports the real risks connected with pesticides for human health and the natural environment. Pesticides may prove to be extremely harmful to humans and other organisms. Even at very low levels, they may negatively impact health during the early stages of development. Moreover, children are extremely vulnerable to these substances due to their physical structure as well as behavior and physiology. As a result, people can be exposed to pesticides in different ways. Ways in which pesticides enter human bodies.

The easiest and most common way of exposure to pesticides is dermal. Applying or simply being present where the pesticides are used can expose people to pesticides that can be absorbed through their skin through splashing, spilling, or aerosol drift.
As previously mentioned, different pesticides exist and have varying formulation types and abilities to be absorbed. Hence, the absorption risk depends on the type of pesticide used. In addition, the amount and duration of exposure and the presence of various disappearing creams, powders, or other materials on the skin affect the level of toxicity. Temperature, humidity, and the use of personal protective equipment also play a pivotal role.
Pesticides in solid forms, such as powders and granules, are not absorbed through the skin as easily as the liquid prolificates. However, the risk of dermal absorption of pesticides exists when workers come in contact with them. Additionally, the rate also depends on the part of the body; for instance, areas such as the genital region![]() , the ear canals
, the ear canals![]() , and the nostrils are especially prone and sensitive to dermal absorption.
, and the nostrils are especially prone and sensitive to dermal absorption.
The oral method of pesticide application is the most dangerous method of absorption. Ingestion occurs most often due to improper handling and accidental exposure to the pesticide. Substantial cases of oral exposure have been observed where pesticides have been removed or transferred from a container, either marked or unmarked, if it was a food container or bottle.
Workers who carry out the application also suffer from exposure when they fail to wash their hands before eating or smoking. The workers in these positions should be the most cautious and regard the rules. A maximum pesticide residue limit should be set for food with its maximum exposure to pesticides before harvest so that it does not end up being transferred to humans in this manner.
Pesticides harm the human respiratory system, too. Plant protection products contain volatile compounds, which are inhaled into the nozzle, the throat, and even the lungs. Nevertheless, exposure to such an inhalation route is low. The latter increases with the physical solubility in the respiratory system and present quantities.
Consequently, inhalation risk increases when a particular pesticide is sprayed in large amounts. Nowadays, it is accepted that the respiratory exposure route is of particular significance, especially when such plant protection products are applied in enclosed spaces. Moreover, it is necessary to note that many pesticides exhibit high vapor levels over an enormous range of temperatures and cause even higher respiratory exposure. Therefore, pesticides with a high vapor pressure hazard should be applied with respiratory protection.
The eye is a very sensitive organ. It is also exposed to pesticides. Some dangerous substances may be absorbed by the eye and thus cause chemical injury to the eye tissues. Eye damage can be very severe. If these pesticides are used with mechanical equipment, the first may bounce off the sprayed vegetation or the surface on which they are sprayed, hitting the eye at a high speed and causing further injury.
Therefore, eye protectors are also required when dealing with pesticides. When spraying pesticides, a face shield or protective goggles may be worn to protect the eyes. Depending on the size and weight of the granules, granulated band pesticides can also threaten the eyes.
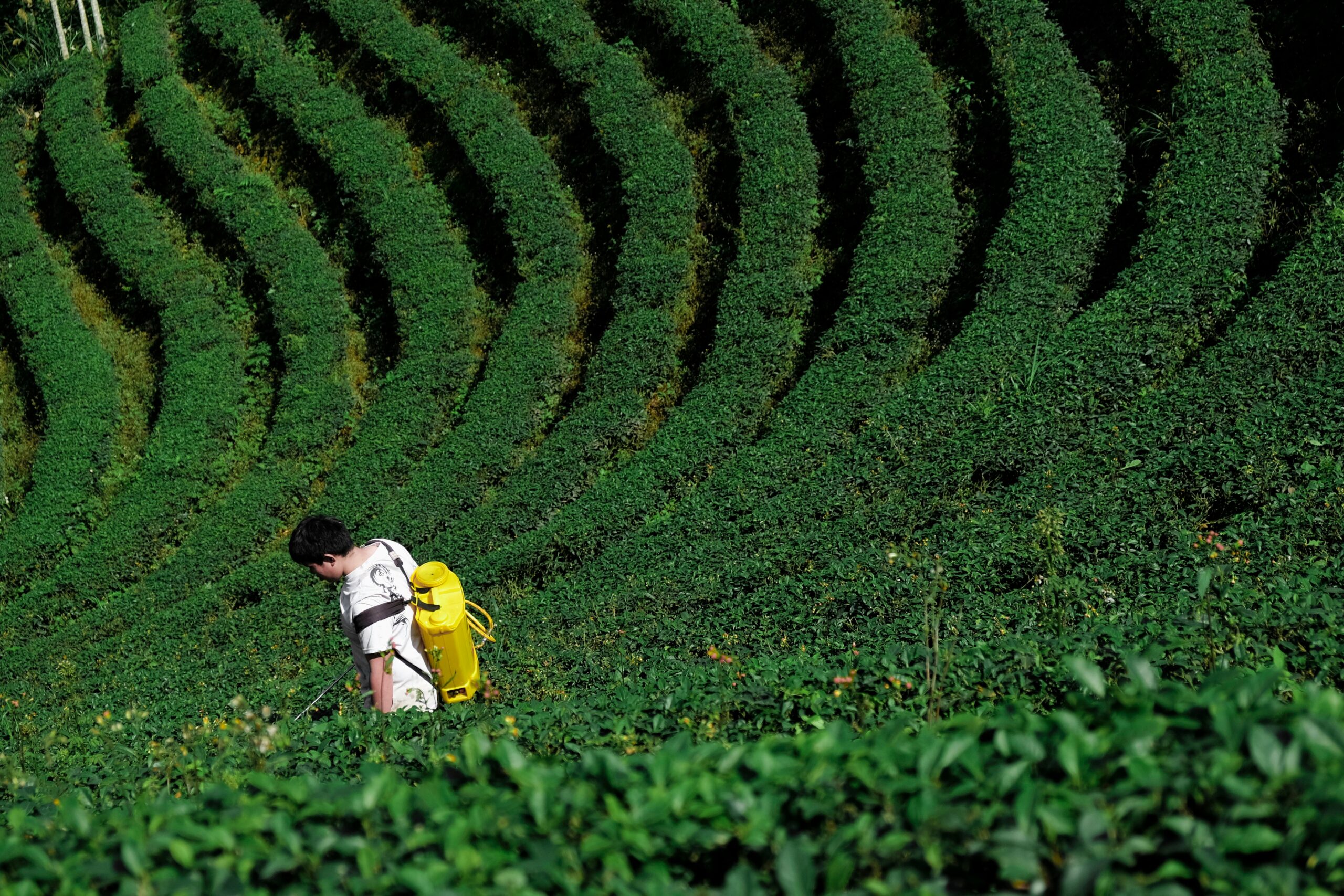

Numerous researches show that different pesticides can affect the development of this or that disease. However, the effect of pesticide exposure on a person depends on the toxicity of the agents and several other circumstances. Vulnerable to harmful pesticides may be sick and older people, pregnant women, and children: their organisms are more sensible, and besides, the consequences can be more severe. Also, the degree of impact depends on the way a person interacts with hazardous chemicals: workers in factories and laboratories run the danger.
According to the results of some studies, pesticides are capable of activating and exacerbating the course of asthma. Any substance that can cause injury, irritation, immunosuppression, and inflammation in sensitive individuals can produce a case of asthma. The effect should occur early in life for the exposed person to develop an incarnation of asthma. Most pesticides are weakly immunogenic, so their ability to immunize the airways of exposed populations is probably slight. However, a few pesticides are potent enough to destroy bronchial mucosa. Hence, the issue of pesticides causing asthma depends on the variety of pesticides.
Many studies have similarly demonstrated that pesticides are carcinogenic. It has been noted, for example, that among the male agricultural workers who are most likely to be in contact with pesticides, the prevalence of bladder cancer![]() has increased. This would suggest that pesticides are similarly linked to bladder cancer. Many scientists also highlight that exposure to harmful pesticides is one of the most important causes of acute leukemia
has increased. This would suggest that pesticides are similarly linked to bladder cancer. Many scientists also highlight that exposure to harmful pesticides is one of the most important causes of acute leukemia![]() .
.
Moreover, pesticides may also be linked to several cases of brain cancer![]() . However, female agricultural workers may be at risk of breast cancer
. However, female agricultural workers may be at risk of breast cancer![]() if they come into contact with pesticides. It is, therefore, sufficiently clear that pesticides are carcinogenic and, as the results of considerable mechanistic work would suggest, they can induce mutation in oncogenes.
if they come into contact with pesticides. It is, therefore, sufficiently clear that pesticides are carcinogenic and, as the results of considerable mechanistic work would suggest, they can induce mutation in oncogenes.

While it has been observed that foods contaminated with pesticide residues result in heightened toxicity, certain studies have concluded that exposure, be it acute or chronic, to such pesticides results in respiratory diseases, such as allergic rhinitis![]() . In addition, people who are exposed to chemicals can also develop food allergies. It would appear that chemicals can potentially modify the microbiota of the human body, which can subsequently affect the human immune system and thereby cause such illnesses.
. In addition, people who are exposed to chemicals can also develop food allergies. It would appear that chemicals can potentially modify the microbiota of the human body, which can subsequently affect the human immune system and thereby cause such illnesses.
Another observation is that the onset of food allergies in youngsters makes them more susceptible to the risk of developing allergies as they grow up. Also, any pollutants in the food can make people with allergies hypersensitive.
When farmers spray pesticides on a given area or plant, they move with time and become degraded to the environment. They have several effects on the non-target plants and the animal kingdom when they become part of the ecosystem. This is because once there is an attraction between the soil particles and pesticides, they will remain in the soil. The effects of pesticides on the soil and ecosystem are explainable; they remain in the soil for a long time.
In the leaching processes, the pesticides may have moved to the level of groundwater. By remaining long in the soil, they make the water vulnerable to contamination. Thus, the leaching of pesticides into the groundwater may pose more danger to animal and human health. In this regard, it originates from the fact that agricultural activities that rely on pesticides tend to be responsible for the translocation of pesticides to the environment, either the soil or the water, and may take a long time to persist.
Consequently, the use of pesticides would be responsible for several effects, such as climate change![]() and changes in soil texture, pH, temperature, moisture, and mineral and organic content.
and changes in soil texture, pH, temperature, moisture, and mineral and organic content.
Table of Contents

Eye infections are common conditions where an eye becomes red, itchy, and painful. What are the common causes? How is… read more »

An ophthalmologist is an eye doctor. They are trained to diagnose, treat, and manage eye and vision conditions. Each part… read more »

Eye drops are liquid medications designed to be applied directly into the eyes for various purposes. They are used to… read more »

Strabismus is an eye misalignment, a condition when eyes look in different directions. It can affect both children and adults.… read more »

Biotechnology is massive – blending biology and technology in a way that, in turn, affects our daily lives. Indeed, we… read more »
The first symptoms of pancreatic cancer are nonspecific, so it is difficult to make a quick diagnosis. Learn about pancreatic… read more »
Pink eye is one of the most frequently diagnosed ophthalmological diseases. It may be bacterial, allergic or viral. What are… read more »

Myopia, also called nearsightedness, is an eye condition in which distant objects appear blurry. Here is everything you need to… read more »
A cataract occurs when the natural eye lens becomes cloudy. The condition is most often associated with older age. When… read more »