We still consider 36.6 degrees Celsius the normal body temperature. However, the average value of an adult's temperature depends on many conditions.
Some external factors also affect normal body temperature. These include, for example, ambient temperature (heat and cold), stress, recent exercise, hunger, fatigue, and taking hot or cold baths. Interestingly, an increase in temperature may also result from overheating the body and prolonged screaming – however, this occurs mainly in the case of small children. In turn, some drugs used, such as paracetamol and many others, cause some reduction in normal body temperature. Body temperature may fluctuate within particular ranges depending on the seasons and climatic zones.
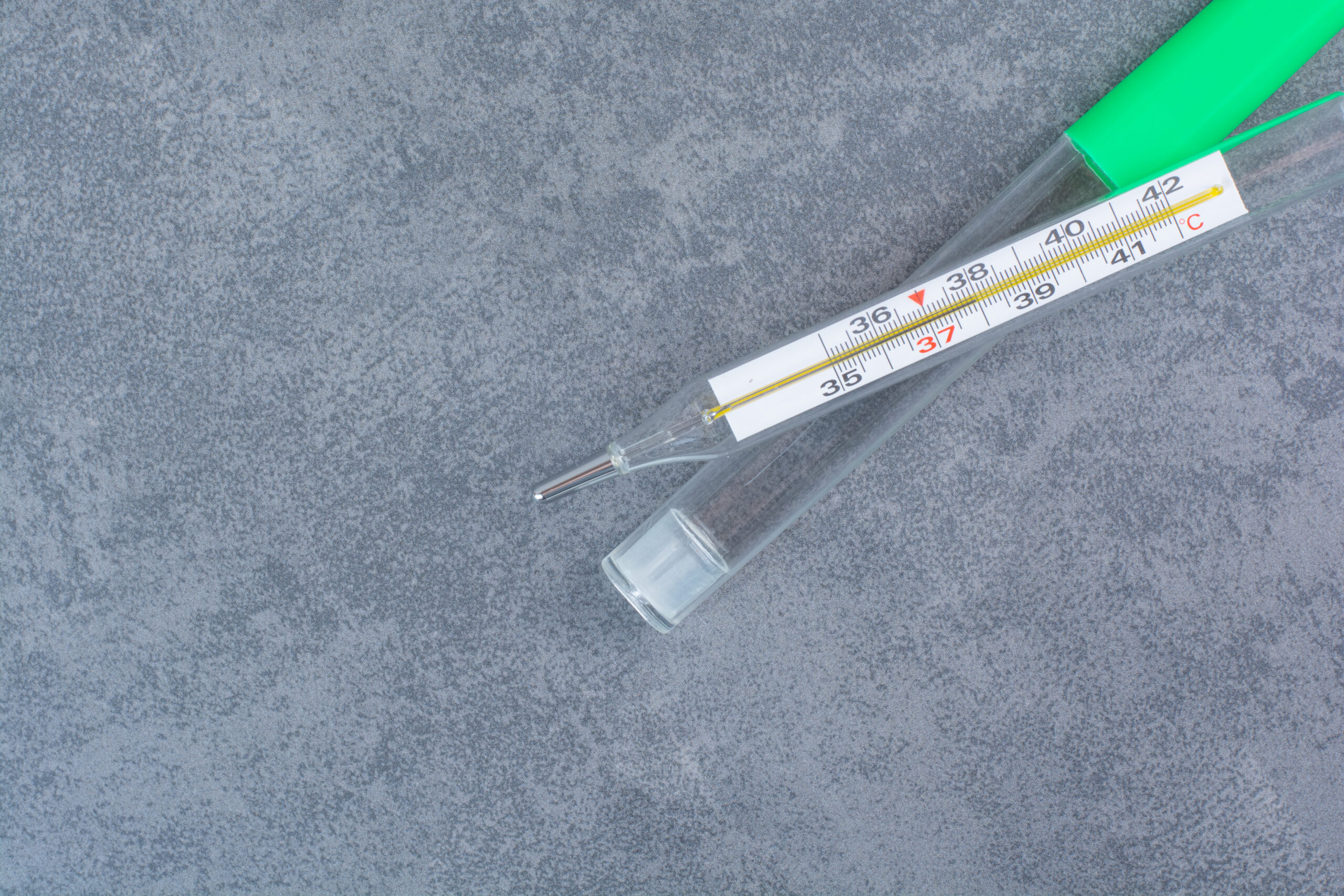

It is also worth remembering that the value depends on the measurement method. The temperature measured in natural body openings (mouth, ear, anus, or vagina) is higher than at the body surface. The highest temperature is in the rectum. The lowest is in the armpit.
Children and the elderly have lower body temperatures than adults. In the youngest, the norm ranges from 35.5 to 37.5 degrees Celsius, while in seniors, it ranges from 35.8 to 36.9 degrees Celsius. The normal body temperature![]() in adults ranges from 36.4 to 37.6 degrees Celsius.
in adults ranges from 36.4 to 37.6 degrees Celsius.
The average normal body temperature in the mouth is 37 degrees Celsius. The temperature in the rectum and ear is 0.3 to 0.6 degrees Celsius, higher than in the oral cavity. Measuring the temperature under the armpits or on the forehead will most often indicate 0.3 to 0.6 degrees Celsius lower than the temperature measured in the mouth.
It is worth noting that temperature measurement is a fundamental parameter for assessing the patient's condition, so remember to perform it appropriately.
Each measurement location![]() has a specific range of values. There is no single value that corresponds to normal body temperature or the temperature of a healthy person. The commonly accepted value for internal body temperature is 36.6 degrees Celsius.
has a specific range of values. There is no single value that corresponds to normal body temperature or the temperature of a healthy person. The commonly accepted value for internal body temperature is 36.6 degrees Celsius.
Correct temperature measurement depends mainly on the tools used. Until recently, the most popular model was a mercury thermometer![]() , but due to the high toxicity of mercury, they were withdrawn from the market in the European Union in 2009.
, but due to the high toxicity of mercury, they were withdrawn from the market in the European Union in 2009.
Liquid thermometers![]() replaced them. A mercury-free thermometer has an interior usually filled with g*****m, indium, and tin. The liquid rises as the temperature increases. Take measurements using a mercury-free glass thermometer under the arm, under the tongue, or in the anus, and after use, you can easily clean them with glass disinfectant.
replaced them. A mercury-free thermometer has an interior usually filled with g*****m, indium, and tin. The liquid rises as the temperature increases. Take measurements using a mercury-free glass thermometer under the arm, under the tongue, or in the anus, and after use, you can easily clean them with glass disinfectant.
Such a thermometer must be left in a given place for several minutes to measure the fever, which is a disadvantage for many people. In addition, the liquid that almost fills the thermometer's interior may be challenging for some people, making reading the measurement difficult, especially for the elderly or people with poor eyesight.
We also have electronic![]() and contactless thermometers available on the market. Small batteries power the former. The test result appears on the LCD, and a sound signals the end of the measurement. There may be slight differences in measurement results between thermometer models from different manufacturers because individual types have different sensitivity. These thermometers also differ in their tips. Those with a soft tip are suitable for use in more delicate places, such as the anus.
and contactless thermometers available on the market. Small batteries power the former. The test result appears on the LCD, and a sound signals the end of the measurement. There may be slight differences in measurement results between thermometer models from different manufacturers because individual types have different sensitivity. These thermometers also differ in their tips. Those with a soft tip are suitable for use in more delicate places, such as the anus.
An alternative to the above is non-contact thermometers![]() . All of them are characterized by short testing time and multifunctional use because they can be used to measure body, liquid, or environment temperature. It is worth noting, however, that they are the most expensive. Moreover, for some people, they may be too large a one-time expense.
. All of them are characterized by short testing time and multifunctional use because they can be used to measure body, liquid, or environment temperature. It is worth noting, however, that they are the most expensive. Moreover, for some people, they may be too large a one-time expense.
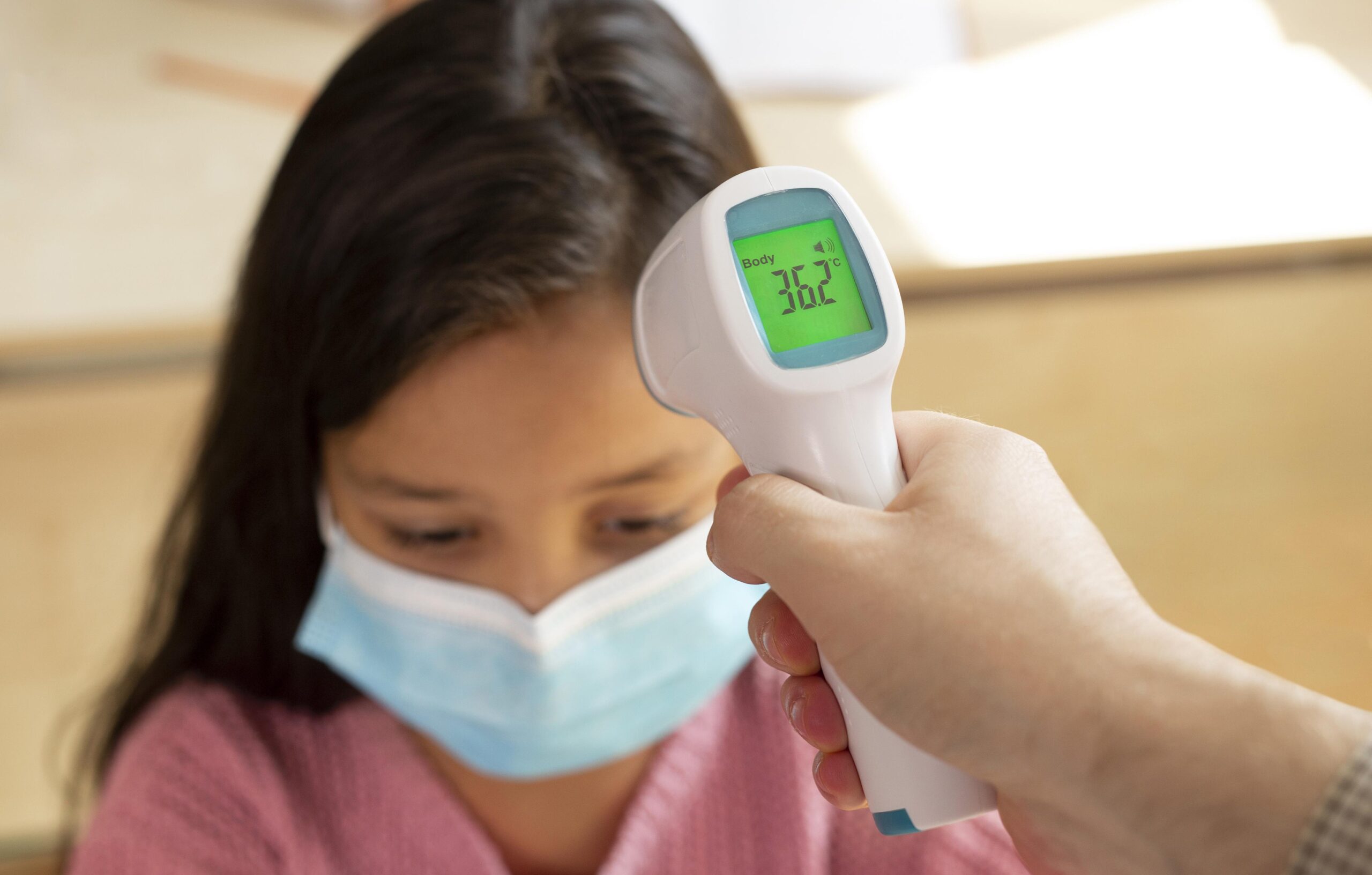
The device works thanks to infrared technology. It is battery-powered. There is no need for direct contact of the thermometer with the skin, which reduces the risk of transmitting pathogens to many people. The result appears on the LCD and after an audible alarm sounds. The most common mistake when measuring temperature with a non-contact thermometer is keeping the device at the wrong distance from the forehead.
To measure temperature correctly, hold it at a maximum distance of 5 centimeters from the forehead. Too large a distance may cause the device to provide us with the ambient temperature. Moreover, the temperature value considered correct varies depending on the measurement location.
The correctness of the measurement is influenced not only by the type of thermometer but also by the place of measurement. We use non-contact thermometers to measure the temperature on the forehead and infrared touch thermometers for the ear. Other thermometer types give us a choice, but they are usually used to measure temperature in the mouth, armpit, or rectum using electronic or liquid thermometers.
It is significant to differentiate between the technical precision with which a thermometer takes a reading and the clinical trustworthiness of a specific measurement technique. The thermometer accuracy is determined under ideal conditions by the relevant technical standards to guarantee the quality of the measuring instrument. Modern, high-quality thermometers measure with an accuracy of +/- 0.1 degrees Celsius.
Technical accuracy and clinical dependability in the thermometer use should not be confused. Human normal body temperature differs depending on the area where the temperature is measured and the measurement time. Physiological factors cause this and must be distinguished from a thermometer malfunction. The measurement accuracy depends primarily on the correct thermometer use, so always read the instruction manual for a given tool.
Each woman's body temperature is at a different level. It depends on where you are in your menstrual cycle![]() . The temperature before ovulation always remains lower, increases during ovulation, and then remains high throughout the next menstrual cycle phase, only to drop again with the onset of the next period.
. The temperature before ovulation always remains lower, increases during ovulation, and then remains high throughout the next menstrual cycle phase, only to drop again with the onset of the next period.
In the first part of the menstrual cycle (i.e., the period from the beginning of bleeding to ovulation), a decrease in body temperature is natural. It is related to the high level of estrogen occurring during this period. In most cases, the decreases are small, but in some people, the temperature measured at this moment may even fluctuate around 36 degrees Celsius. During this time, women can enjoy good well-being and improved mental condition.
The second part of the cycle (after ovulation) is characterized by increased body temperature. During this period, estrogen levels decrease, and progesterone levels increase. These hormonal changes can cause the thermometer to show a temperature of up to 37 degrees Celsius, but you should not worry too much about it because it will not be a sign of a cold or other inflammation.
Additional factors indicating the occurrence of the post-ovulatory phase may include deterioration of general well-being, grander irritability, or mood swings. A common symptom of the second phase of the cycle is also deterioration of the skin, decreased libido, and increased breast tenderness.
Pregnancy![]() is when a woman should pay even more attention to her health. Regular temperature measurements taken at fixed times of the day are necessary. This is because both too high and too low temperatures pose a serious threat to the woman's health and fetal development.
is when a woman should pay even more attention to her health. Regular temperature measurements taken at fixed times of the day are necessary. This is because both too high and too low temperatures pose a serious threat to the woman's health and fetal development.
Interestingly, a slightly elevated body temperature is a standard pregnancy symptom. Numerous hormonal and metabolic changes in the body cause it. The normal body temperature during pregnancy is 37-38 degrees Celsius. Above 38 degrees Celsius, miscarriage and premature termination of pregnancy may occur, while below 37 degrees Celsius, apart from miscarriage, other pregnancy threats may occur. It may indicate hypothyroidism or kidney or liver dysfunction. It also happens in the case of a systemic infection, anemia, or malnutrition.
All of the mentioned conditions are dangerous for both the mother and the developing fetus. If a pregnant woman experiences any disturbing symptoms, she should immediately see a doctor, as the symptoms may indicate a miscarriage or other problems with the fetus.
The average adult has a normal body temperature of 36.6 degrees Celsius, although, as we already know, even in healthy individuals, there may be some departures from this norm. The standard temperature in infants![]() is slightly higher and, depending on where the measurement is taken, can range from 36.6 to 37.5 degrees Celsius. This difference results from the incompletely developed thermoregulation system. Moreover, temperature fluctuations can be observed several times a day and should not cause concern for parents.
is slightly higher and, depending on where the measurement is taken, can range from 36.6 to 37.5 degrees Celsius. This difference results from the incompletely developed thermoregulation system. Moreover, temperature fluctuations can be observed several times a day and should not cause concern for parents.
Your baby's temperature may rise suddenly due to crying, tiredness, or intense breastfeeding. When the baby is rested in the morning, the temperature is usually half a degree lower. It should also be noted that small children![]() , due to the immaturity of their thermoregulation system, are more sensitive to fluctuations in ambient temperature – they cool down quickly when it is too cold and warm up when it is too hot. That's why it's so important to adapt your child's clothes to the season and the climate in a given environment.
, due to the immaturity of their thermoregulation system, are more sensitive to fluctuations in ambient temperature – they cool down quickly when it is too cold and warm up when it is too hot. That's why it's so important to adapt your child's clothes to the season and the climate in a given environment.
When a child's temperature exceeds 37.5 degrees Celsius, we deal with sub febrile conditions. It is a reason for closer observation, but it does not always have to cause concern. A high temperature may be due to fatigue, emotional state, severe anxiety, or overheating. Just calm the child down, give them water, lower the temperature in the room, and continue to look after the baby.

When a child's temperature rises and exceeds 38 degrees Celsius, it can be considered a fever, which is most likely a symptom of a viral or bacterial disease and may also be a consequence of teething or a reaction to a vaccine. If the temperature remains at this level, you should see your child's doctor.
A child's body temperature that is too low raises particular concerns for parents. This condition, as in the case of adults, may result from environmental conditions – too low air temperature or incorrect clothing. If the body temperature in children remains too low, you should see a doctor and perform the necessary tests to rule out the possibility of infection.
The normal body temperature range for people over 65 is between 35.8 degrees Celsius and 36.9 degrees Celsius. Seniors![]() , especially those with chronic diseases, may experience thermoregulation disorders, but body temperature should not fall below the hypothermia threshold, i.e., 35 degrees Celsius.
, especially those with chronic diseases, may experience thermoregulation disorders, but body temperature should not fall below the hypothermia threshold, i.e., 35 degrees Celsius.
Moreover, older people's bodies cannot adapt as well to sudden temperature changes as in the case of young people. In older people, this process no longer works as efficiently, and for this reason, in the 60+ age group, overheating causes discomfort and, above all, is dangerous to health and life. If you observe symptoms of overheating in an elderly person, you should immediately consult a specialist.
We discuss reduced body temperature when the values are above 35 degrees Celsius but do not exceed 36.6 degrees Celsius. It may decrease due to environmental factors or be one of the symptoms of various diseases. While this condition is not always a cause for concern, it should be considered, and more severe causes should be ruled out.
The most common causes of low body temperature are situations of increased heat loss by the body. However, some diseases may be accompanied by a drop in body temperature:
It is also worth mentioning hypothermia![]() . It is a condition in which the body becomes hypothermic, and the body temperature drops below 35 degrees Celsius. The body then tries to generate heat, and muscle tremors may be observed. We may also feel cold in the hands and feet due to constriction of blood vessels or notice the body's pallor. If the temperature does not rise, you need to see a specialist because it is a life-threatening condition.
. It is a condition in which the body becomes hypothermic, and the body temperature drops below 35 degrees Celsius. The body then tries to generate heat, and muscle tremors may be observed. We may also feel cold in the hands and feet due to constriction of blood vessels or notice the body's pallor. If the temperature does not rise, you need to see a specialist because it is a life-threatening condition.
We assume that a fever is a body temperature above 38.0 degrees Celsius. However, the range of 37.1-38.0 degrees Celsius is subfebrile. Fever![]() is one of the body's basic defense mechanisms. It was created as a non-specific support for the immune system in response to the attack of infectious agents.
is one of the body's basic defense mechanisms. It was created as a non-specific support for the immune system in response to the attack of infectious agents.
The causes of increased body temperature may differ, but in most cases, it accompanies infectious conditions. It can also be a symptom of severe diseases and everyday conditions:
Temporary low-grade fever should not be fought because it triggers the body's desired defense reactions. However, when we have a fever, it should be reduced pharmacologically using appropriate medications. In addition to taking medications, you should hydrate your body and rest. If the fever does not go away after taking drugs and persists for a long time, you should consult a specialist, as such a condition threatens the body.