It is the swelling of various body parts, but in most cases, it concerns the legs. Edema arises due to too much fluid retention in the body tissues. In your bloodstream, blood is constantly circulating through your blood vessels. From the ventricles of your heart, through the arteries, it goes to the organs and then returns through the veins to the heart atria.
In this process, approximately three liters of plasma per day pass through the capillaries into the body’s tissues, forming a fluid called lymph. The lymphatic system collects and carries away the lymph through its vessels, returning it back to the circulatory system.
If, at any stage of this complex process one of the elements fails to function properly, the fluid accumulates excessively in the body tissues creating edema.
There are many causes of edema: standing work, various diseases, pregnancy, and it can even be a side effect of some medications.
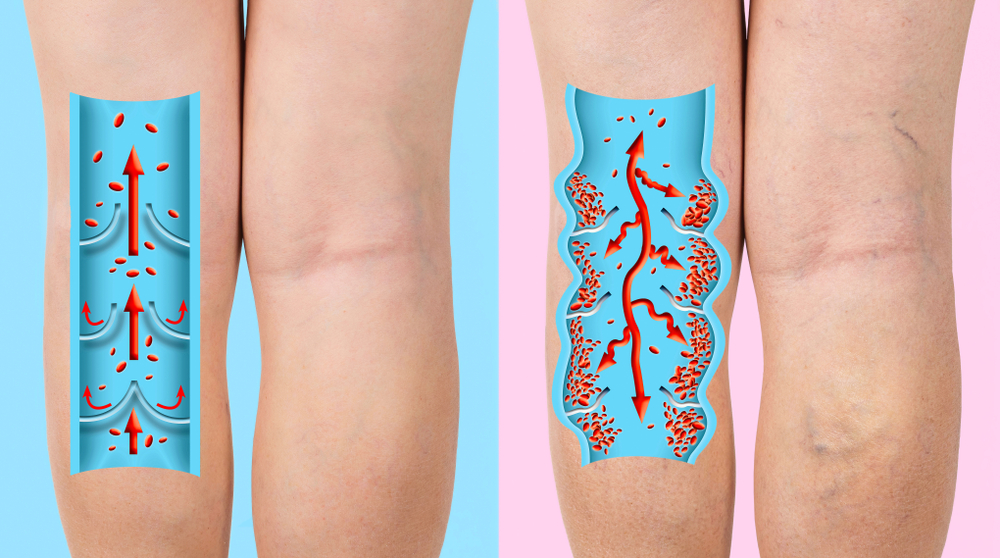
Standing work promotes stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs. It is difficult for blood to flow against gravity towards the heart without the help of the working leg muscles, which, like a pump, push blood upwards. Too much blood in the veins creates plasma leakage into the surrounding tissues hence edema.
In most pregnant women, swelling is caused by the physiological and natural changes this condition brings. Swelling is connected with an increase in the amount of blood in the female body.
During the first three months of pregnancy, the volume of blood in the woman's body increases by about 15%. It may happen that in the supine position, the enlarged uterus press on the inferior vena cava – a vein that carries blood from the entire lower half of the body. That also can lead to edema.
The varicose vein is the elongation and widening of the vein, as a result of which it acquires a winding course. The main cause is genetically determined abnormalities of the venous valves or disorders of the venous wall. Blood stagnates in dilated vessels, which in turn leads to edema.
Congestive heart failure![]() is a condition in which a damaged heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. This cause the blood to stagnate in the blood vessels. The heart acts as a suction pump: during diastole it creates negative pressure, which sucks blood from the veins, facilitating circulation.
is a condition in which a damaged heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. This cause the blood to stagnate in the blood vessels. The heart acts as a suction pump: during diastole it creates negative pressure, which sucks blood from the veins, facilitating circulation.
With right-sided heart failure, edema of the legs is most common. If the failure affects the left side of the heart, blood stagnation occurs in the pulmonary circulation, which can lead to lung edema.
Symptoms of pulmonary edema include shortness of breath, blue lips, coughing, and coughing up a pink foamy secretion. Pulmonary edema is dangerous and it requires emergency medical attention. Other symptoms of heart failure, apart from edema are decreased exercise tolerance, fatigue, prolonged recovery time after exercise, palpitation, and orthopnoea – this symptom consists in worsening shortness of breath when lying down and decreasing when sitting or standing.
Medications used to treat heart failure include diuretics (water pills), high blood pressure medications, and drugs that make the heart beat slower and harder (beta blockers, dopamine).
Lymphedema appears if the lymphatic system does not work correctly. The reasons for this condition include injury, infection, cancer, or genetic disorder of the lymphatic system. However, most frequently it is a side effect of surgical cancer treatment in which the lymph nodes are removed.
In hypothyroidism![]() , the thyroid gland produces too little of its hormones. It can cause fluid retention, which contributes to edema. Most often hypothyroidism is diagnosed with a TSH level test. TSH is the hormone responsible for controlling the work of the thyroid gland.
, the thyroid gland produces too little of its hormones. It can cause fluid retention, which contributes to edema. Most often hypothyroidism is diagnosed with a TSH level test. TSH is the hormone responsible for controlling the work of the thyroid gland.
During menstruation, fluctuations in sex hormones can favor fluid retention in the body, which predisposes to edema.
In cirrhosis![]() , the liver enlarges, and its surface becomes uneven. As a result, the blood vessels running through the liver cannot function properly, and blood stasis forms. It causes water to collect around the abdomen and legs. Fluid accumulation in the stomach is called ascites.
, the liver enlarges, and its surface becomes uneven. As a result, the blood vessels running through the liver cannot function properly, and blood stasis forms. It causes water to collect around the abdomen and legs. Fluid accumulation in the stomach is called ascites.
Liver damage is a result of long-term exposure to factors that damage the liver. The most common factor is alcohol. Cirrhosis is a progressive disease. Liver damage in this condition is irreversible. The 5-year survival rate is less than 50%. There are no drugs that effectively restore liver function.
Edema is one of the symptoms of kidney disease. Regarding severe kidney damage, they do not efficiently remove excess water from the body, which leads to edema.
The second disease in the kidneys in which edema may occur is nephrotic syndrome![]() . The cause of edema in this syndrome is the loss of large amounts of protein in the urine. Eyelid swelling is usually the first symptom. Over time, with the development of the disease, edema of the lower legs, hands, and feet joins the symptoms.
. The cause of edema in this syndrome is the loss of large amounts of protein in the urine. Eyelid swelling is usually the first symptom. Over time, with the development of the disease, edema of the lower legs, hands, and feet joins the symptoms.
Venous thrombosis![]() is a condition associated with the development of a blood clot in a vein. Typically it affects the veins of the lower limbs. Deep vein thrombosis is the cause of 70% of unilateral leg edema. The thrombus can narrow or completely close the lumen of the venous vessel, blocking blood flow and causing edema.
is a condition associated with the development of a blood clot in a vein. Typically it affects the veins of the lower limbs. Deep vein thrombosis is the cause of 70% of unilateral leg edema. The thrombus can narrow or completely close the lumen of the venous vessel, blocking blood flow and causing edema.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-lasting joint condition that affects many people. In its course, there is a characteristic set of symptoms that gets worse over time. The most typical symptoms of the disease are pain and swelling of joints. Its cause is joint inflammation. The joints of the hands and feet are usually the affected ones.
Chronic protein deficiency![]() increases the tendency to retain water in the body, which translates into edema and swelling. These edemas most often affect the legs, specifically the ankle area.
increases the tendency to retain water in the body, which translates into edema and swelling. These edemas most often affect the legs, specifically the ankle area.
Some medications can cause swelling in the feet as a side effect because they cause fluid to build up, especially in the lower body parts.
Medications![]() that can cause edema in the legs include:
that can cause edema in the legs include:
After the injury![]() , fluid and white blood cells move excessively to the injured area, which causes swelling.
, fluid and white blood cells move excessively to the injured area, which causes swelling.
The immune system reacts to an allergen by increasing capillary permeability. Because of that, fluid from the vessels enters the body tissues excessively. Swelling occurs, and substances released by the immune system cause itching.
Symptoms of edema are varied and depend on the cause and the affected body part. The most common symptoms include:
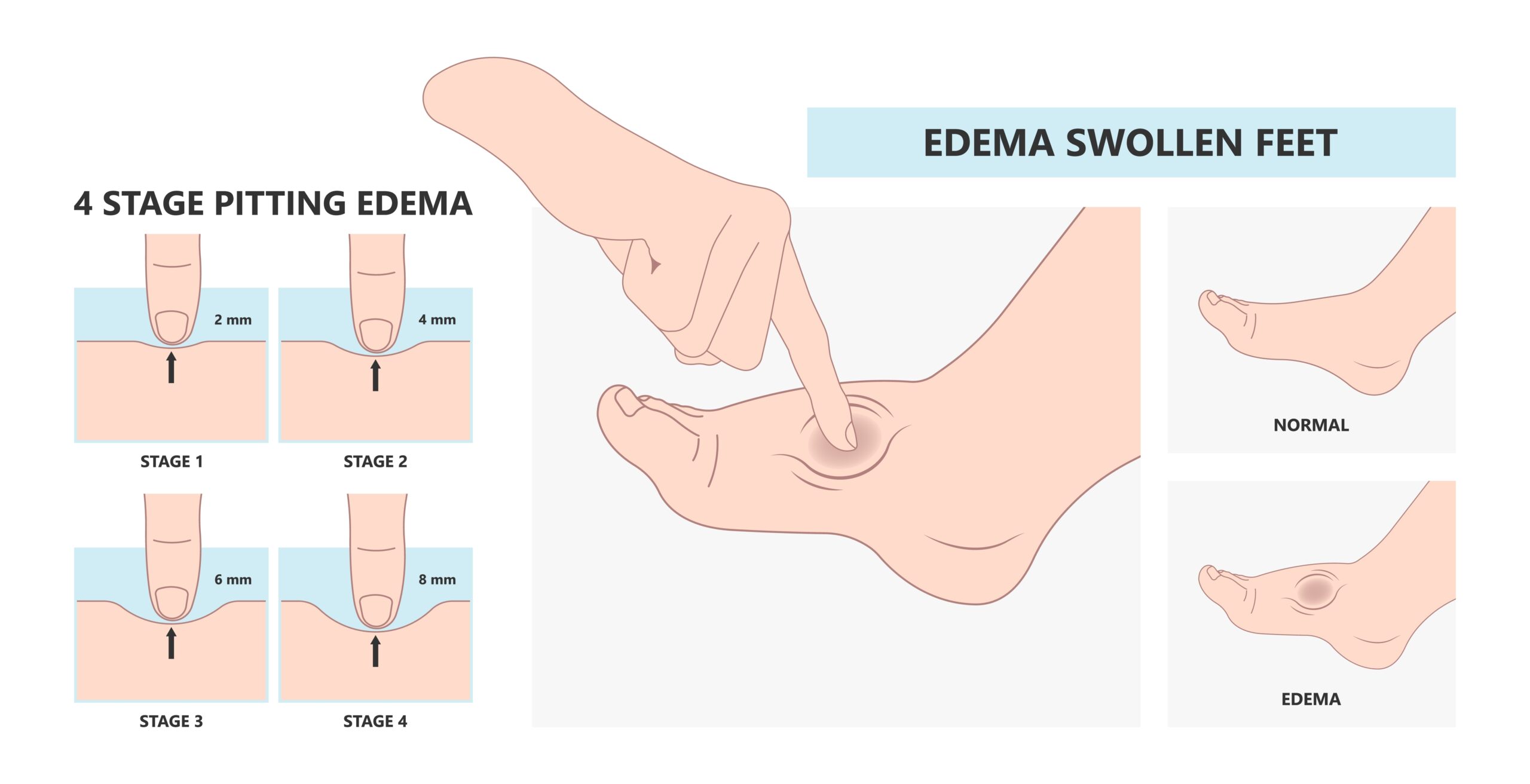
A healthcare professional recognizes edema based on a physical examination: they assess pitting, skin appearance, tension, and tenderness. In finding the cause of edema, laboratory and imaging tests are helpful, in addition to physical examinations.
Based on the depth of pitting and the time of skin rebound, the doctor classifies the swelling into one of 4 categories![]() of severity:
of severity:
Various tests can help explain the cause of edema. In addition to other potential tests, the doctor might request blood and urine tests, a Doppler ultrasound to evaluate blood flow in the vessels and an echocardiogram.
The treatment of leg edema consists in removing the causes of their formation.
In the case of cardiovascular diseases, doctors recommend introducing lifestyle changes such as:
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor weight and fluid intake.
Sometimes, medications or surgical procedures are required. Depending on the cause, it may be:
Compression therapy![]() is useful in reducing swelling. This treatment involves compressing the lower limb with medical elastic products (knee-highs, stockings, or tights) or a specially constructed bandage.
is useful in reducing swelling. This treatment involves compressing the lower limb with medical elastic products (knee-highs, stockings, or tights) or a specially constructed bandage.
Properly selected compression stocking improves venous and lymphatic drainage in the lower limb and supports the mechanisms that maintain proper venous and lymphatic circulation. Therefore compression therapy reduces the risk of venous thrombosis and significantly reduces the discomfort associated with swelling.
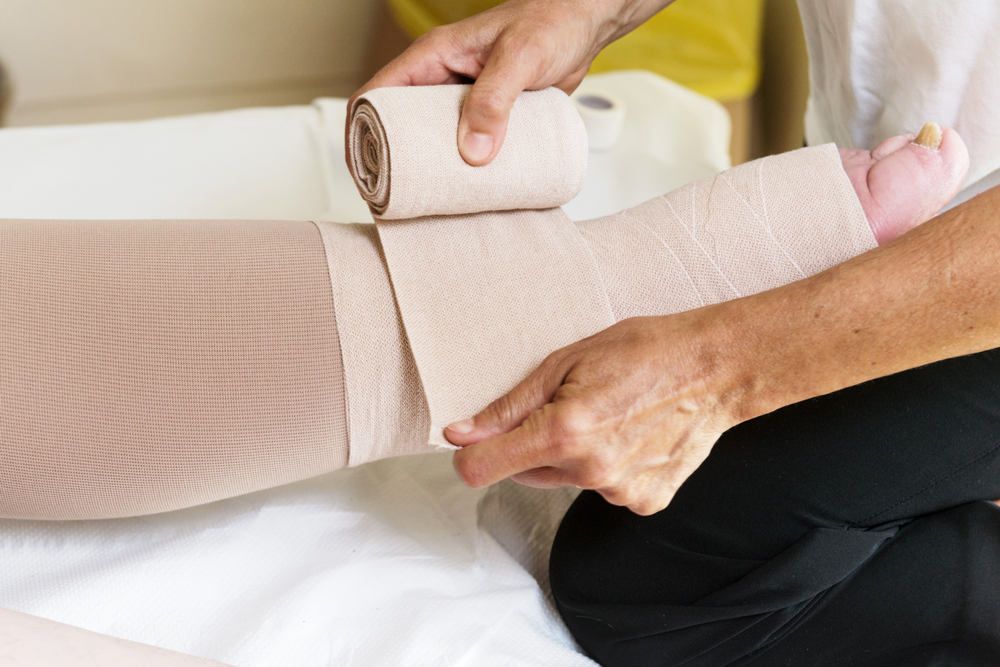

The compression stocking must fit the dimensions of each patient well.
Contraindications to the use of compression therapy are significant issues with the blood flow in the arteries, acute inflammation of the skin, recent venous blood clots, and allergy to compression materials.
Lymphatic drainage affects the lymphatic system. The aim is to improve its motility and reduce edema. This massage can be performed manually by a qualified physiotherapist or with the use of special devices. Lymphatic drainage techniques are performed along the course of lymphatic vessels.
Prevention of edema consists mainly in facilitating the outflow of venous blood from the affected limb.
Working muscles act like a pump. They squeeze blood in the veins and help pump it toward the heart. The muscle pump activates during movement – walking and even moving the lower limbs while standing or sitting can help prevent leg edema.
Sitting with crossed legs is particularly unfavorable. During a prolonged sitting, bend and straighten your feet and take frequent breaks for a short walk to prevent blood stagnation in the vessels.
Wearing flat shoes, resting with the elevation of the lower limbs, or maintaining a healthy body weight are also activities that help prevent swelling.
Do you need a special diet when you have edema? Healthcare professionals recommend a balanced and healthy diet. It should be rich in fruits and vegetables and limit meat and saturated fatty acids. In some patients, reducing salt intake helps to reduce and prevent swelling.
The list of risk factors for edema includes:
Edema could be a symptom of more dangerous diseases or a harmless ailment, for example, related to pregnancy. That is why the prognosis depends on the cause of the swelling. If it affects you, it's important not to ignore this symptom and contact your physician to find the cause. By doing so, you can avoid complications caused by untreated chronic diseases.
In a few situations, edema can be dangerous, and you should consult your doctor immediately. The following situations should raise concern:
Edema is a complex problem with many causes. Home remedies can help reduce swelling, but if the symptoms are severe and last a long time, it is necessary to consult a physician, as this symptom may be hiding a more severe disease.